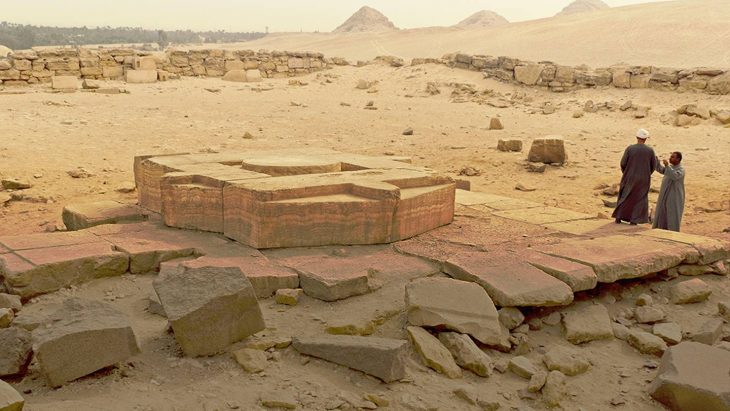
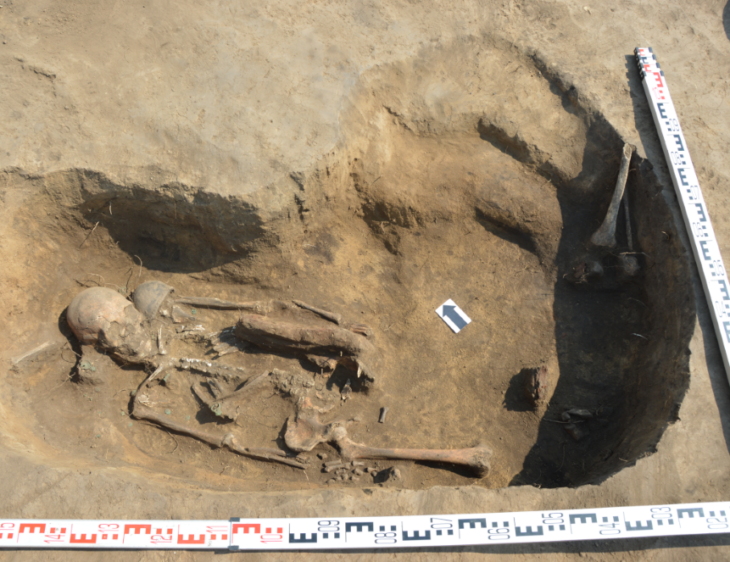
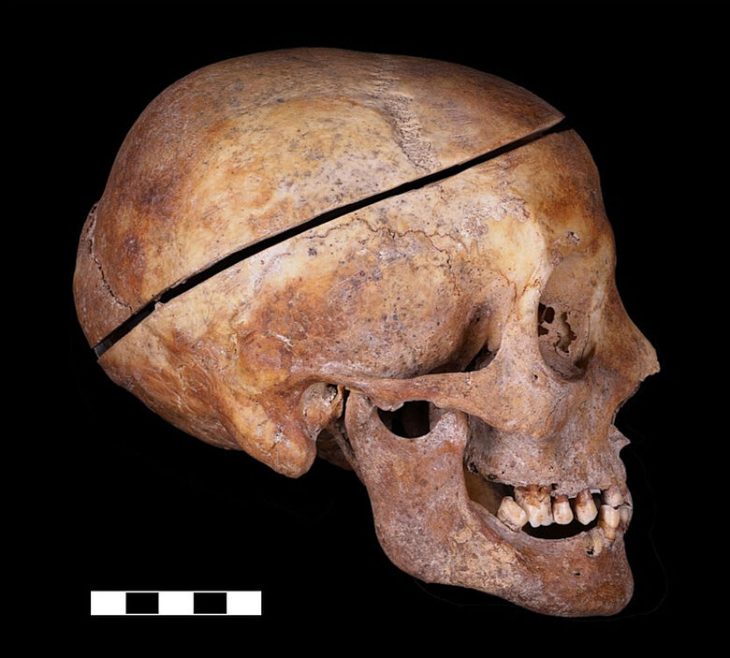
A Swedish archaeological expedition made the extraordinary discovery of tombs outside the Bronze Age trading metropolis of Hala Sultan Tekke in Cyprus.
