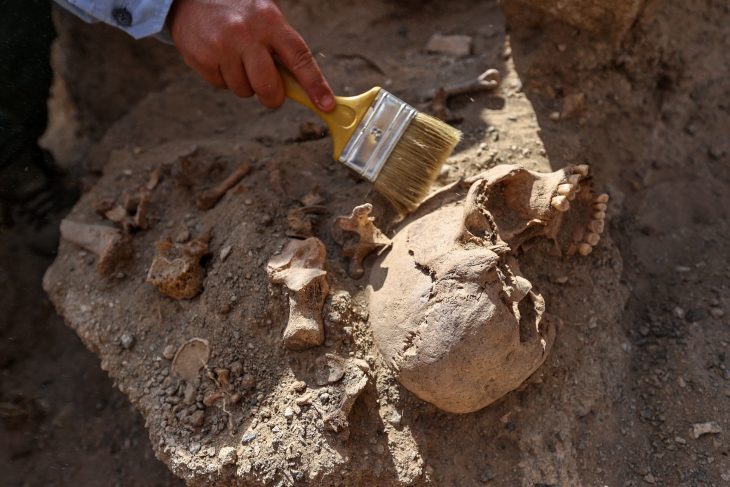
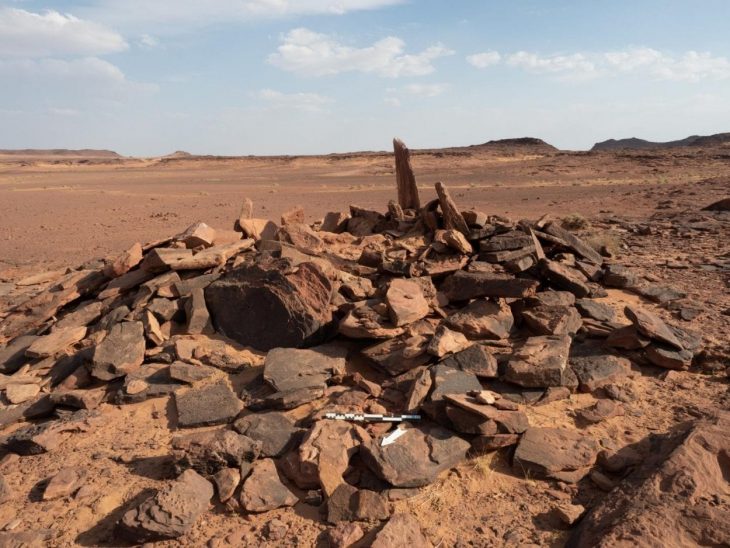
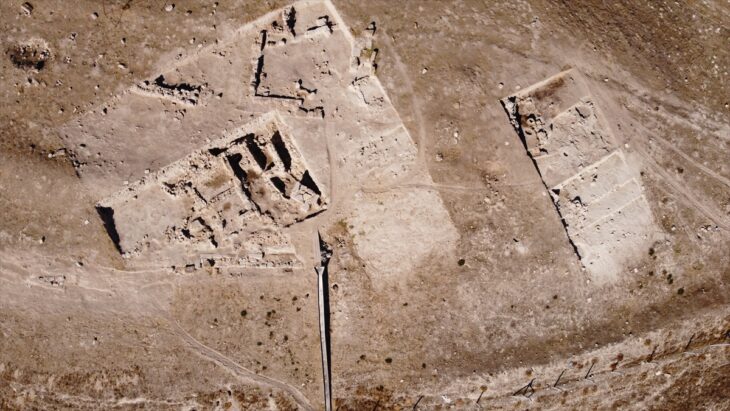
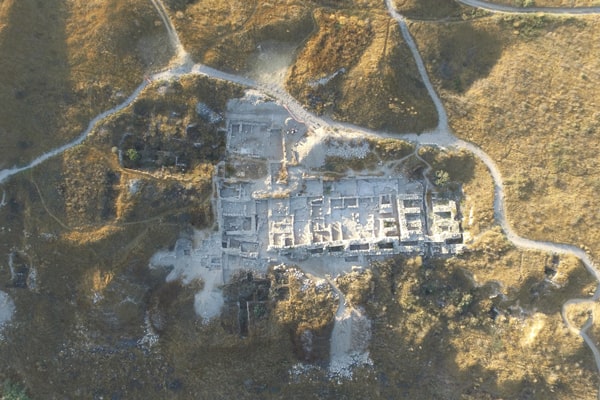
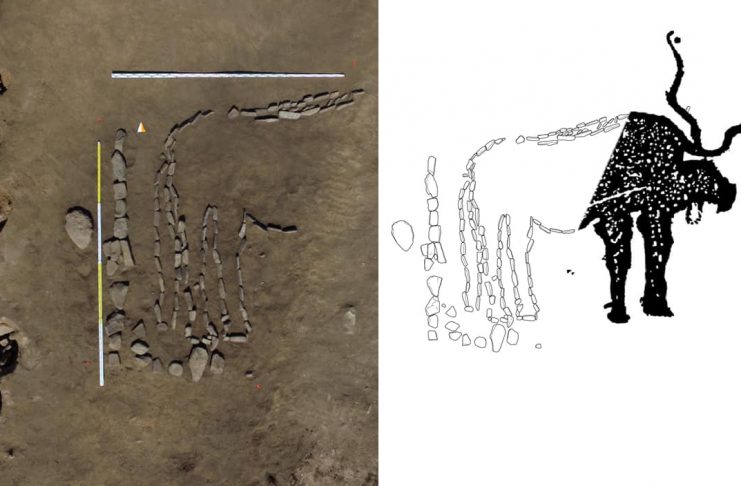
Archaeologists from the Russian Academy of Sciences’ Institute of History of Material Culture (IIMK RAS) and LLC Krasnoyarsk Geoarchaeology discovered a geoglyph showing a bull near the village of Khondergey in the Republic of Tuva, close to Russia’s border with Mongolia.
