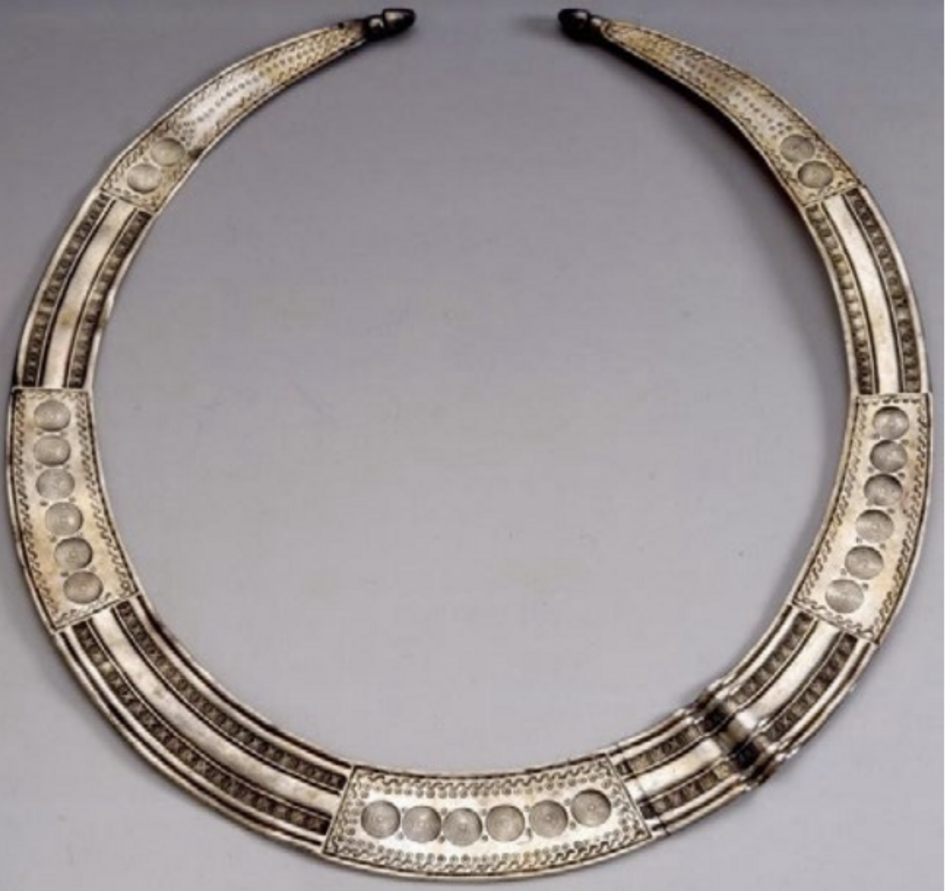
A groundbreaking study published in the journal Palaeohispanica has shed light on the ancient timekeeping practices of the Celts, centering on a unique piece of jewelry known as the lunula from the Chão de Lamas treasure in Portugal. Conducted by Professor Roberto Matesanz Gascón from the University of Valladolid, the research posits that this intricately designed gold artifact may hold crucial information regarding the synchronization of lunar and solar cycles within the Celtic calendar.
Traditionally viewed as a mere decorative item, the lunula—shaped like a half-moon and discovered in Chão de Lamas (Miranda do Corvo, Coimbra)—has now been reinterpreted. Matesanz’s analysis of its complex geometric patterns suggests that it could serve as a visual representation of a Celtic calendrical cycle lasting 114 years. This timeframe aligns with six Metonic cycles, each spanning 19 years, which is a known astronomical framework that facilitates the alignment of lunar and solar calendars.
The Coligny calendar, an important epigraphic source from France dating back to the 2nd century AD, provides detailed insights into how the Celts structured their time. It organizes time into five-year cycles comprising 62 months, totaling 1,835 days. However, scholars have long debated how these cycles correspond to the tropical year of 365.24 days.
Matesanz’s study is particularly innovative as it establishes a connection between the Coligny calendar and the geometric designs of the Chão de Lamas lunula. He theorizes that the circular motifs on the jewel represent a timekeeping system that adjusts the solar year by eliminating 53 days every 114 years. This intriguing figure of 53 days is also referenced in Irish literary sources, hinting at a potential link to Celtic traditions in Ireland.
