Two temples belonging to the Egyptian god Amun and the Greek goddess Aphrodite were found in the sunken city off the coast of Egypt by a team of archaeologists led by Franck Goddio.
The discovery was announced in a press release by the European Institute for Underwater Archeology (IEASM) on Tuesday.
The research team first found the ancient port city of Thonis-Heracleion on Aboukir Bay in 2000 and has now discovered temple ruins in the city’s southern canal.
The remains of Thonis-Heracleion are located under the sea, 7 kilometers (4.3 miles) from the present coast of Egypt. The city was for centuries Egypt’s largest port on the Mediterranean before the founding of Alexandria by Alexander the Great in 331 BC.
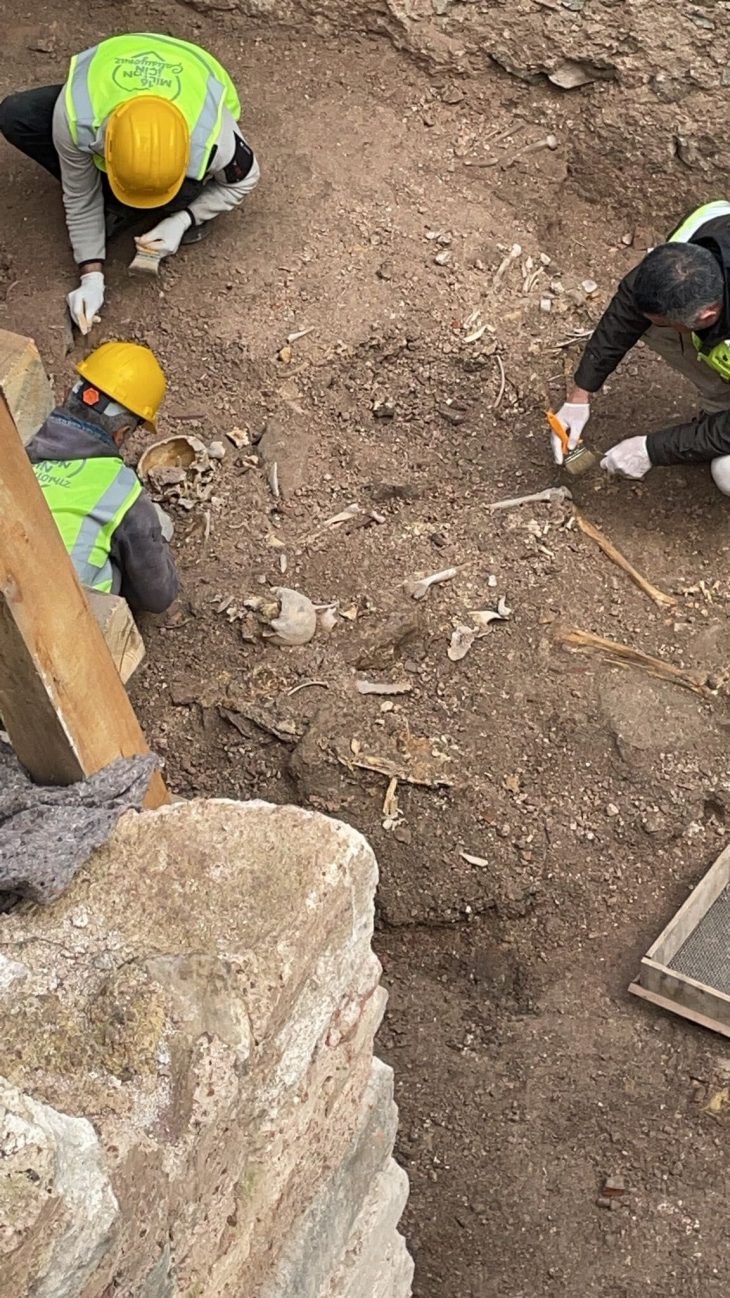
An underwater archaeological team, led by French marine archaeologist Franck Goddio, has made further discoveries at the site of a temple to the god Amun in the ancient port city of Thonis-Heracleion, the institute said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