The bull geoglyph found is the first such discovery for the region and Central Asia.
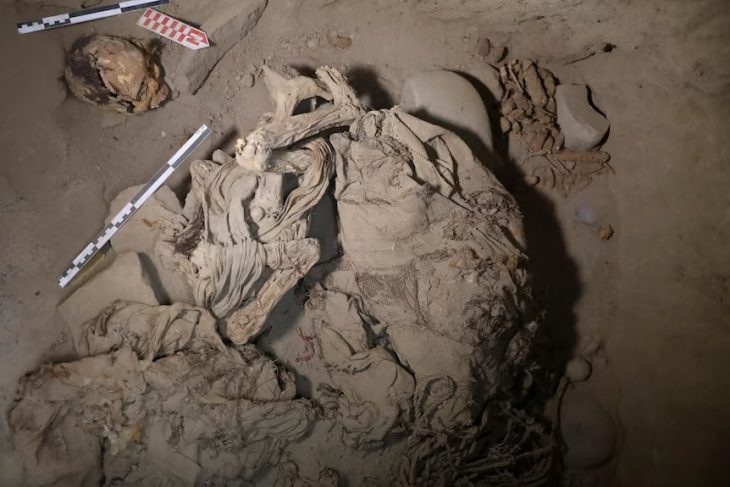
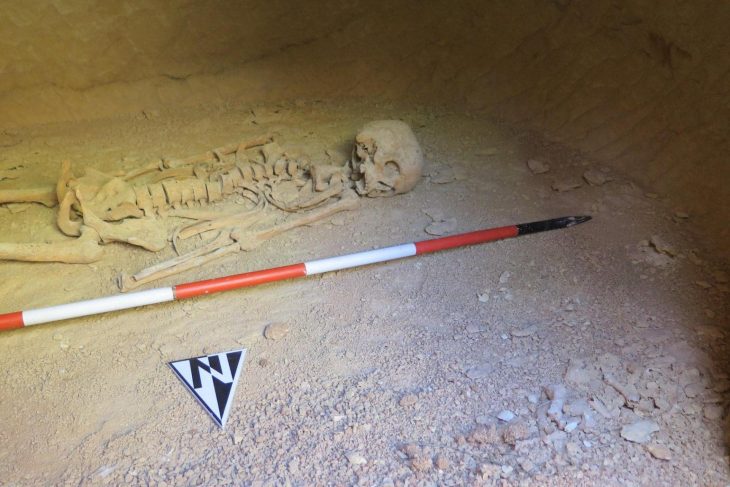
Archaeologists stated that the find was made as part of a wider burial from the Early Bronze Age, which dates back more than 4,000 years, as proven by ceramics recovered in the area. The bull is represented by meticulously arranged pebbles and stone created from locally available sandstone and measures 3 by 4 meters.
Bull geoglyph is the first animal geoglyph discovered in this part of the world.
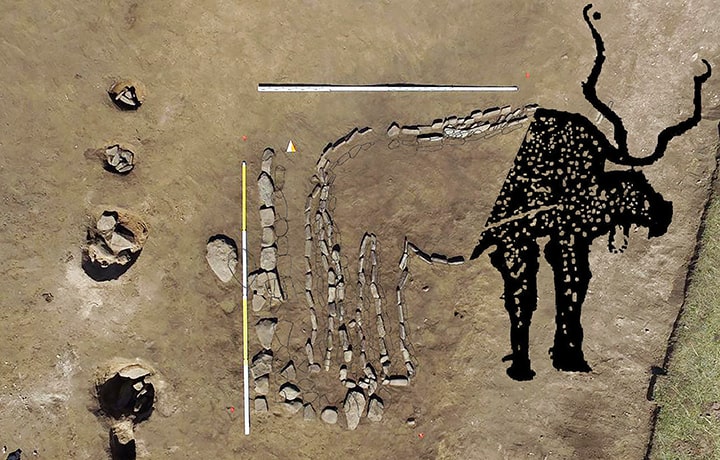
Only the rear of the bull, including the hind legs and tail, was saved; the front portion was unintentionally destroyed by road building in the 1940s.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
‘”The bull motif is very typical for the Central Asia cultures of the Early Bronze Era. Later in the Scythian times, bulls were replaced by deers,” said the head of Tuva Archaeological Expedition, Marina Kilunovskaya.

′′The bull geoglyph has characteristics of Central Asian cultures in the era of the Early Bronze Age. We find bulls in petroglyph groups in Tuva and the surrounding areas, but a geoglyph in the form of an animal figure is a unique phenomenon, perhaps even for the Central Asia region in general.”
Kilunovskaya went on to say: “Although we can recognize the bull depiction, allowing us to reconstruct the lost parts with a high degree of probability, we have never seen stone layouts such as these before. In our opinion, the uniqueness of the find and the threat to the site due to the adjacent road requires further preservation.”
Pictures: Institute of the history of Material Culture, Russian Academy of Sciences
Institute for the History of Material Culture of the Russian Academy of Sciences