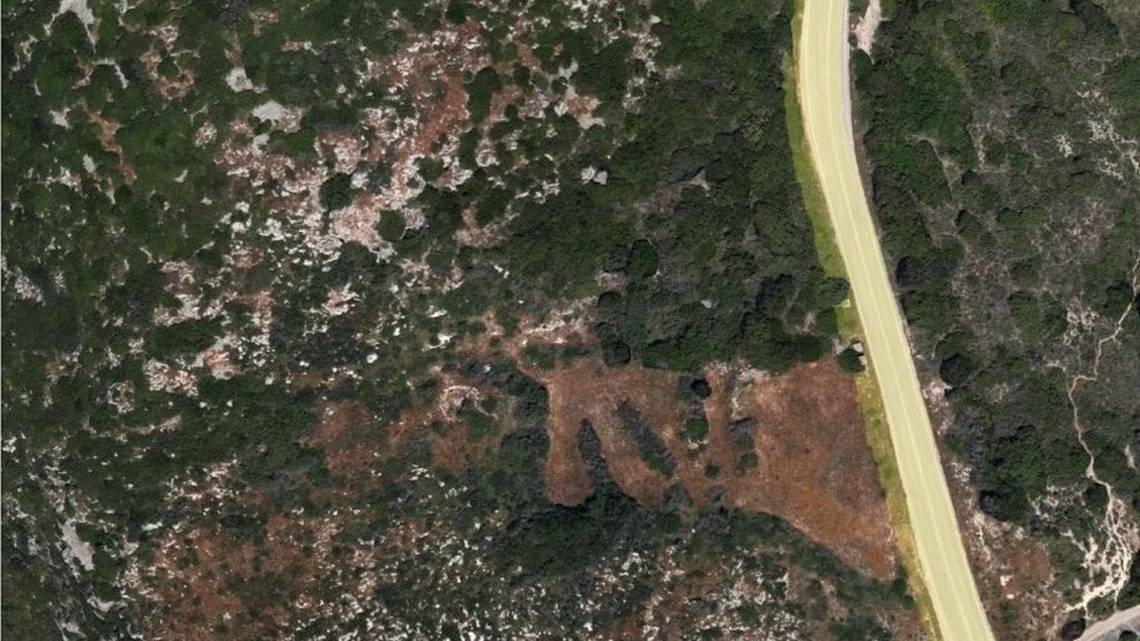
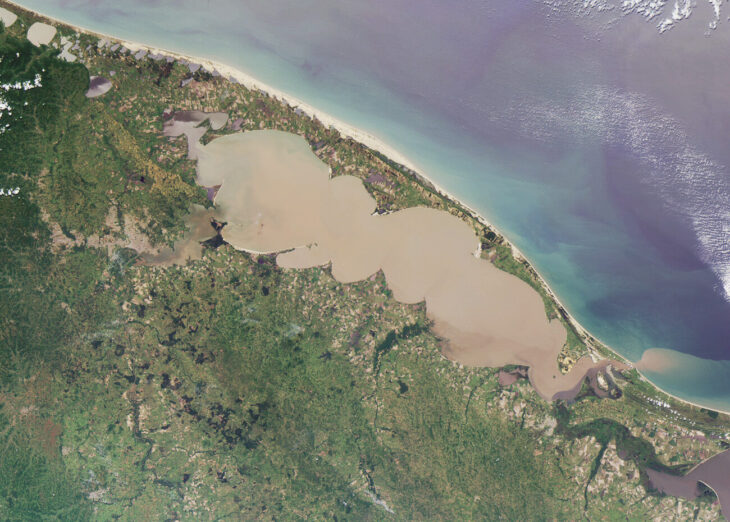
Aerial photographs of the “Kotroni” Lakithra region, strategically located on the island of Cephalonia, west of the Greek mainland, revealed a circular structure poking through vegetation atop an inaccessible hill.
Because of its elevated location, “Kotroni” provides a panoramic view over the whole Leivatho, Kranea region as well as the airport and Zakynthos, indicating its strategic and ceremonial significance in the past.