Researchers from the University of Gothenburg say these tombs are among the richest tombs ever found in the Mediterranean region and provide valuable insight into the ancient city’s history.
The precious artifacts found in the tombs suggest that their occupants held positions of power and authority in the city, which was a significant hub for copper trade between 1500 and 1300 BCE.
Led by Professor Peter Fischer, the expedition team believes that the richness of the grave goods indicates that these were royal tombs, although the exact nature of the city’s government during that time remains uncertain. The individuals buried in these tombs likely played a prominent role in governing the city, which was renowned for its involvement in the copper trade.
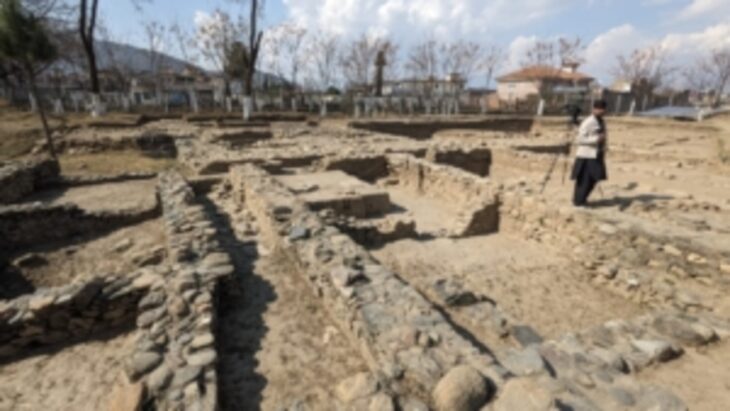
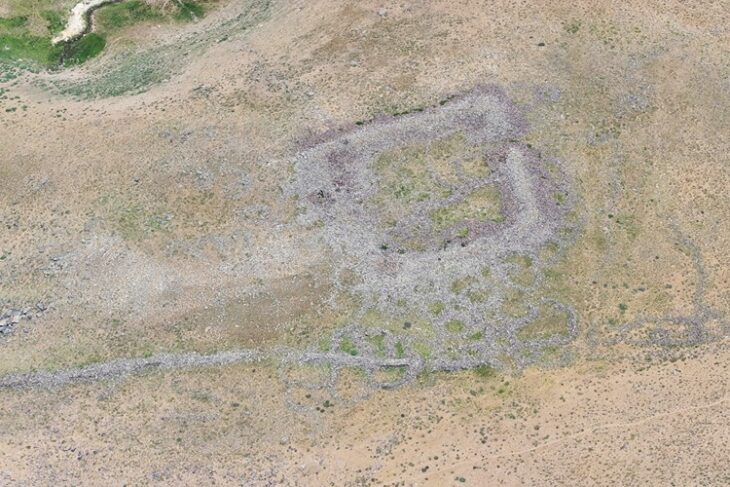
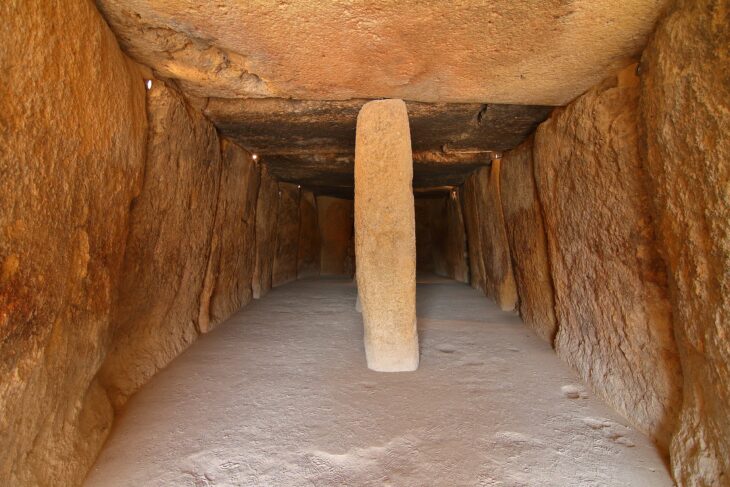
Situated outside the 50-hectare Bronze Age city, the tombs consist of underground chambers accessed through narrow passages from the surface. These chambers varied in size, with some measuring up to 4 x 5 meters.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The Swedish Söderberg expedition, which has been conducting excavations in Hala Sultan Tekke near the city of Larnaca since 2010, has previously uncovered chamber tombs with valuable grave goods. However, the recently discovered tombs stand out due to the sheer quantity and exceptional quality of the artifacts found within them.
