Rock and soil samples taken from the area where the ruins of ‘Noah’s Ark‘ are believed to be located in Doğubayazıt district of Ağrı were examined, and the first results of the research were announced. According to the results, it was determined that there were human activities in the region from the period between 5500 and 3000 BC.
Professor Faruk Kaya stated, “With the dating, it is not possible to say that the ship is here. Extensive research is required for this to emerge. In the upcoming period, we have reached an agreement to collaborate on joint research led by Istanbul Technical University (İTÜ), Andrew University, and Ağrı İbrahim Çeçen University (AİÇÜ). In the future, these three universities will continue their work in this field.”
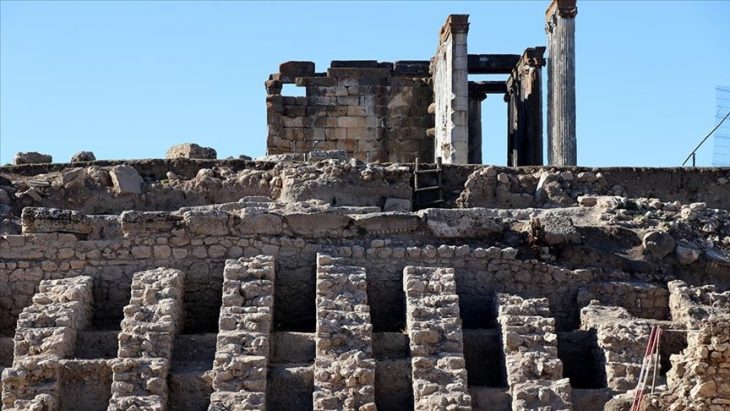
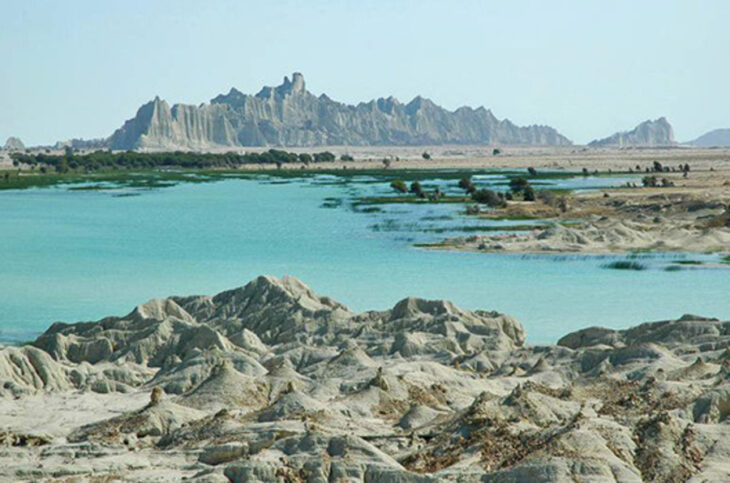
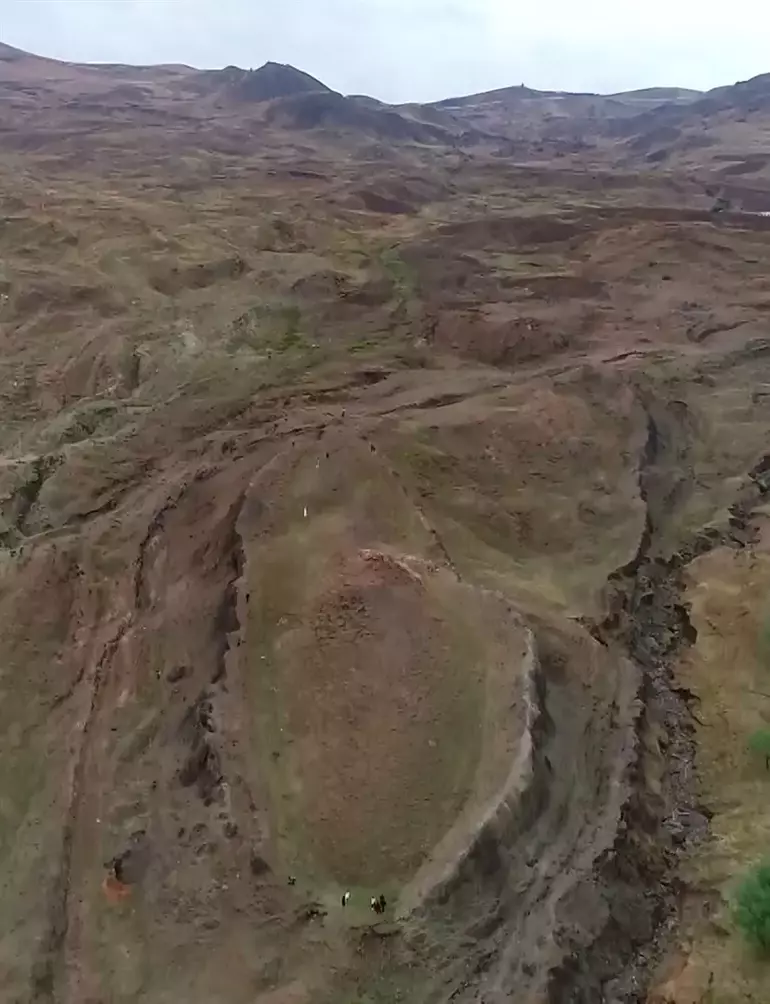
The ruins, claimed to belong to ‘Noah’s Ark’, discovered by expert cartographer Captain İlhan Durupınar in 1959 in the land between Telçeker and Üzengili villages of Doğubayazıt district of Ağrı, attract the attention of local and foreign tourists.
