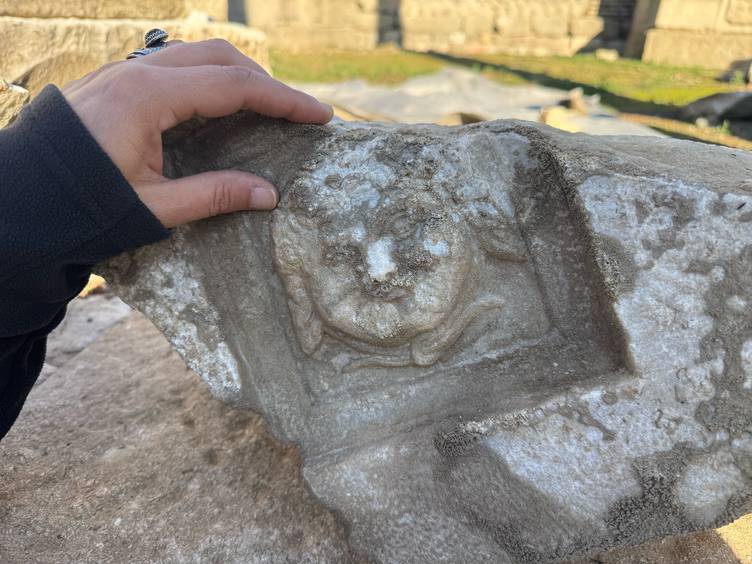
Archaeologists working in the ancient city of Amastris, located in the modern-day town of Amasra in Türkiye’s Bartın province, have unearthed an extraordinarily rare depiction of Medusa with a gentle, almost childlike smile. The carving—described by experts as “Eros-like”—was found during ongoing excavations in a monumental Roman stoa. The site stands within the ancient city established by Queen Amastris, one of the most influential female rulers of the Hellenistic period.
The discovery has sparked excitement not only among archaeologists but also among cultural historians, as the smiling Medusa diverges strikingly from the traditional imagery of the mythological creature known for her serpent hair and the power to turn onlookers to stone. Instead of a fearsome guardian, this Medusa appears serene—an artistic choice that researchers believe reflects the prosperity and peaceful atmosphere of the city during the Roman era.
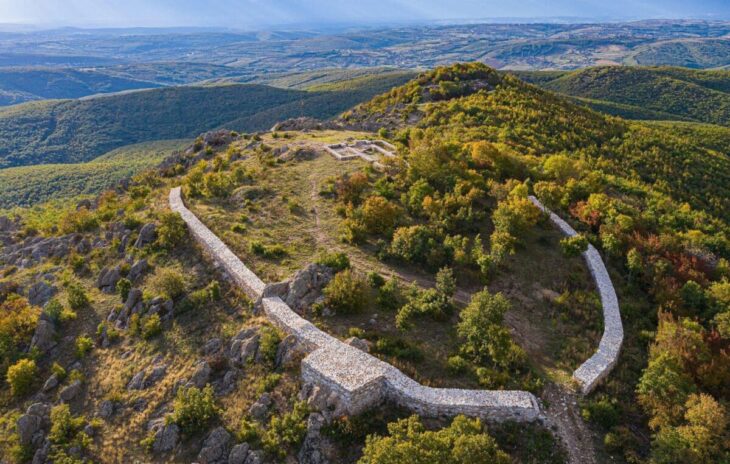
A Monumental Stoa Reveals the Grandeur of Ancient Amastris
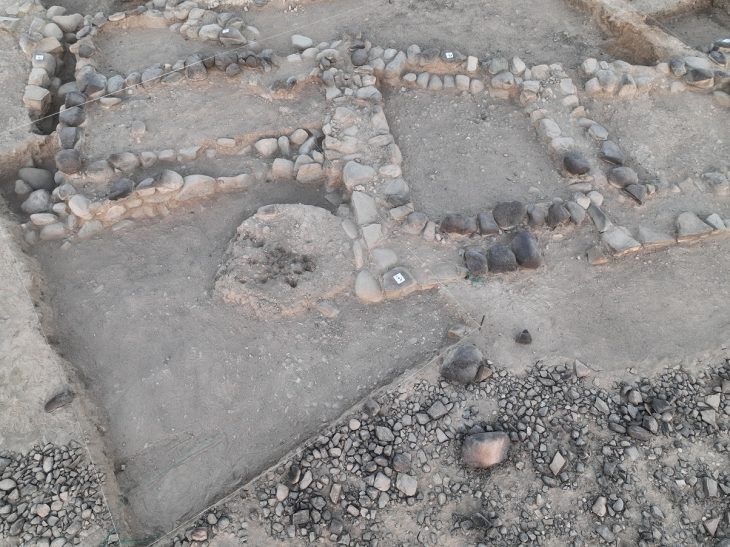
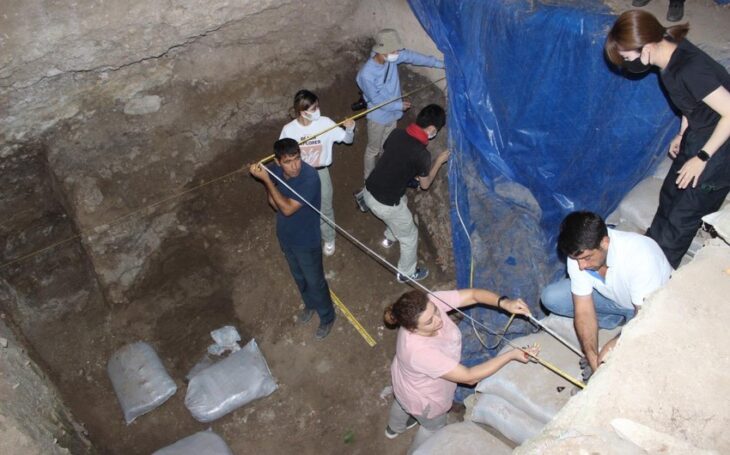
The excavation, conducted by Bartın University under the leadership of Prof. Dr. Fatma Bağdatlı Çam, focuses on a 2,850-square-meter area where a massive Roman-period stoa was uncovered. This public structure, distinguished