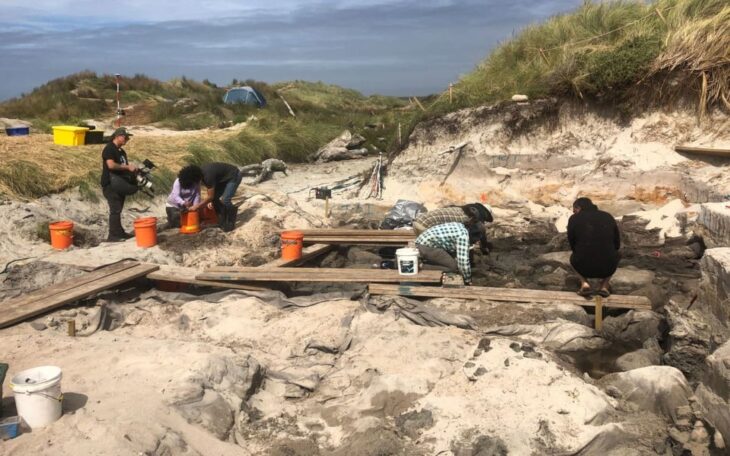
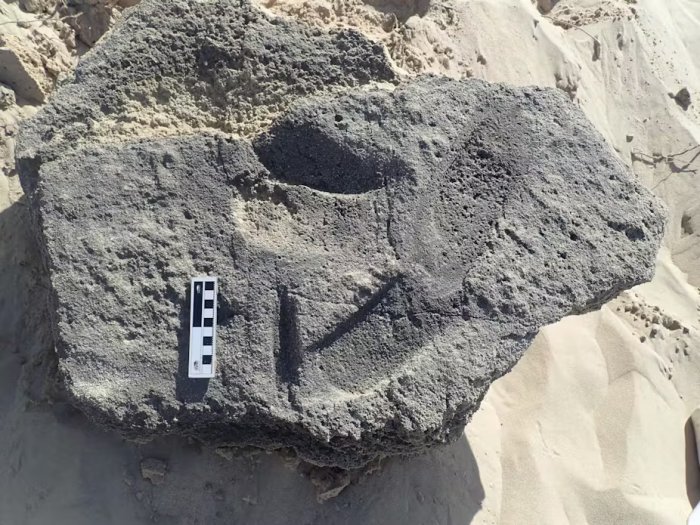
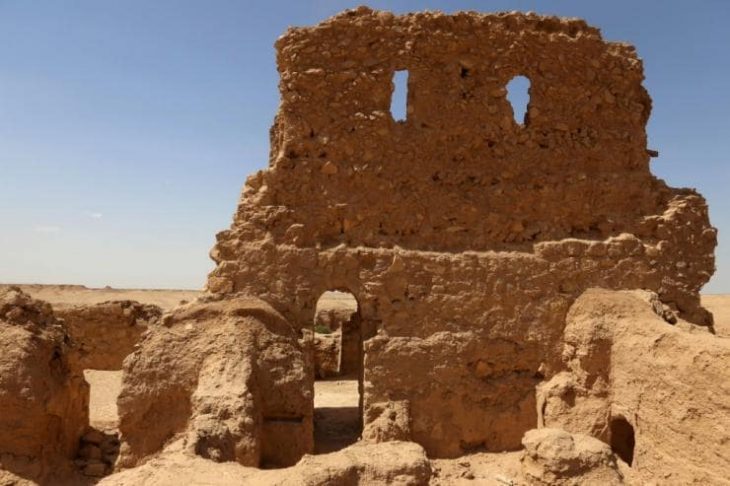
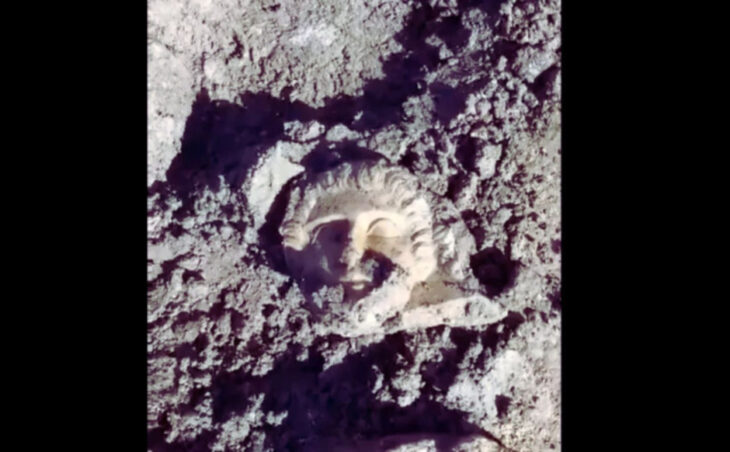
Turkey reported on Sunday the discovery of 11 new hills in the vicinity of the renowned ancient site of Gobeklitepe in southern Sanliurfa province.
