Viking Age teeth at Varnhem indicate surprisingly advanced dentistry, according to the results of a study conducted at the University of Gothenburg.
In 2005, excavations in Varnhem, Sweden uncovered the remains of a Christian church, near which was a cemetery containing thousands of Viking graves dating to the 10th to 12th century AD. The site is known for extensive excavations of Viking and medieval environments, including tombs where skeletons and teeth have been preserved well in favorable soil conditions.
In this study, Carolina Bertilsson and colleagues performed clinical and radiographical examinations of the dentition of individuals from this site. In total, the team analyzed more than 3,293 teeth from 171 individuals individuals.
The teeth underwent clinical examinations using standard dentistry tools under bright light. A number of X-ray examinations were also performed using the same technique used in dentistry, where the patient bites down on a small square imaging plate in the mouth.
The results, which have been published in the journal PLOS ONE, show that 49% of the Viking population had one or more caries lesions. Of the adults’ teeth, 13% were affected by caries – often at the roots. However, children with milk teeth – or with both milk and adult teeth – were entirely caries-free.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Tooth loss was also common among adults. The studied adults had lost an average of 6% of their teeth, excluding wisdom teeth, over their lifetimes. The risk of tooth loss increased with age.
The findings suggest that caries, tooth infections, and toothache were common among the Viking population in Varnhem. However, the study also reveals examples of attempts to look after teeth in various ways.
“There were several signs that the Vikings had modified their teeth, including evidence of using toothpicks, filing front teeth, and even dental treatment of teeth with infections,” says Carolina Bertilsson, a dentist and Associate Researcher, and the study’s first-named and corresponding author.
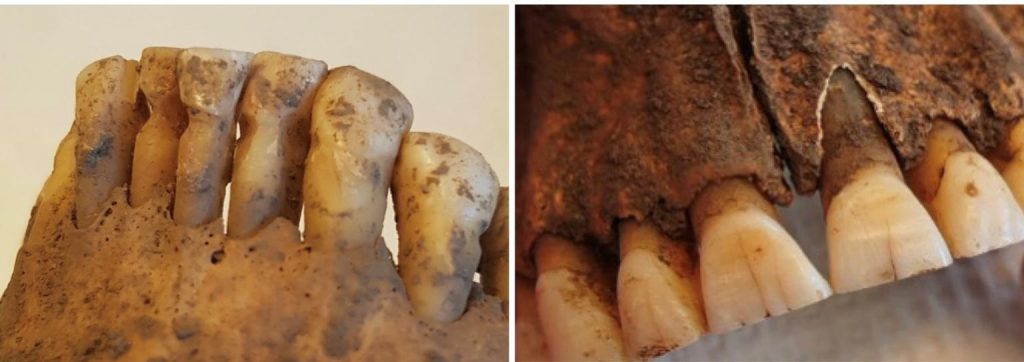
Not unlike today’s treatments
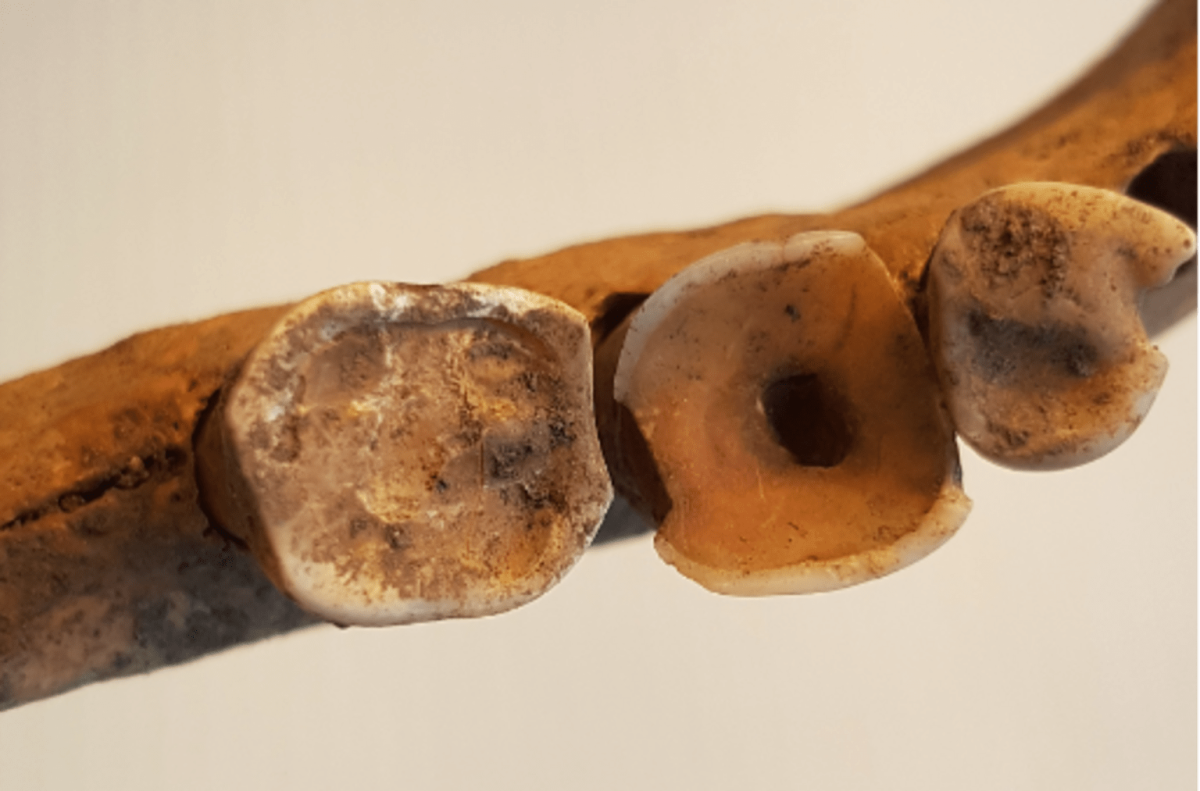
One sign of more sophisticated procedures was molars with filed holes, from the crown of the tooth and into the pulp, probably in order to relieve pressure and alleviate severe toothache due to infection.
“This is very exciting to see, and not unlike the dental treatments we carry out today when we drill into infected teeth. The Vikings seem to have had knowledge about teeth, but we don’t know whether they did these procedures themselves or had help.”
The filed front teeth may have been a form of identity marker. In both this and previous studies, the cases found were male. Carolina Bertilsson continues:
“This study provides new insights into Viking oral health, and indicates that teeth were important in Varnhem’s Viking culture. It also suggests that dentistry in the Viking Age was probably more sophisticated than previously thought.”
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0295282
Cover Photo: A filed hole from the crown of the tooth into the pulp – a procedure that reduces toothache and infection. Photo: Carolina Bertilsson
