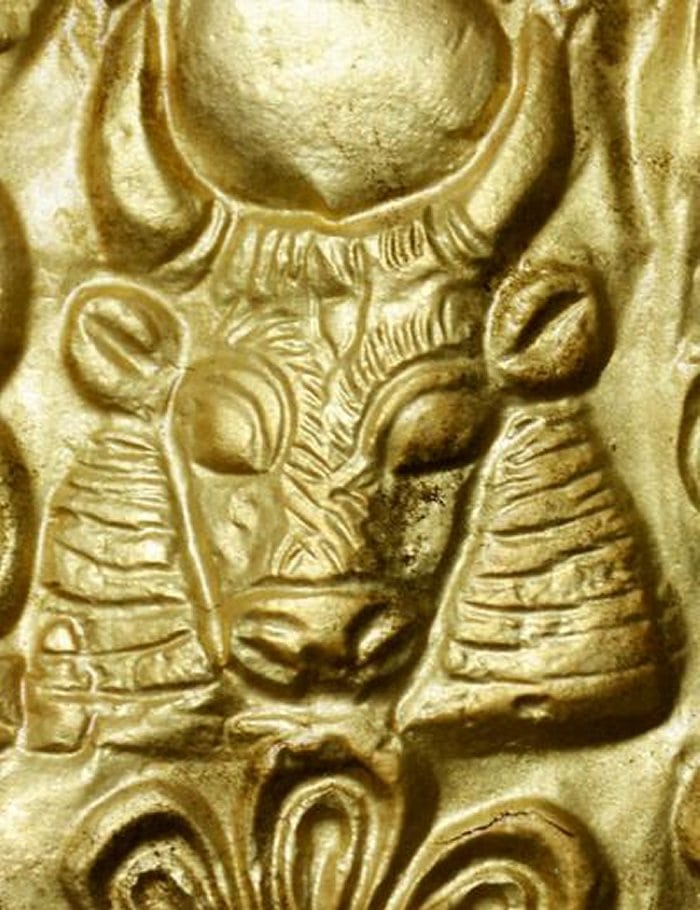

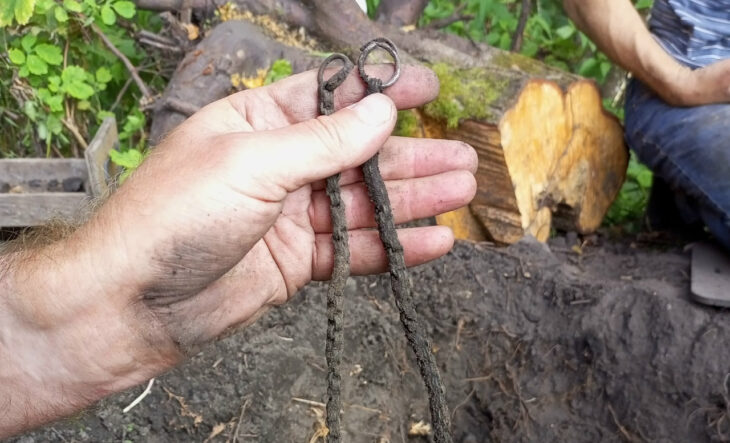
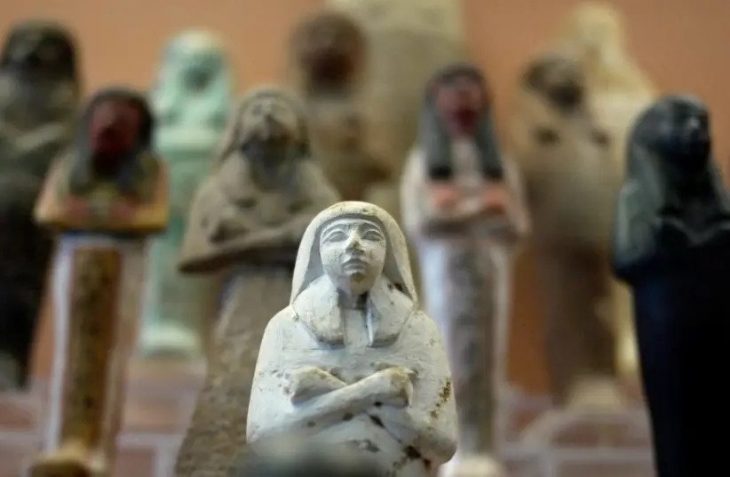
More than 500 complete artifacts were unearthed from the two tombs. Many of these items were crafted from precious metals, gems, ivory, and high-quality ceramics. Approximately half of the artifacts were imported from neighboring cultures. Gold and ivory were sourced from Egypt, while precious stones such as lapis lazuli, carnelian, and turquoise were imported from Afghanistan, India, and Sinai, respectively. The tombs also contained amber objects originating from the Baltic region.