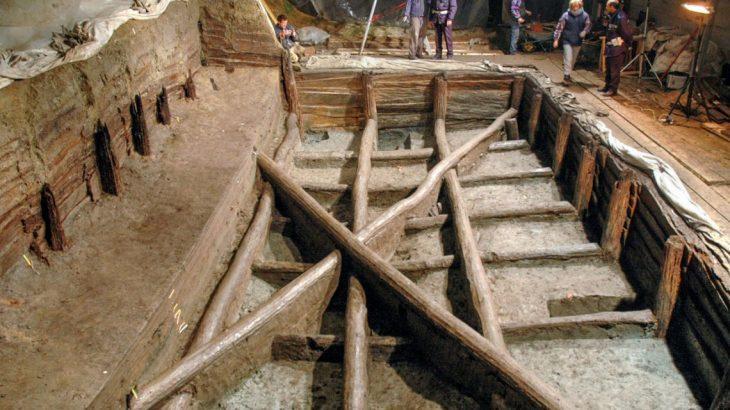
The temple, dedicated to the Egyptian god of air, Amun, was believed to have collapsed “during a cataclysmic event dated to the mid-second century BC,” the European Institute for Underwater Archaeology (IEASM) institute said. “Rising sea levels and earthquakes followed by tidal waves triggering land liquefaction events, caused a 110 square kilometer portion of the Nile delta to totally disappear under the sea, taking with it the city of Thonis-Heracleion.”
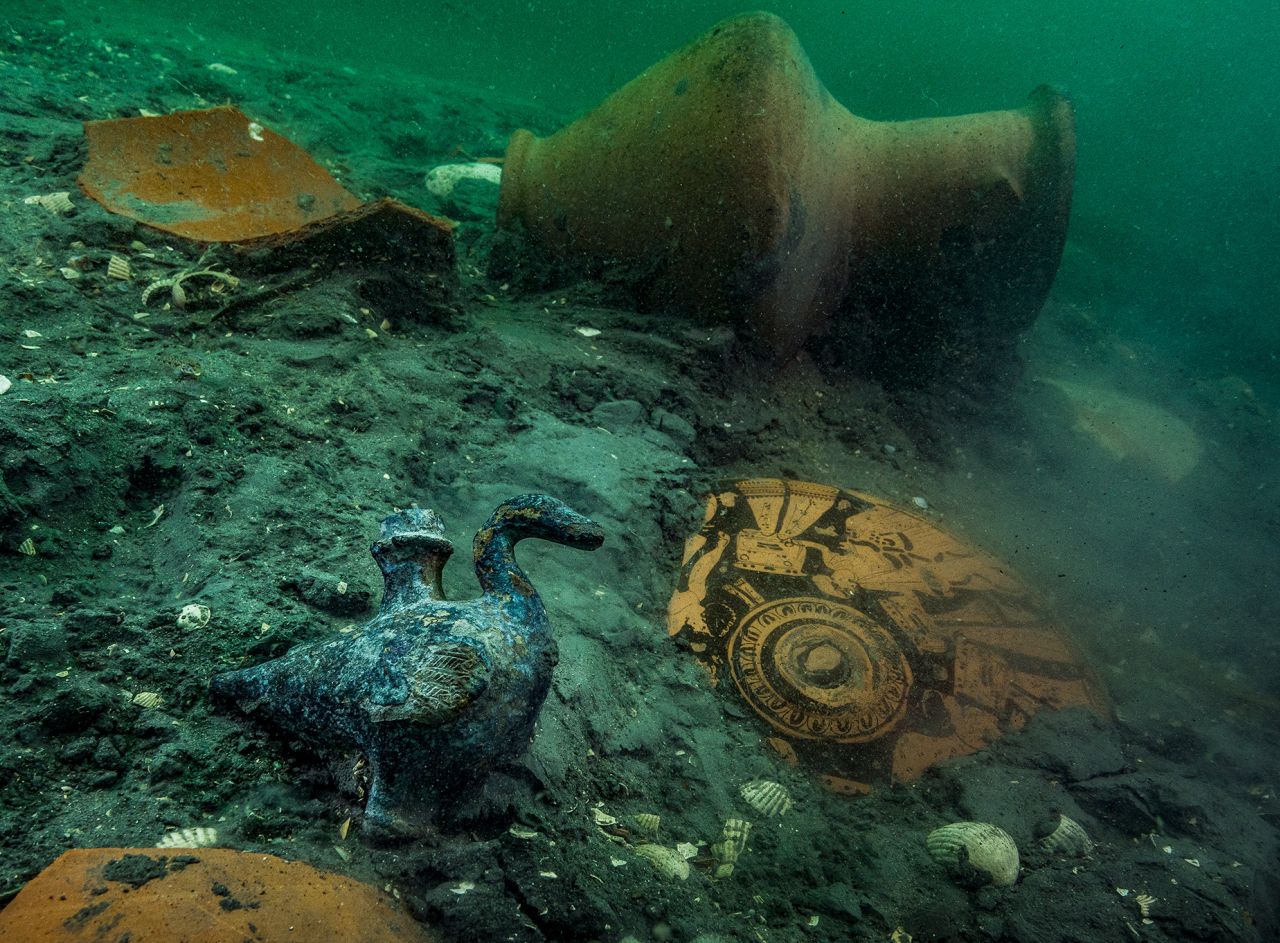
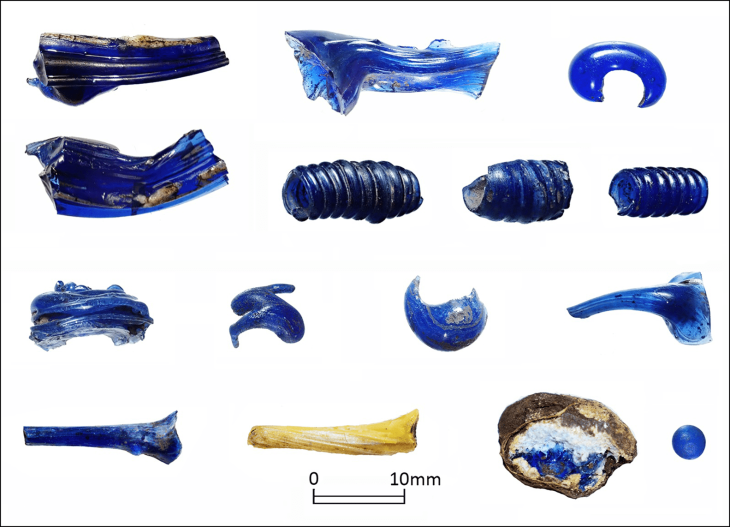
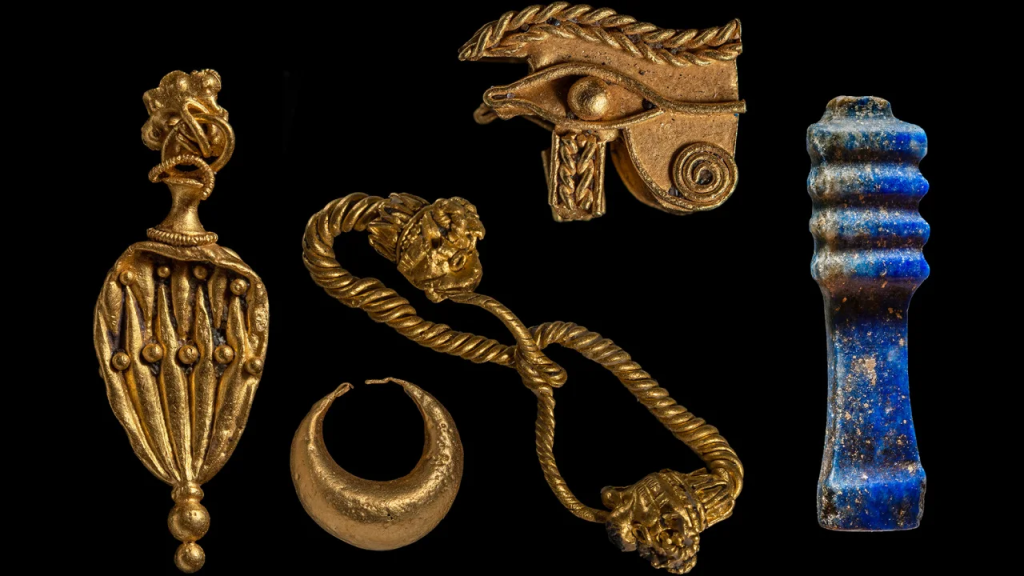
“Precious objects belonging to the temple treasury have been unearthed, such as silver ritual instruments, gold jewelry and fragile alabaster containers for perfumes or unguents,” IEASM said. “They bear witness to the wealth of this sanctuary and the piety of the former inhabitants of the port city.”
