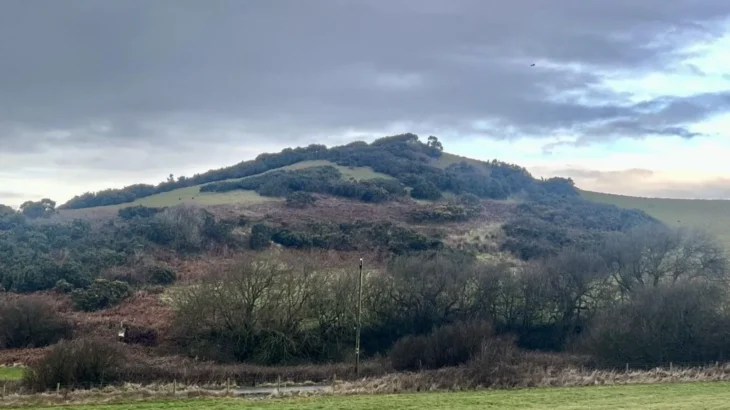
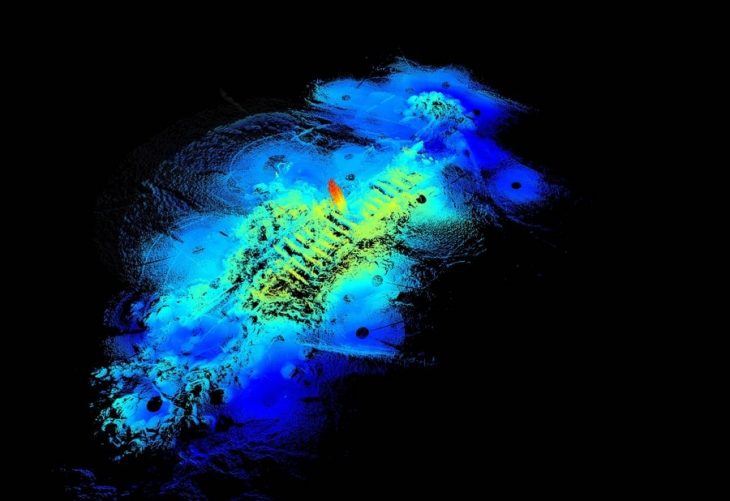
A monumental Bronze Age fortress has been uncovered at the summit of Papuk Mountain in northeastern Croatia, reshaping our understanding of prehistoric settlement, defense, and social organization in the Balkans. The discovery was made at a site known as Gradina, located 611 meters above sea level, where a team of archaeologists led by Professor Hrvoje Potrebica from the University of Zagreb has revealed an unexpectedly sophisticated fortification system dating to the Late Bronze Age.
Unprecedented Defensive Architecture
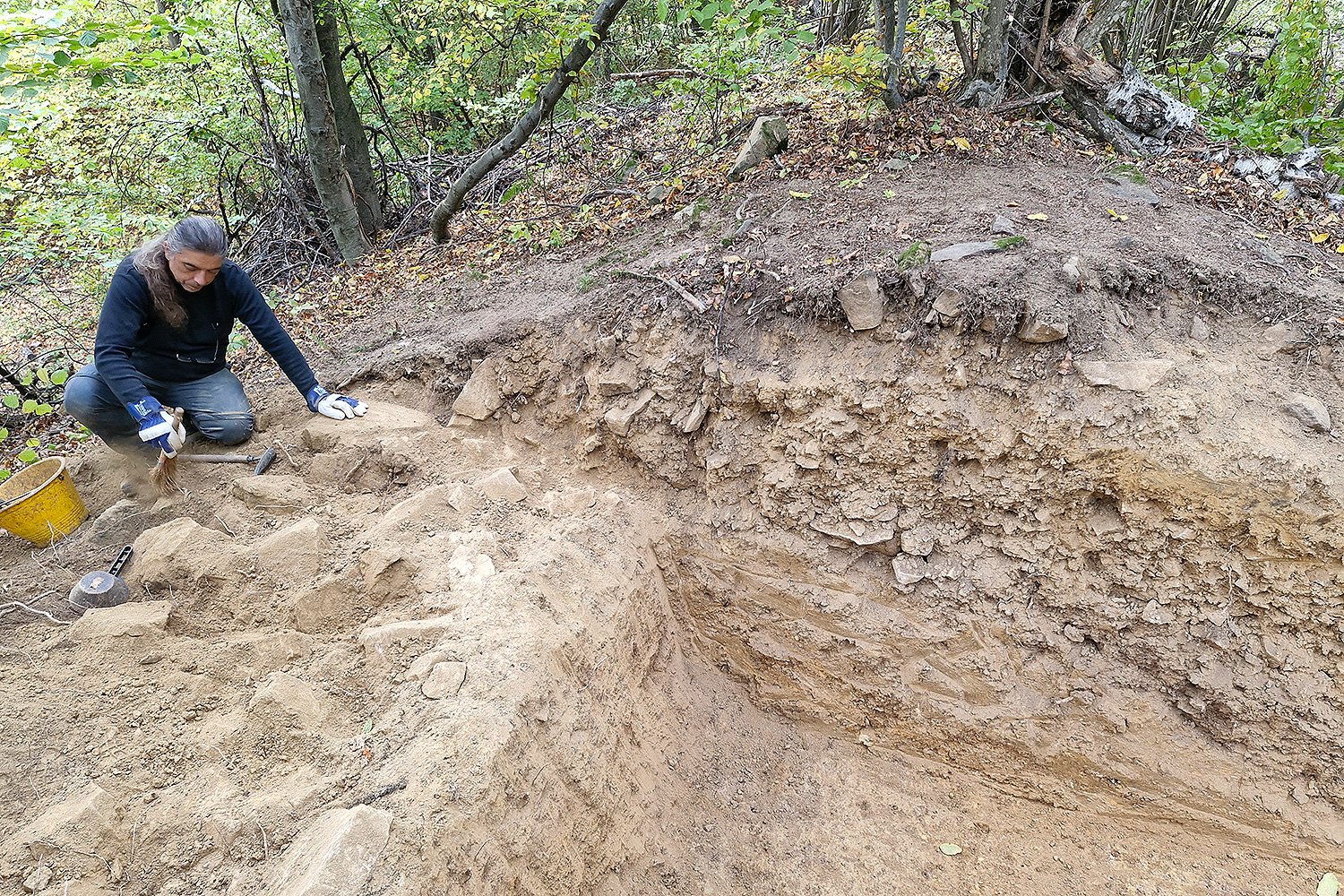
What sets the Gradina fortress apart is its complex, three-layered defensive system. Archaeologists identified an inner core of tamped earth, surrounded by a massive framework made of large stone blocks, and finally an outer shell of compacted soil. This multi-part design demonstrates exceptional engineering skill for its time. In certain sections, the inner surface of the rampart stands two meters high, while the exterior side reaches an imposing seven to eight meters, thanks to the steep natural incline of the mountain slope.
Even more remarkable is the discovery of a second wall inside the exterior fortification. This inner wall, built using dry-stone masonry without mortar, exceeds 1.5 meters in thickness. According to the excavation team, such a structure is highly unusual for Bronze Age settlements in this part of Europe. Its durability and scale indicate that the builders were not only technically skilled but also socially organized and resource-rich.
A Fortress Covering Four Hectares
The Gradina site spans approximately four hectares, making it far larger than an isolated defensive lookout or simple hillfort. The scale suggests a planned settlement, likely supporting a community with a defined social structure and possibly even political influence over the surrounding region. Archaeologists have also uncovered traces of dwellings within the walls, along with fragments of pottery. These everyday artifacts provide a glimpse into the lives of the people who inhabited the stronghold, showing that it was not merely a refuge during conflict but a long-term residential space.