The tombs were discovered using magnetometers, a type of instrument that can produce images showing objects and structures up to two meters beneath the surface.
By comparing the site where broken pottery had been unearthed through farming activities with the magnetometer map, the researchers identified large cavities below the surface, leading them to further investigate the area and ultimately discover the tombs.
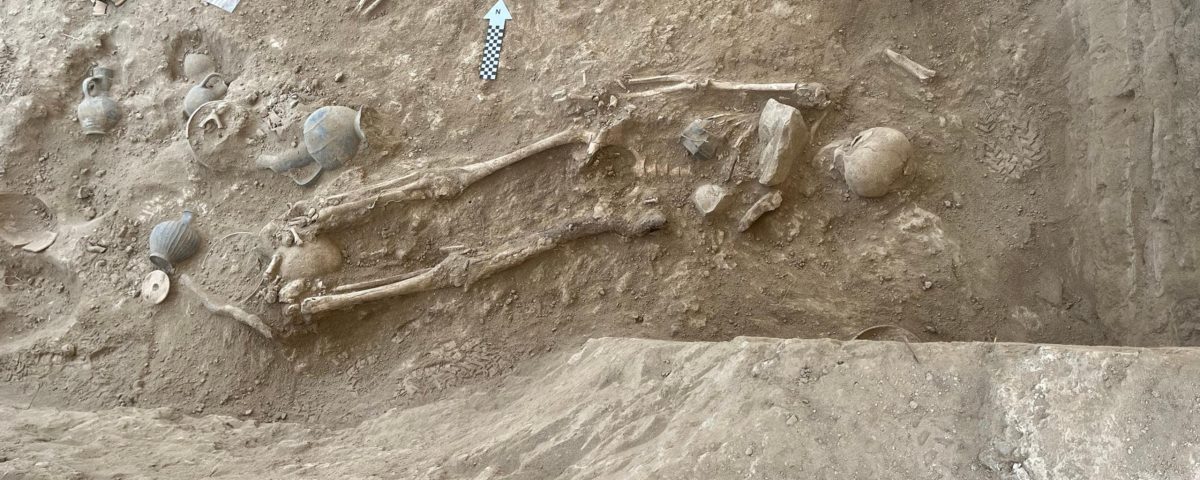
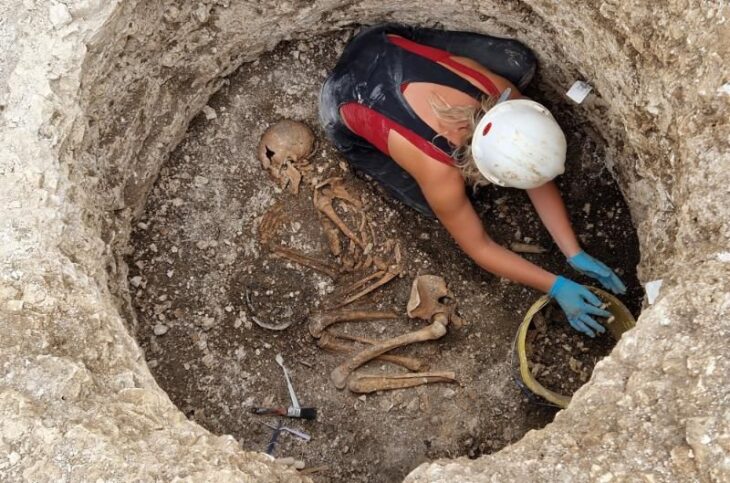
Among the well-preserved skeletons found in the tombs was that of a woman surrounded by dozens of ceramic vessels, jewelry, and a polished round bronze mirror. Additionally, a one-year-old child was laid beside her, accompanied by a ceramic toy.