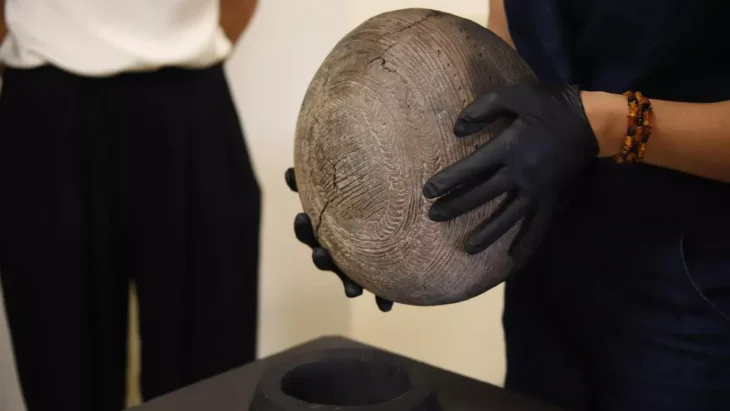
The circular construction, which was faintly visible in the bushy, orgiastic vegetation, created expectations for a new burial monument of the type of the Tzanata but turned out to be something much more unusual. (Tzannata Tomb: In the Mycenean period, elites buried their dead in large beehive-shaped tombs.)
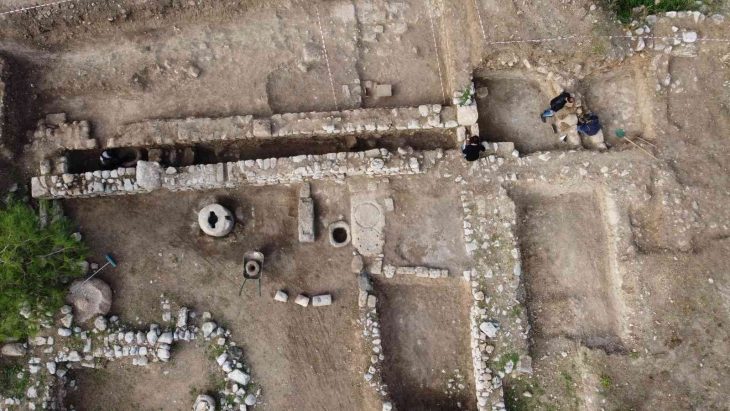
Archaeologists excavated the mysterious site on Cephalonia and found a pair of large ancient wells surrounded by rings of carefully arranged rock, Greece’s Ministry of Culture and Sports said in an Aug. 2 news release.
Archaeologists said the wells dated back at least 3,100 years. The structures were roughly 16 feet deep (5 meters) but had been filled in at some point. The architectural design gave the appearance of a large mound-like landmark surrounded by stone rings.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
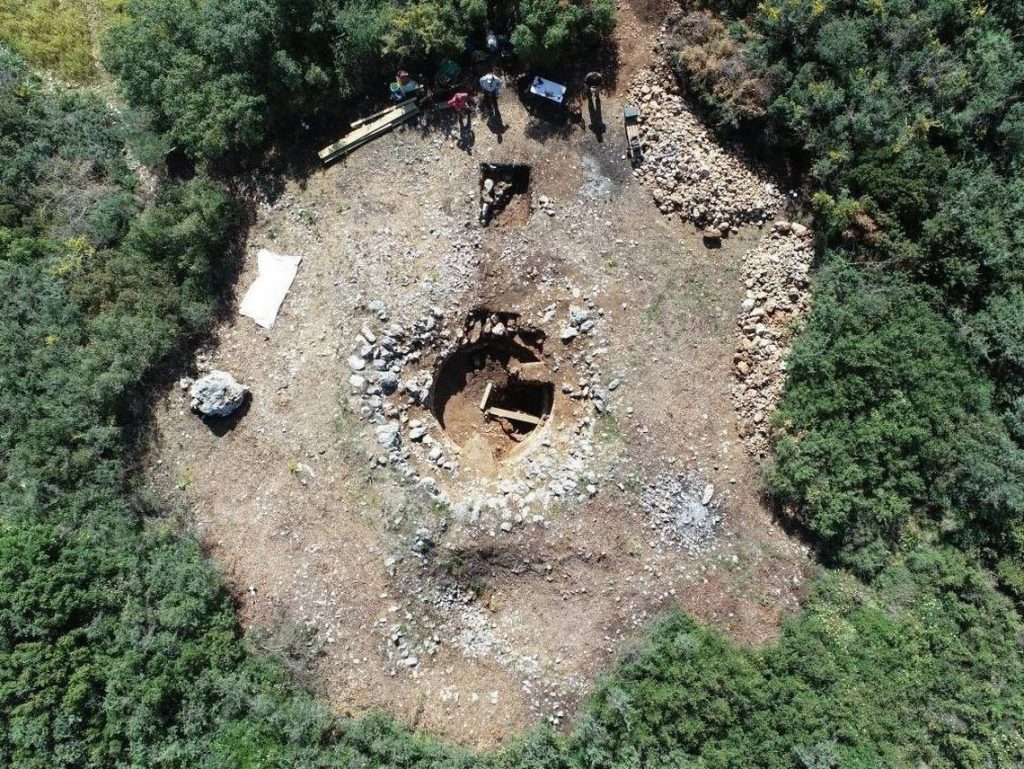

These rings give the outer slopes support in addition to adding to their monumental quality, implying that the structures may have served some ceremonial or ritualistic function.