Giant fissures have formed in the ruins, which are under increasing threat of landslides every year. ‘Mount Ararat and Noah’s Ark Research Team’ was established in cooperation between AİÇÜ and ITU for scientific research on the ruins, whose structure was damaged due to landslides.
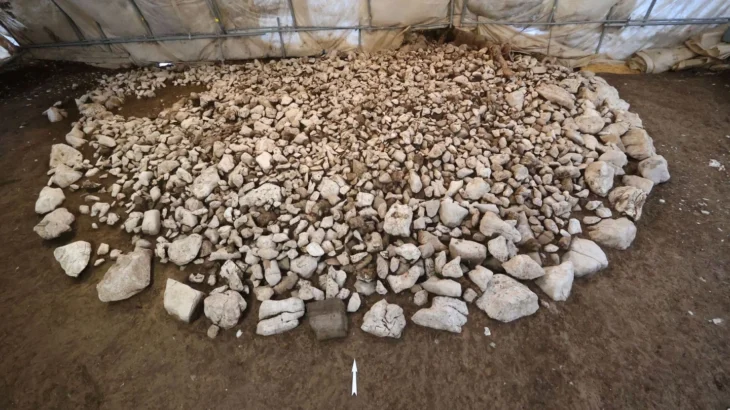
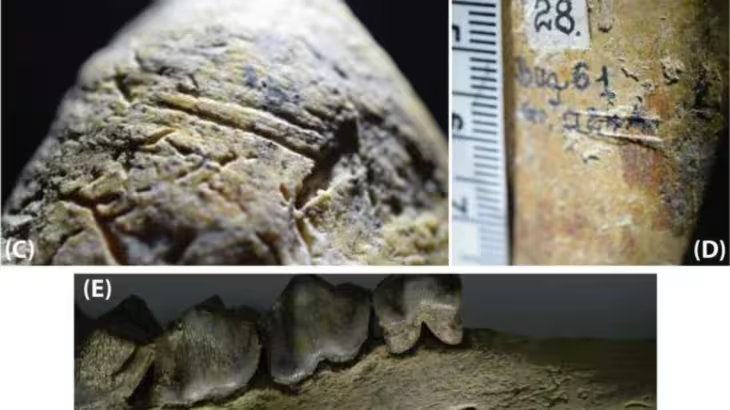
The team formed within the scope of the academic cooperation protocol carried out its first study in the region in December last year. The group, which included academics specialized in geophysics, chemistry and geoarchaeology research, collected many samples consisting of soil and rock fragments during their investigations in the region. Samples taken from the remains were sent to ITU laboratories for examination.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Nearly 30 rock and soil samples collected with special permission were examined in ITU laboratories. After approximately 1 year of work, the samples taken were aged. According to the first results from the laboratories, the samples taken from the region were determined to be clayey materials, marine materials, and seafood.
Evaluating the laboratory results, AİÇÜ Vice Rector Professor Faruk Kaya stated that the samples examined were determined to be between 3500 and 5000 years old in the dating study and said:
The results of ongoing laboratory studies related to the area believed to be the remnants of Noah’s Ark, located between the villages of Telçeker and Üzengili, as part of the project we conducted with Istanbul Technical University in 2022, have partially emerged. Since it is a long-term project, the laboratory work has not been fully completed yet. However, based on the initial findings from the work conducted in the area, it is believed that human activities have been present in the region since the Chalcolithic period, between 5500 and 3000 BCE.”
It is known that the event of Prophet Noah’s flood dates back approximately 5,000 years from today. In terms of dating, it is stated that there was human activity in this region. This was revealed in the laboratory results. However, with the dating, it is not possible to definitively say that the ship was here. Extensive research is needed for this to be established. In the coming period, we have reached an agreement to collaborate on joint research led by Istanbul Technical University, Andrew University, and Ağrı İbrahim Çeçen University. In the future, these three universities will come together and establish new commissions to continue their work in this field.”
Professor Kaya also mentioned that the 7th International Ararat and Noah’s Ark Symposium, organized in collaboration between Ağrı İbrahim Çeçen University (AİÇÜ) and Istanbul Technical University (İTÜ), addressed the topic. He stated, “Another important aspect of the symposium is the decision to conduct joint research in the Cudi and Ararat regions, which are known as the Mesopotamia region and are mentioned in the Quran and the Holy Bible. From now on, we will continue to intensify our work in both Cudi and Mount Ararat,” he said.