Diadems, adorned with embossed images of bulls, gazelles, lions, and flowers, were worn by several individuals, both men and women. The expedition team also found necklaces with high-quality pendants, likely made in Egypt during the 18th dynasty, a period associated with pharaohs such as Thutmose III, Amenophis IV (Akhenaten), and his wife Nefertiti.
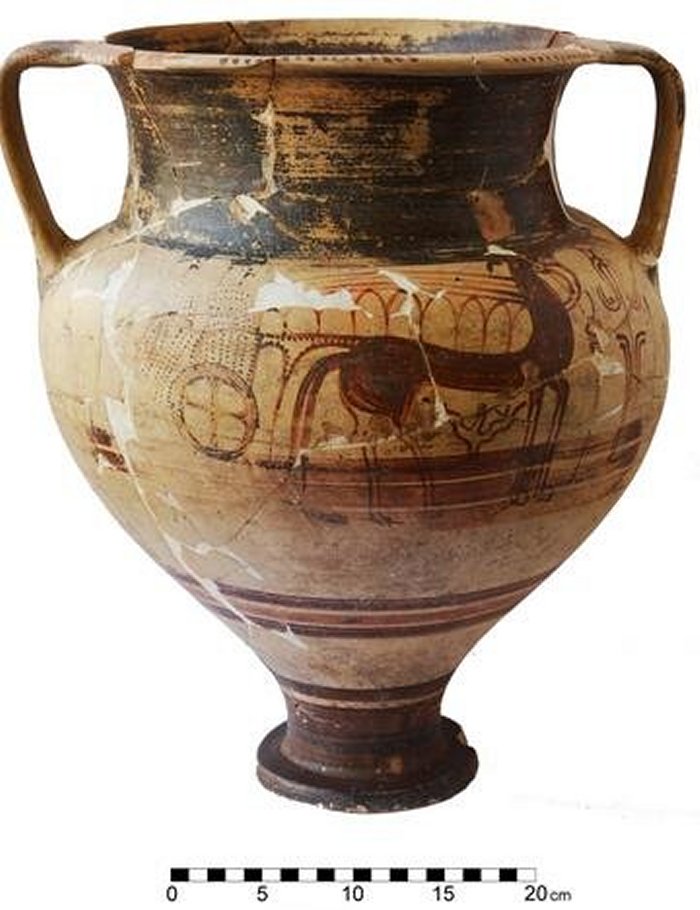

Most of the ceramic vessels came from what we now call Greece, and the expedition also found pots from Turkey, Syria, Palestine, and Egypt.
The grave goods also included bronze weapons, some inlaid with ivory, and a gold-framed seal made of the hard mineral haematite with inscriptions of gods and rulers.
“The vast wealth of the entombed individuals came from the production of copper. Nearby mines in the Troodos Mountains produced copper ore, which was refined in the city. This port city then exported the refined metal in large quantities to neighboring cultures. Copper was an important commodity because, combined with tin, it becomes the hard alloy bronze, which gave its name to the Bronze Age,” says Peter Fischer.
The recent discovery of these lavish tombs near Hala Sultan Tekke offers a fascinating glimpse into the opulence and sophistication of ancient Cyprus during the Bronze Age. The rich grave goods found within the tombs provide valuable insights into the lives and status of the city’s elite rulers.
The University of Gothenburg’s archaeological expedition’s remarkable findings contribute to our understanding of the ancient Mediterranean region’s trade networks and the significance of Hala Sultan Tekke as a center for the copper trade.
Cover Photo: One of the skeletons with tomb gifts (c. 1350 BCE). Photo: P.M. Fischer