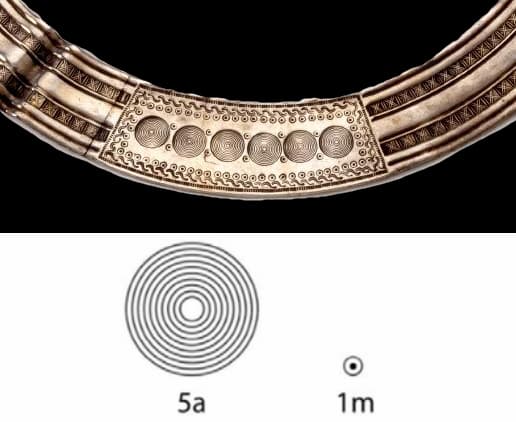

Geometric Patterns and Celestial Alignments
The lunula’s design is more than decorative; it features large concentric circles and smaller circles with central dots, organized into five distinct sections. Matesanz suggests that these elements may correspond to the months within the Celtic calendar’s five-year cycle.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The arrangement of these geometric motifs is critical. The study indicates that the lunula’s elements could symbolize six five-year cycles, each containing 62 months, culminating in a total of 30 years—referred to as the Celtic saeculum by Pliny the Elder in his Natural History. However, this calculation results in an excess of 53 days compared to the solar cycle.
To address this discrepancy, Matesanz proposes that the Celts would have adjusted their calendar every 114 years by omitting these days, ensuring that their festivals and astronomical observations remained in sync with the changing seasons.
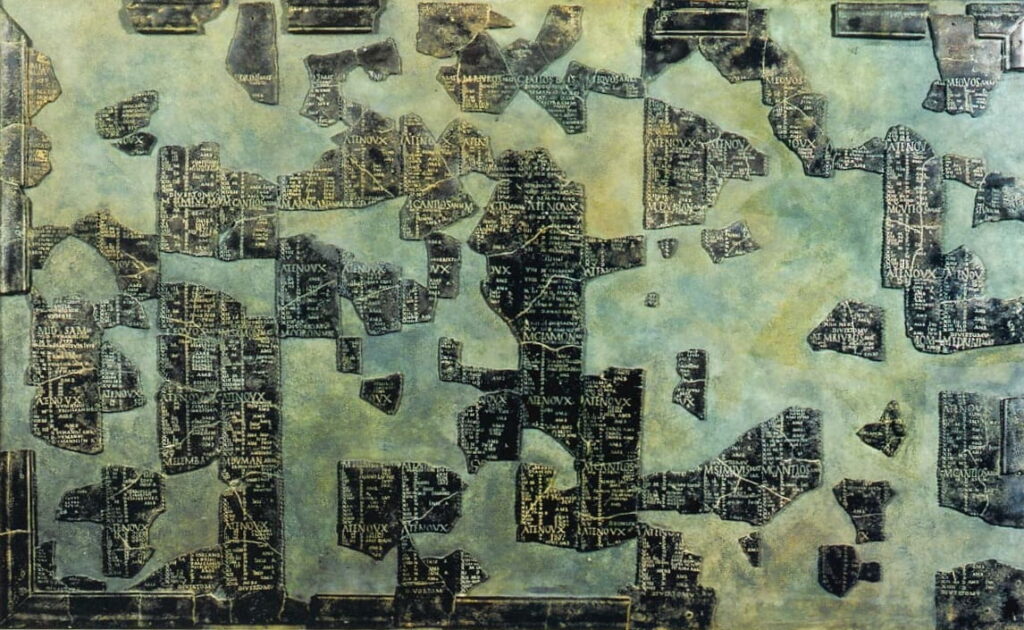

Connections to Irish Mythology
One of the most captivating aspects of this research is the appearance of the 53-day figure in Irish Gaelic texts, particularly in the medieval tale Baile in Scáil. In this narrative, the legendary king Conn Cétchathach encounters a magical stone on the Hill of Tara, with his druids stating they cannot reveal his name until 53 days have elapsed. This period of silence may correspond to the days omitted in the Celtic calendar to maintain its alignment with the solar year.
If validated, this hypothesis would indicate that Celtic oral traditions preserved elements of an ancient time synchronization method, even centuries after Roman influence. It would further support the notion that Celtic civilization possessed sophisticated astronomical knowledge, evident in both their artifacts and mythology.
The study also prompts a reevaluation of the role of art as a symbolic language among the Celts. The Chão de Lamas lunula may exemplify how they integrated abstract and mathematical concepts into their artistic expressions.
Additional archaeological discoveries bolster this perspective. In the Iberian Peninsula, similar iconographic objects, such as the Axtroki bowls and the Leiro helmet, suggest potential calendrical functions. Meanwhile, in Central Europe, artifacts like the Schifferstadt-type golden hats have been interpreted as timekeeping instruments, reinforcing the idea of a shared understanding of time across ancient cultures.
Roberto Matesanz Gascón, The lunula with geometric decoration of the treasure of Chão de Lamas and the Celtic calendar. Palaeohispanica, vol.24 (2024). doi.org/10.36707/palaeohispanica.v24i1.543
Cover Image Credit: Piero Baguzzi / R. Matesanz / MAN, Ministerio de Cultura de España