“We have [discovered] 11 more major hills on a 100-kilometer line around Gobeklitepe. Here, we will give the details for the first time, and now call it 12 hills,” Culture and Tourism Minister Mehmet Nuri Ersoy said at an AA in Sanliurfa.
Speaking to reporters, Ersoy said a “major study” on the 12 hills is about to be completed and will be presented in September.
He said the area could even be referred to as the “pyramids of southeast Turkey.”
“When you look at Mesopotamia, this region has a unique culture. It has its own registered gastronomy. It has many products. And when you combine that with its unique archaeological value, it’s a wonderful thing,” he added.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Citing the establishment of Turkey’s Tourism Promotion and Development Agency in 2019, Ersoy said the main goal of the agency is “to spread tourism across our 81 provinces in Turkey by 2023.”
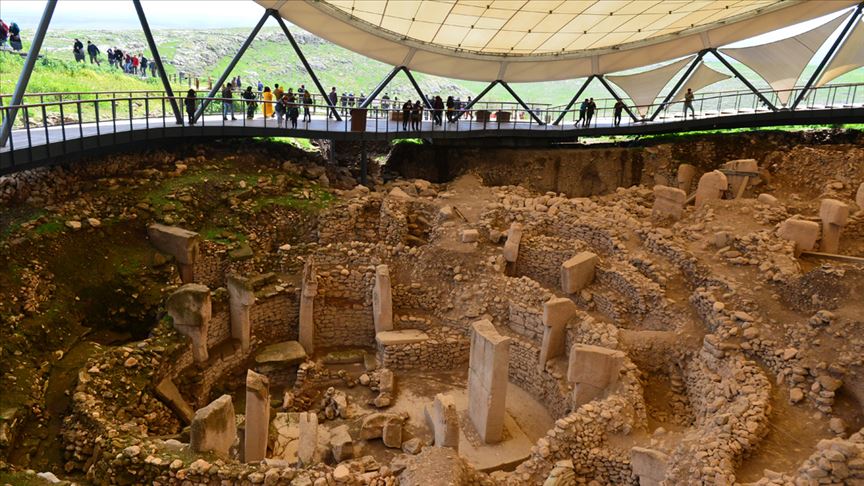
Göbeklitepe, near Sanliurfa, is located around 15 kilometers northeast of the city center, near the town of Örencik.
Göbeklitepe, Turkish for “Potbelly Hill,” is the world’s oldest and biggest known temple. The building of Göbeklitepe — a structure comprised of enormous columns and massive stones – is still a mystery, as instruments such as wheelbarrows, etc., did not exist. Human and pack animal labor are thought to have been employed to move and position the temple’s stones.
The reliefs of animal images on the columns are definitely beyond time. Göbeklitepe is an old building that demonstrates that people held systematic gatherings even when they lived as hunters, although the structure’s final purpose is unknown.
The Ministry of Culture and Tourism designated the monument as a 1st Degree Archaeological Site in 2005, and it was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Temporary List in April 2011. With the act of the Committee assembled in Bahrain in July 2018, Göbeklitepe, which had been on the candidate list for seven years and changed history, was eligible to enter the UNESCO World, Heritage List.