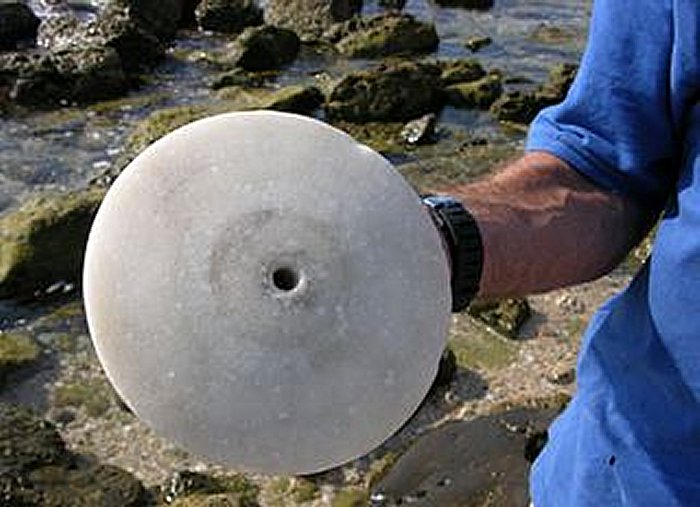
Surprisingly well-preserved tool marks from the extraction of limestone have been found inside the wells. Grooves up to 20 cm deep have been discovered; these may have been utilized to set wooden beams for a platform or material removal system. Access to these structures was via wooden staircases, whose marks are still visible in the rocky environment.
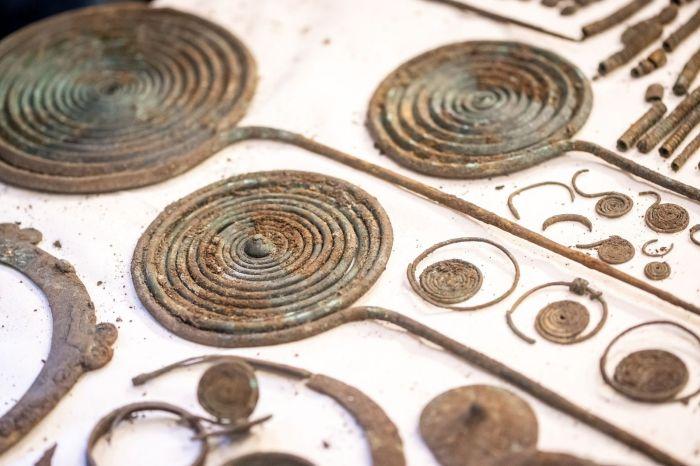
In front of the larger well, a carefully stratified floor was discovered, composed of a layer of clay mixed with fragmented ceramics and flint debris. This layer of ceramics belongs to the so-called “domestic” ceramics of the Late Bronze Age, synchronized with Mycenaean ceramics of the period (LHIIIC). Although few fragments of actual Mycenaean pottery were found, analysis suggests local production, indicating that the area had a rich and complex cultural life.
Excavations also uncovered several carefully arranged layers of clay, stone and pottery. Archaeologists described the pottery pieces as being intentionally broken then scattered in different layers.

The pottery, deliberately broken, has been found in different areas of the site, a practice that contrasts with the typical accumulation of ceramics in funerary monuments. This intentional act of fragmentation is unique in Cephalonia and suggests previously unexplored ceremonial behavior in the region.
A thick layer of pure white calcium carbonate seals the entrance to the southern well; the northern well has a similar feature. This particular detail implies a deliberate attempt to preserve or identify these areas as significant.
The wells, dating between 1200 and 1100 B.C., present some of the earliest evidence of material extraction in the Aegean region during the Late Bronze Age.
Cover Photo: Ministry of Culture of Greece