by towering marble Corinthian columns reaching approximately nine meters in height, once served as a vibrant social and commercial hub in Amastris. In Roman cities, stoas functioned as covered walkways and gathering spaces, forming essential parts of agoras or forums.
The restoration of the building has progressed through an extensive anastylosis effort, a meticulous reconstruction technique using original architectural elements. Three columns have already been re-erected, and four more are planned to rise by the end of the year. The project, carried out with the approval of Türkiye’s Ministry of Culture and Tourism and supported by Turkish Petroleum Corporation, brings together experts and students from multiple universities.
According to Prof. Çam, the stoa is likely the most monumental marble structure in the entire Black Sea region, making it a landmark both archaeologically and architecturally. Its discovery offers invaluable evidence about the social life, trade networks, and cultural sophistication of the ancient city.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A Smiling Medusa Unlike Any Other
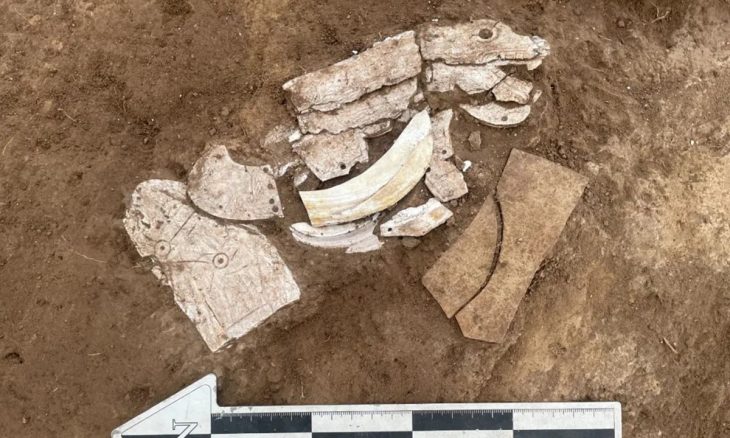
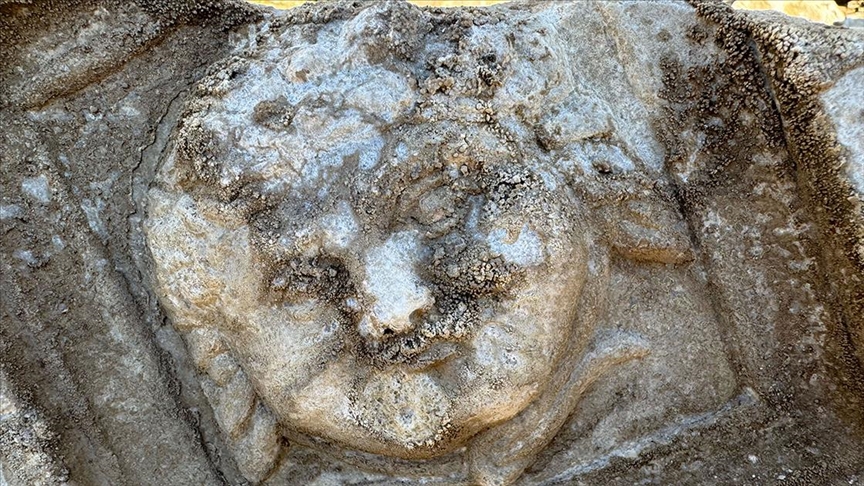
What sets this excavation season apart is the finding that appeared on the ceiling coffers positioned above the monumental columns: a smiling Medusa, carved in marble.
