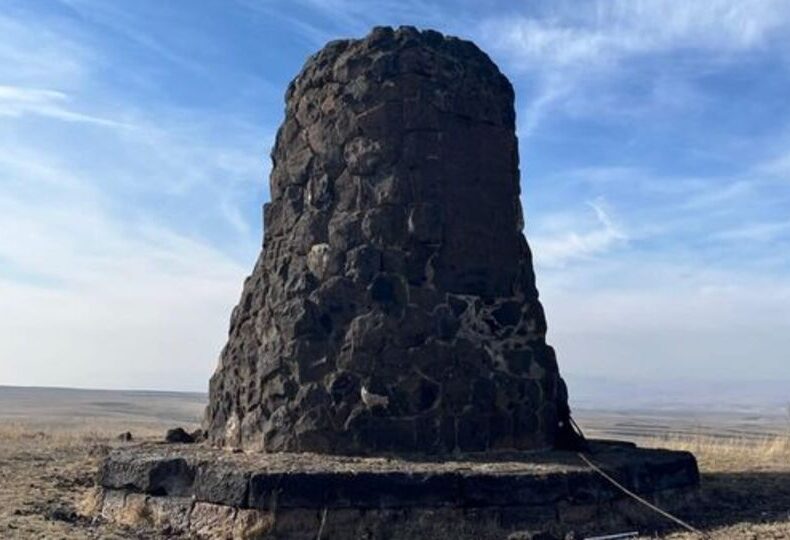
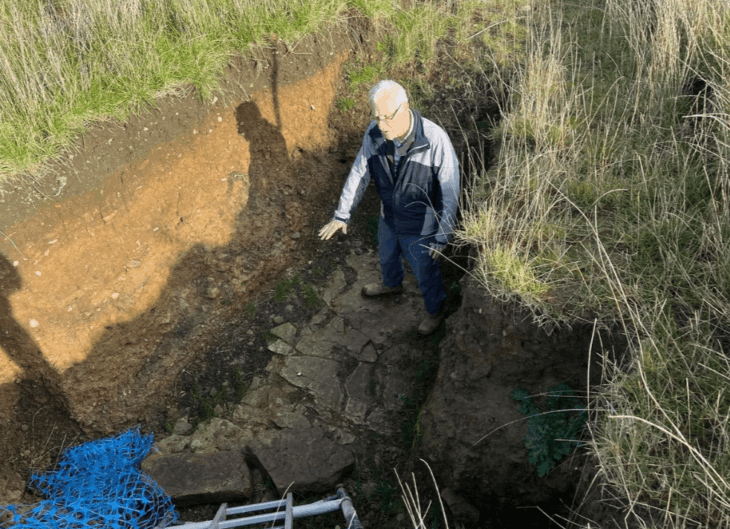
A lone stone structure standing silently on a windswept hill near Kars has begun to draw growing curiosity. Rising from the summit of what locals call Ziyaret Tepesi or Evliya Tepesi, this enigmatic monument appears to watch over the vast plains leading all the way to the ancient city of Ani. Yet despite its striking presence, almost nothing is known about who built it—or why.
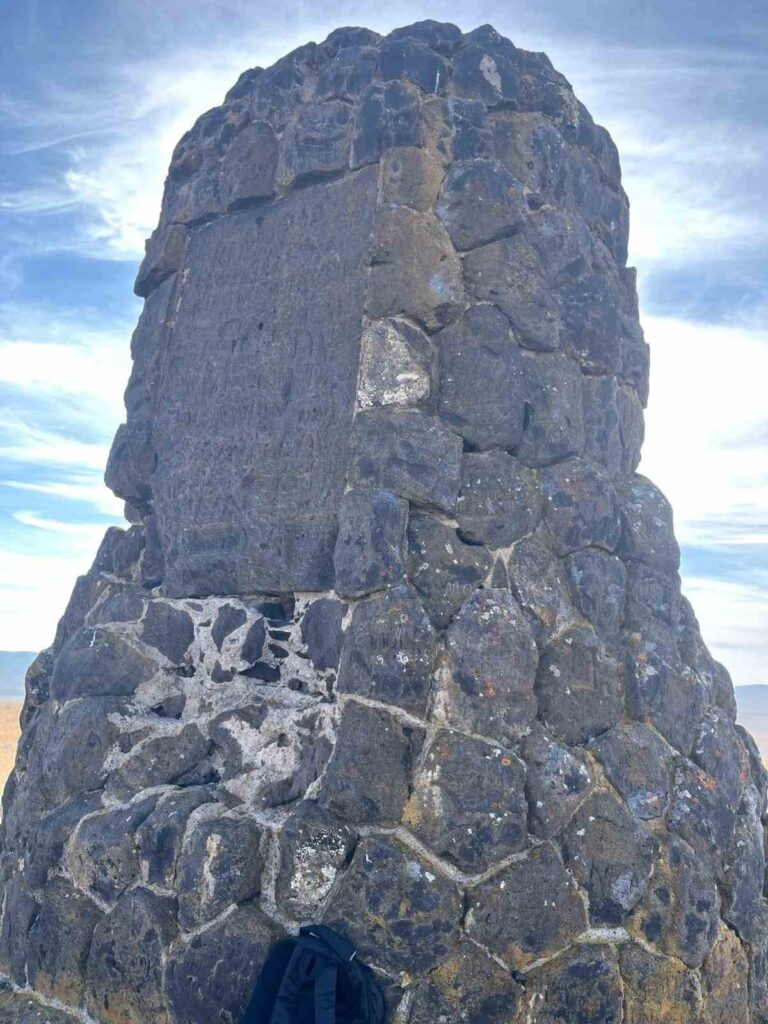
Located about 26 kilometers from Kars city center, within the borders of Bulanık Village, the hill lies between Yahni Mountain and Dumanlı Mountain. At its peak stands a roughly 5-meter-tall construction built from soft, dark stones. Weathered and irregular, the structure resembles a tower or marker, but no official research has yet revealed its age, cultural origins, or purpose.