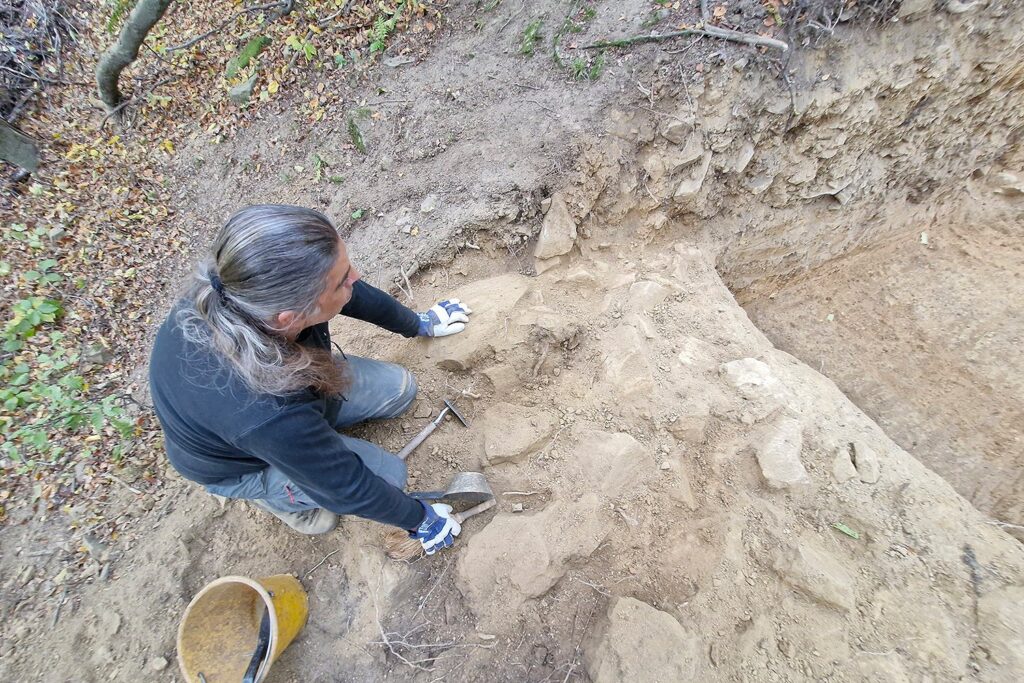

Rewriting the Timeline: From Celtic Hypotheses to the Bronze Age
Before excavations began, some researchers believed that the site might belong to the La Tène period, associated with Celtic culture. This assumption was influenced by silver Celtic coins that illegal metal detectorists had previously found in the area. However, once systematic excavations were carried out, the ceramic fragments recovered from the foundational layers told a different story. The pottery dates to the Late Bronze Age, approximately 1200–1000 BCE, pushing the origins of the settlement nearly eight centuries earlier than previously thought.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This dramatic shift in chronology has major implications for the cultural history of the region. It suggests that the Papuk area was home to a highly organized Bronze Age community long before Celtic groups appeared in Central Europe. The scale and complexity of the fortification point to a society that invested significant labor, planning, and resources into creating a lasting defensive and communal center.
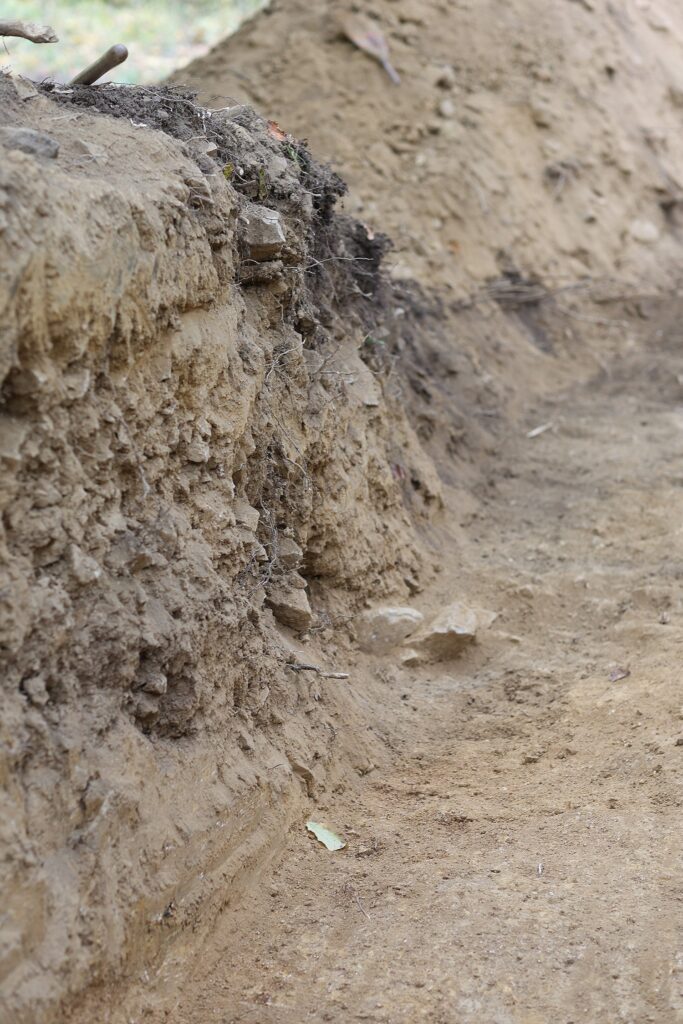

The Far-Reaching Importance of a Fortress Frozen in Time
The Gradina fortress is significant for several reasons. First, stone fortifications of this scale are exceptionally rare in the prehistoric Balkans, where most fortifications were constructed from wood, soil, or other perishable materials. The decision to build with stone indicates a deliberate effort to create something permanent and resilient—perhaps a statement of political power or strategic dominance in the region.