Traditionally, Medusa—one of the three Gorgon sisters in Greek mythology—served as an apotropaic symbol. Her terrifying visage was carved onto shields, pediments, armor, and building facades to ward off evil. Her threatening expression and snake-entwined hair were visual cues meant to instill fear and protect the structures they adorned.
Yet the Medusa discovered in Amastris defies this convention.
Prof. Çam explains that the figure’s face resembles that of a young child or an Eros figure, a symbol of harmony and well-being in classical art. Rather than projecting terror, this Medusa radiates tranquility. Such a depiction is extremely rare, leading researchers to believe that the artisan—and perhaps the city’s elite—wanted the Medusa to symbolize peace, prosperity, and protection through beauty rather than fear.
Amastris: A City Born from the Vision of a Queen
This remarkable discovery gains further significance when viewed in the context of Amastris’s origins. The ancient city was founded by Queen Amastris, a powerful Hellenistic ruler born into Persian nobility and educated in Greek culture. She was the niece of the Persian king Darius III and later became the wife of Dionysius of Heraclea and subsequently Lysimachus, one of Alexander the Great’s successors.
After navigating the turbulent political landscape of the era, Amastris established her own autonomous city in the late 4th century BCE by uniting four coastal settlements. The city became a thriving center of culture and trade along the Black Sea. Her rule is remembered for significant urban development, including fortification walls, temples, and public buildings.
Finding a unique art piece such as the smiling Medusa in the city she founded underscores Amastris’s legacy of blending Persian heritage with Hellenistic and Roman influences. The unusual artistic choice may reflect the city’s distinctive cultural identity—cosmopolitan, prosperous, and open to artistic experimentation.

Previous Discoveries Reveal a Rich Cultural Layer
The smiling Medusa is only the latest addition to a growing collection of artifacts unearthed in Amastris. Previous seasons have revealed:
- A finely crafted head of Alexander the Great
- Sculptures of Nymphs and household deities known as Lares
- Amulets, coins, and inscribed fragments from multiple periods
Together, these finds confirm that Amastris was a significant urban center with strongmythological, political, and commercial connections across the ancient world.
A Future Tourism Landmark in the Making
The restoration efforts aim to open the site partially to visitors by late 2026 or early 2027. With its monumental columns, rare artworks, and historically rich urban fabric, the stoa is expected to become a major cultural tourism destination in the Black Sea region.
Prof. Çam highlights that seeing these ancient structures rise again, piece by piece, offers both archaeological insight and public excitement. For locals and tourists alike, the rebirth of Amastris Ancient City provides a rare opportunity to witness the gradual revival of a forgotten Roman metropolis.
A Symbol of Hope for the Archaeological Future of Amasra
The smiling Medusa—radiant, serene, and unexpectedly gentle—has become an emblem of hope for the excavation team. It symbolizes not only the artistic uniqueness of the ancient city but also the promising future of archaeological work in the area.
As Prof. Çam notes, the discovery encourages researchers and visitors alike to imagine Amastris as it once was: a flourishing coastal city, shaped by a visionary queen, enriched by Roman architecture, and guarded—rather softly—by a smiling Medusa.
Cover Image Selim Bostancı/AA