A Mysterious Inscription Facing Ani
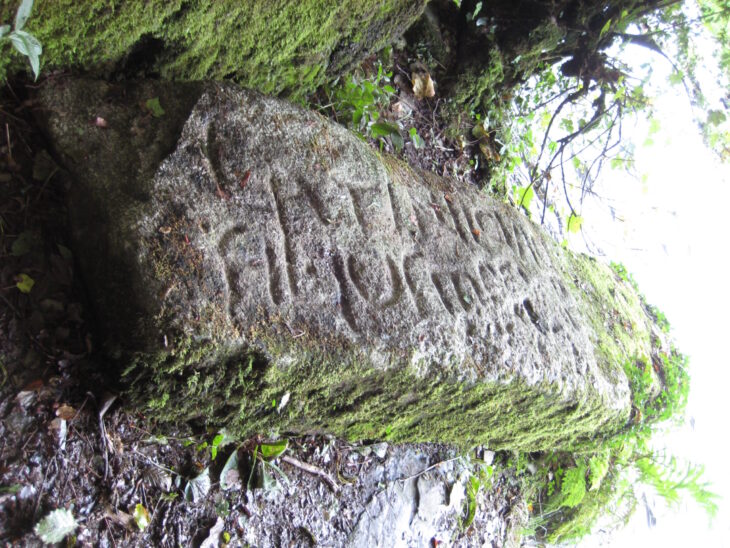
One of the most intriguing features of the site is found on the side facing the ruins of Ani. There, a flat stone bears an inscription nearly 2 meters in height. It appears meticulously carved, but the language and meaning of the writing remain undeciphered.
Local villagers believe the script could belong to an ancient civilization once active in the region. The proximity to Ani—a medieval city rich with Armenian, Seljuk, and Georgian heritage—only deepens the speculation. Experts who have heard of the monument emphasize the need for detailed archaeological surveys to determine whether the inscription represents a known language, an unrecorded variant, or possibly decorative symbols rather than formal writing.
Watchtower, Boundary Marker, or Sacred Monument?
Within the community, many theories circulate about the structure’s original function.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Some villagers claim the tower-like design suggests a watchtower, offering a clear vantage point over the open plains. Others propose that it may have served as a boundary stone, identifying territorial lines between ancient settlements or kingdoms.
Another group believes the hill may once have been a ritual or pilgrimage site, especially since many peaks in Anatolia traditionally hosted shrines, tombs of holy figures, or ceremonial structures. The lack of definitive data only amplifies the sense of mystery the hill carries.
A Site Drawn to Treasure Hunters, Now Protected
Like many ancient or unexplored sites in eastern Türkiye, the hill has at times attracted treasure hunters. In recent years, however, local security teams have increased protection of the area, preventing unauthorized digging and helping preserve what remains. Residents of Bulanık Village hope the site will soon be studied properly so that its historical value can be documented and protected.

How This Structure Compares to Similar Ancient Monuments: Preliminary Observations Based on the Image
Although no archaeological study has yet been conducted at the site, a few preliminary comparisons can be made solely based on visual observations from the provided image. These comparisons do not represent definitive conclusions, but rather the type of early-stage assessments an archaeologist might make before an on-site survey:
Resemblance to cairns and marker piles in Eastern Anatolia and Central Asia: The stacked-stone appearance and the rough, unshaped blocks recall the cairn-like formations used in various historical periods for navigation, memorial purposes, or territorial marking.
Similarities to small, early-period lookout structures in the Caucasus region: The monument’s vertical form and placement on an elevated ridge resemble simple, stone-built lookout points seen in mountainous parts of the Caucasus. This does not confirm a defensive function, but the visual parallel is noteworthy.
Use of dark volcanic stone similar to monuments around the Armenian Highlands: The texture and coloration of the stones in the image suggest basalt or another locally available volcanic material. Many ancient structures around Ani and the highlands used comparable stone types, which may indicate regional construction traditions.
These observations remain tentative and entirely based on the photograph, not on field measurements, excavations, or material analysis. Proper archaeological investigation would be required to validate or refute any of these preliminary possibilities.

A Call for Archaeological Exploration
Residents of Bulanık Village are hopeful that an official excavation or research initiative will finally peel back the layers of mystery surrounding the hill. Many believe the structure could reveal a previously unknown chapter in the region’s long and multicultural history.
Until professional studies begin, Ziyaret Tepesi remains one of Kars’ most intriguing unsolved puzzles—a silent stone guardian overlooking the ancient plains and the timeless ruins of Ani, waiting for its secrets to be discovered.
Cover Image Credit: Serkan Çağlar/Kars-İHA