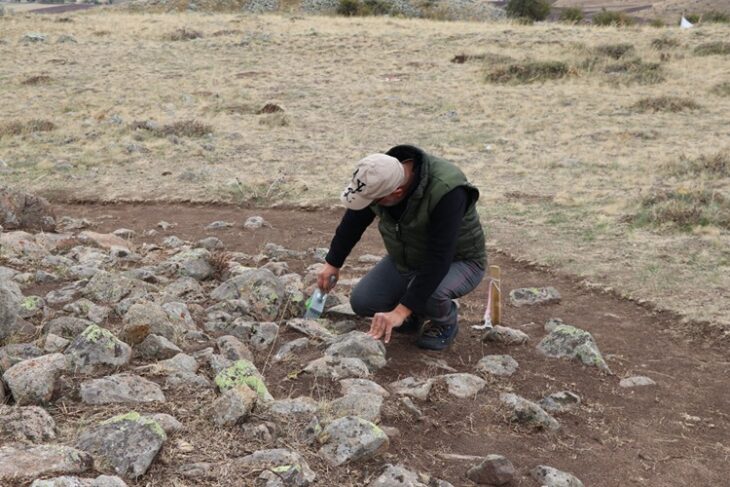
Hungarian archaeologists discovered the tomb of a Roman doctor 1st-century man buried with high-quality surgical tools near the city of Jászberény, about 80 km from Budapest.
The discovery was made by archaeologists from the ELTE Faculty of Humanities, the Jász Museum, and the Eötvös Loránd Research Network, according to ELTE’s official website.
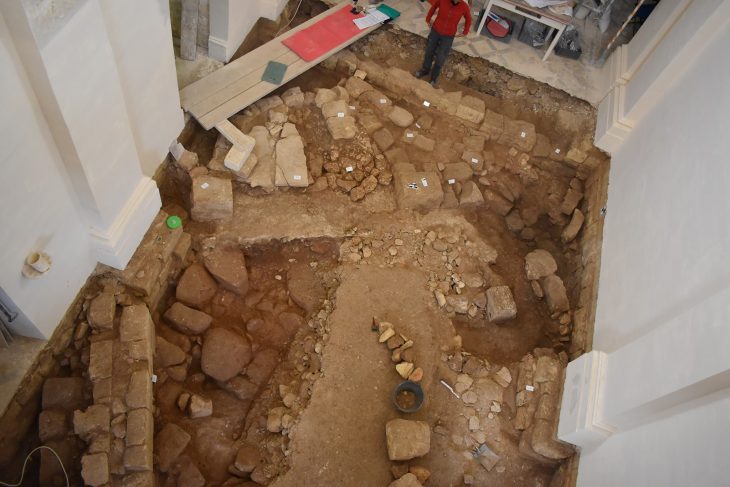
Excavations were conducted following a preliminary magnetometer field survey that indicated archaeological features beneath the ground surface.
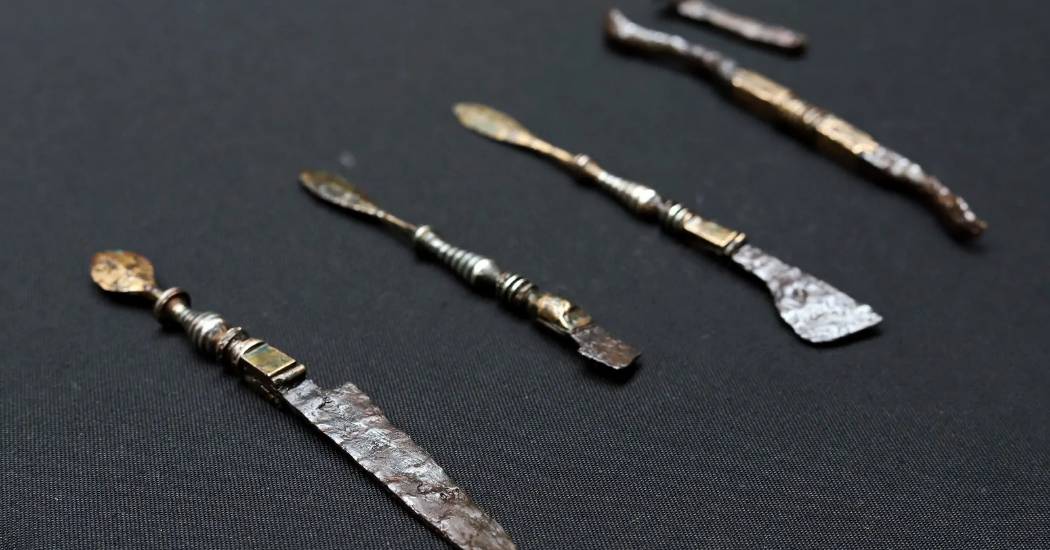
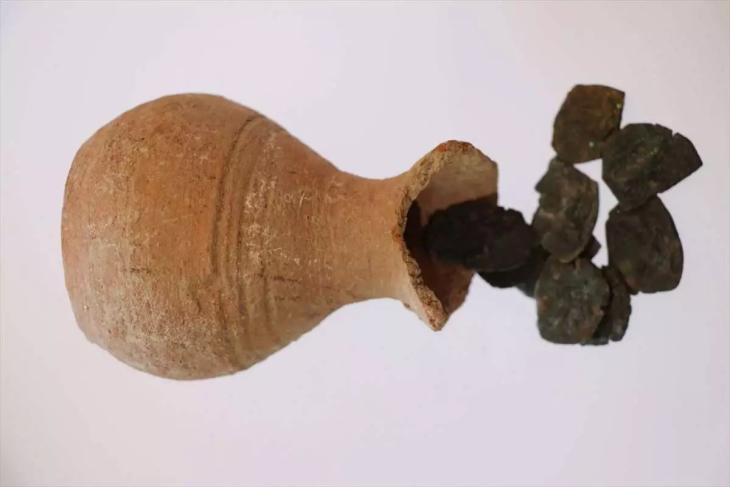
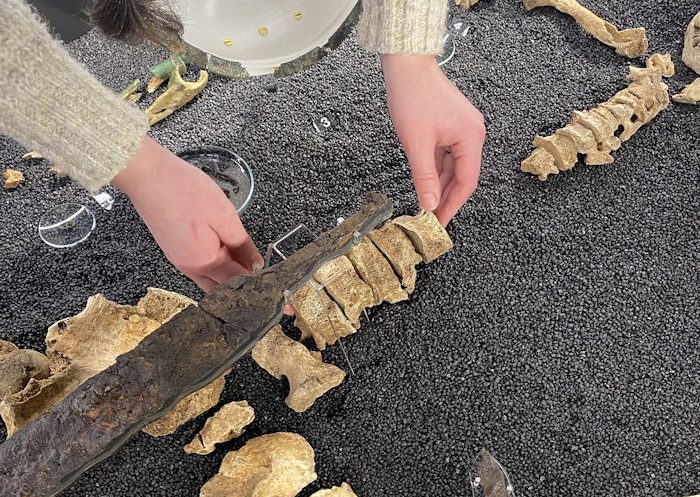
The tomb hasn’t been touched in about 2,000 years, according to a press release from Eötvös Loránd University. It includes the physician’s skeletal remains, with intact skull and leg bones, found alongside wooden chests containing an exceptional collection of medical tools. The equipment was of high quality, with pliers, needles, and scalpels with replaceable blades included. It also had a grinding stone, which could be used to mix medicines or sharpen blades.
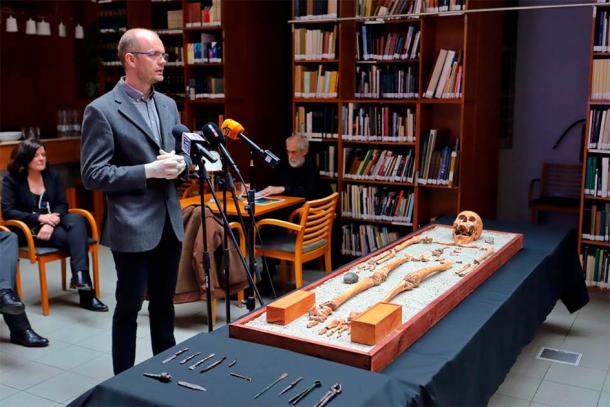

When the tools were examined more closely, it was discovered that they were of Roman origin and were placed in the burial of a Roman doctor in two wooden boxes. The tools were used for medical interventions, which includes forceps, needles and tweezers, and decorated scalpels made from copper alloy equipped with replaceable blades.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
He was a man between the ages of 50 and 60, according to an analysis of the skeleton, but the cause of death is still unknown because there are no signs of trauma or illness in the remains. To ascertain whether he was of local origin, the team intends to perform an isotopic analysis on the skeleton.
This collection of medical tools is only the second complete set of similar ancient Roman medical tools ever been found. The only other collection of this type was discovered in Pompeii.
It is not clear from the current data whether the physician buried in the tomb was there to heal a local leader of high prestige or whether he was accompanying a military movement of the Roman legions, explained András Gulyás, archaeologist and museologist at Jász Museum.
This period in Jászság may have been a transitional period between the Celtic and Roman Sarmatian populations.
This discovery has given researchers a starting point for learning more about the ancient Romans’ medical practices and, possibly, their travels to other areas to provide healthcare.