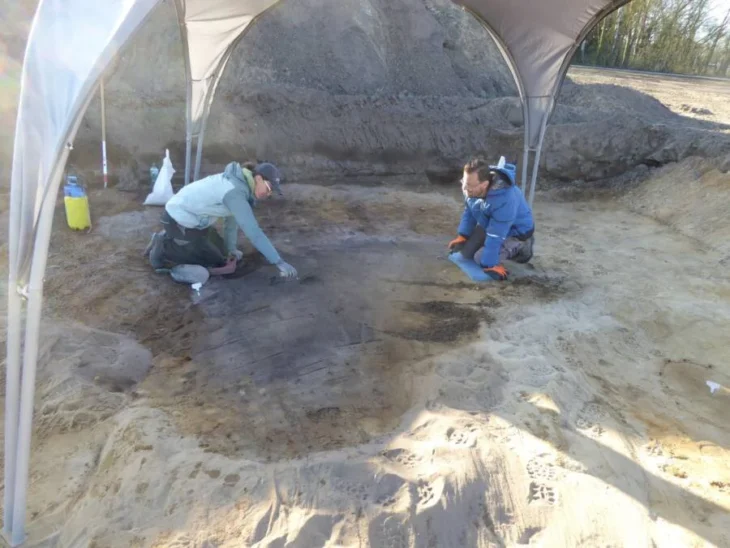
The traces of the ancient harbor on the Black Sea coast of Kerpe, in Kocaeli’s Kandıra district, are being brought to light again.
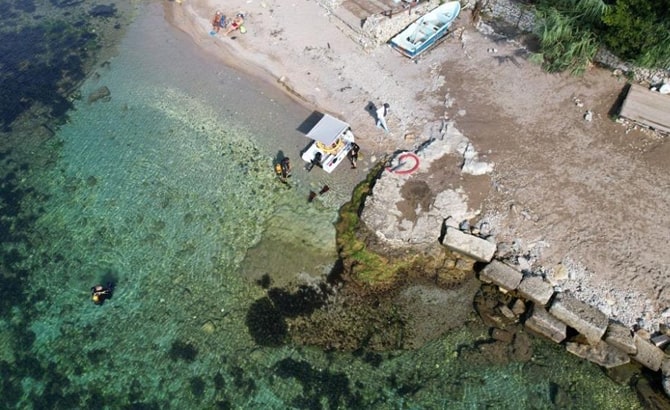
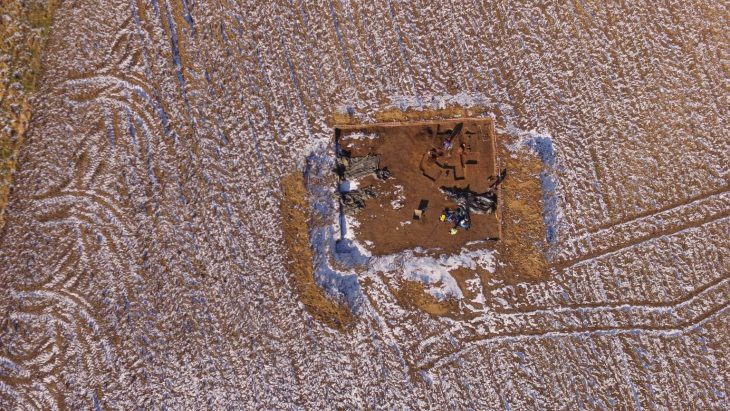
Underwater excavations have begun to excavate the historic port, which is located on the Kerpe shore of Kocaeli, on the Black Sea coast, and operated as an important trade route from the ancient through the Ottoman periods.
The 1,700-year-old port in the bay was built by the colonists of the Megara settlement, which was originally based in modern-day Greece and offered access to Black Sea commerce routes as well as a vital site for a military presence.
In this context, the Kocaeli Provincial Directorate of Culture and Tourism and the Kocaeli Museum Directorate began underwater excavations at the Ancient Kerpe Harbor and underwater research on the Black Sea coast of Kocaeli with the approval of the General Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums of the Republic of Turkey Ministry of Culture and Tourism.
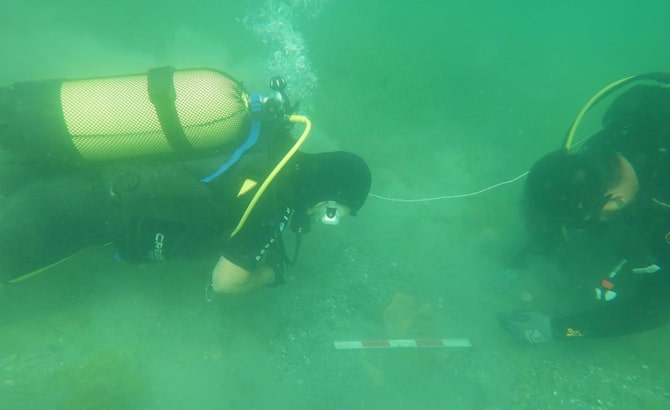

In addition, Kocaeli Metropolitan Municipality, Kandıra Municipality, Düzce University Underwater Application, and Research Center, Watsan Elektrik, and Kerpe Sea Stars Diving School are also participating in the excavations.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Researchers think that beneath the depths of Kerpe Harbor, once part of important settlements during both the Roman and Byzantine eras, a plethora of historically significant artifacts and ruins await discovery.
Researchers hope the excavations will lead to the discovery of cultural assets in the region. Along with artifacts, the team hopes to also determine the Black Sea trade route used by the Ottoman Empire and uncover information regarding regions that once hosted intense trade activity.