The archaeological excavations, conducted jointly by Goddio’s team and the Department of Underwater Archaeology of the Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities of Egypt, revealed underground structures “supported by very well-preserved wooden posts and beams dating from the 5th century BC,” the institute said.
“It is extremely moving to discover such delicate objects, which survived intact despite the violence and magnitude of the cataclysm,” said Goddio, president of IEASM and director of excavations.
The discoveries were made possible thanks to the development and use of new geophysical prospecting technologies that can detect cavities and objects “buried under layers of clay several meters thick,” the institute said.
Aphrodite’s temple off Heracleion
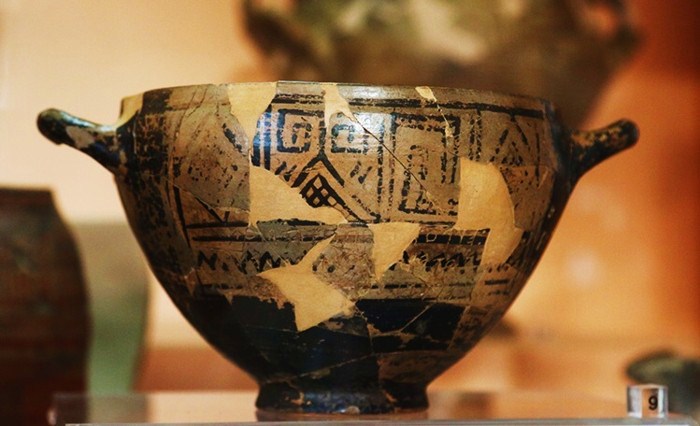
The temple dedicated to the Greek goddess of love Aphrodite was identified by a number of bronze and ceramic idols found.
This find is thought to have been particularly significant as it “illustrates that Greeks who were allowed to trade and settle in the city during the time of the Pharaohs of the Saïte dynasty (664 – 525 BC) had their sanctuaries to their own gods,” the European Institute for Underwater Archaeology (IEASM) institute said.
A number of weapons belonging to Greek mercenaries were also found. “They were defending the access to the Kingdom at the mouth of the Canopic Branch of the Nile. This branch was the largest and the best navigable one in antiquity,” IEASM explained.
Cover Photo: Demonstrating the Greek presence in Ancient Egypt, a delicate bronze duck-shaped pourer was discovered among ceramics at the site of a newly discovered Greek sanctuary to Aphrodite in the submerged ruins of Thonis-Heracleion. Photo: Christoph Gerigk ©Franck Goddio/Hilti Foundation