Second, the discovery provides a missing link in understanding the social and defensive systems of Late Bronze Age communities in southeastern Europe. Its architecture reflects a level of organization comparable to contemporaneous fortified sites in other parts of Europe and the Near East, suggesting that the region played a more active role in Bronze Age cultural networks than previously assumed.
The Team Behind the Breakthrough
The excavation has been led by Professor Hrvoje Potrebica, a specialist in prehistoric archaeology with decades of field experience. He has been supported by collaborators who have worked on the site for multiple campaigns, combining meticulous excavation techniques with modern analytical methods. Their efforts have revealed a site far more complex than initial surface surveys suggested.
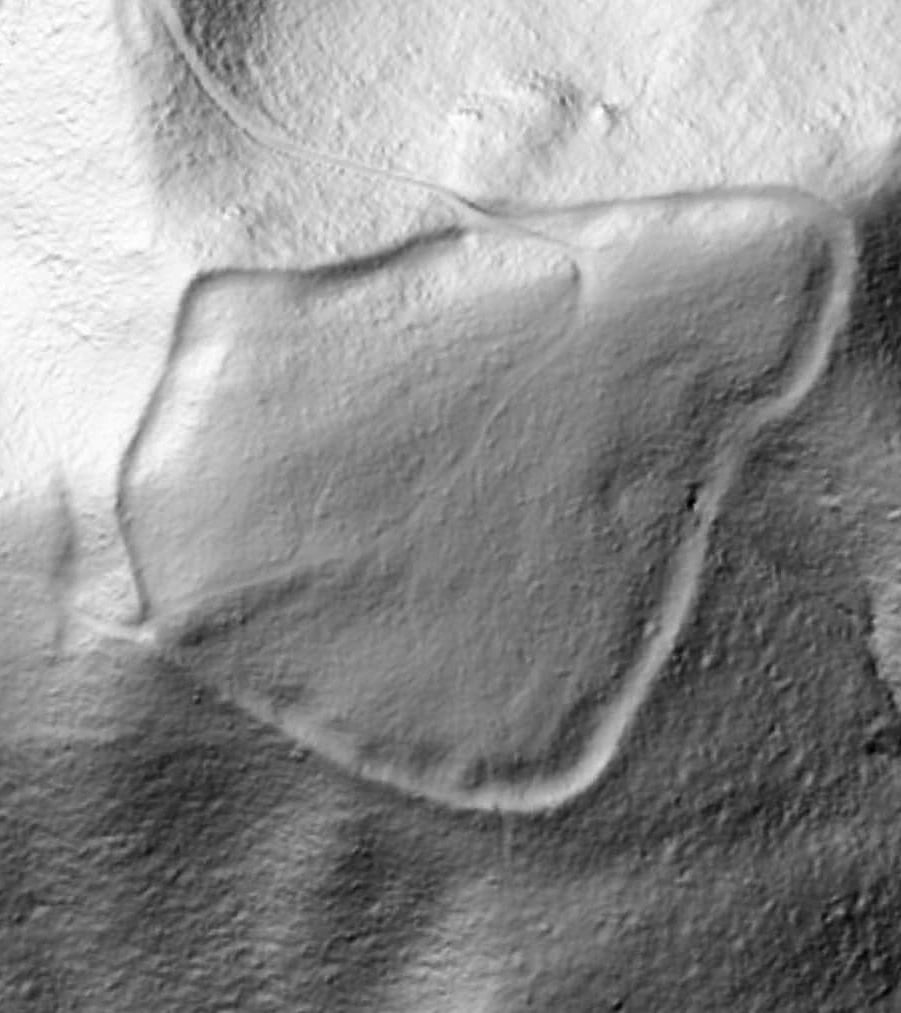
A New Chapter in Balkan Prehistory
The Gradina fortress promises to become a landmark site for understanding Bronze Age societies in the Balkans. Its discovery challenges long-standing assumptions, opens new avenues for research, and highlights the strategic importance of the Papuk region in prehistoric times. Ongoing and future excavations may reveal even more about the settlement’s inhabitants, their social structures, their trade networks, and their role in the shifting political landscape of the Late Bronze Age.
The monumental architecture of Gradina—hidden for more than three thousand years—now stands as a testament to the ingenuity, resilience, and organizational power of a long-forgotten community.
Virovitica-Podravina County (Virovitičko-podravska županija)
Cover Image Credit: Kristijan Toplak / Virovitičko-podravska županija