During this year’s excavations at Ephesus in Turkey, archaeologists from the Austrian Academy of Sciences (AW) discovered an incredibly well-preserved early Byzantine business and dining space that had apparently been destroyed suddenly in AD 614/615.
The discovery, according to the head of the excavation Sabine Ladstätter, is the most significant one to have occurred in the ancient city since the discovery of its renowned hill houses.
Ephesus is one of the world’s largest and most impressive ancient cities, as well as one of Turkey’s most important ancient cities. Its cultural and historical significance was highlighted in its addition to the UNESCO World Heritage Site list in 2015. The remains of the city lie just 80 km inland from the popular seaside city of İzmir and close to the charming towns of Selcuk and Sirince.

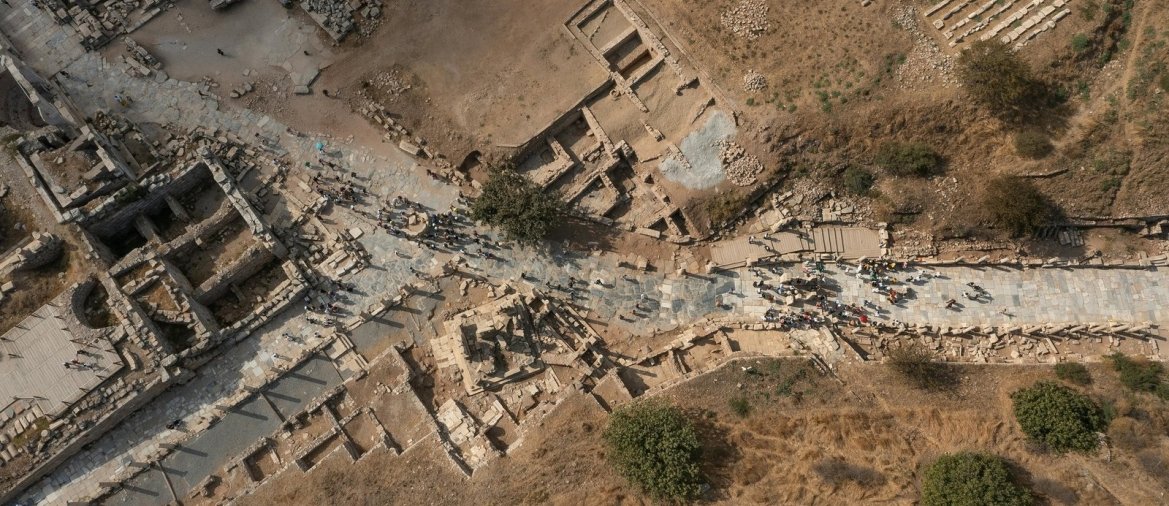
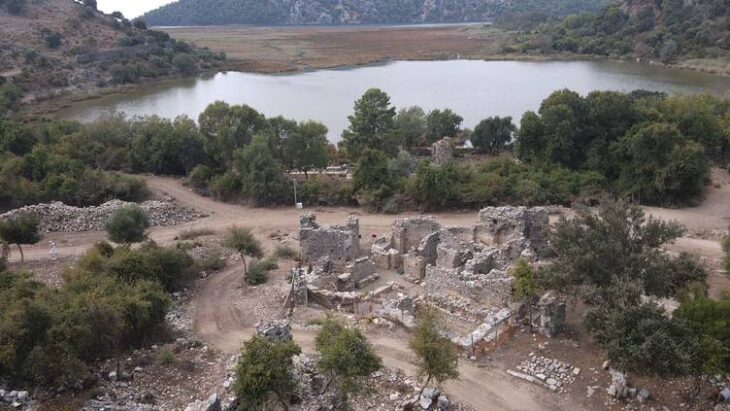
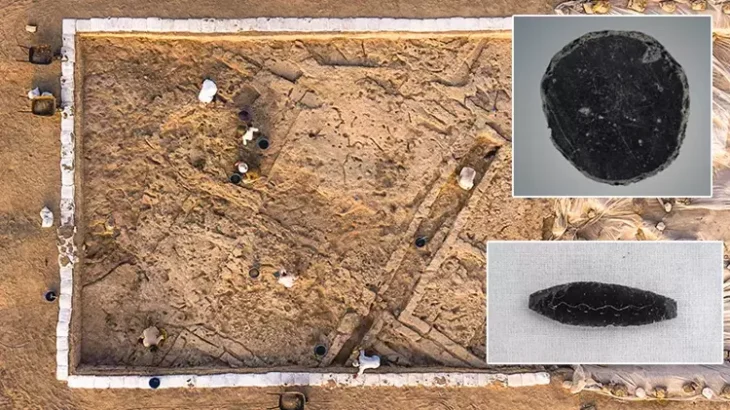
The newly discovered neighborhood is on Domitian Square, a prominent square directly adjacent to the Roman city’s political center, the Upper Agora. The excavations this year are part of a large research project on Ephesus’ changes between the Roman Empire and Late Antiquity.
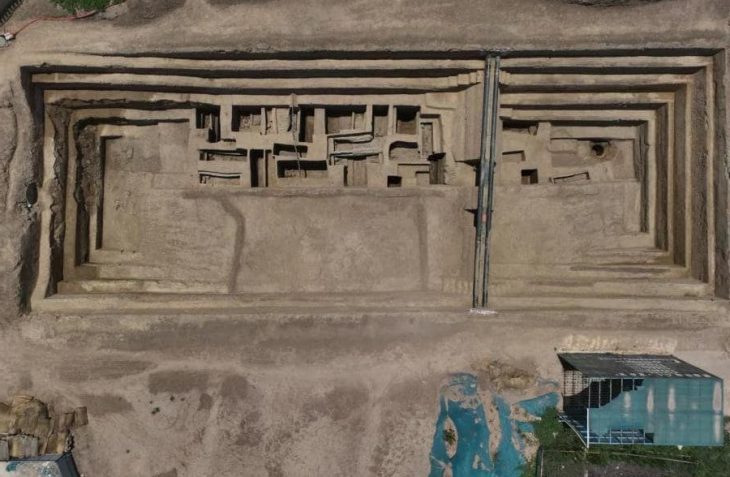
Byzantine shops and workshops were built over a large Roman square complex, with the team focusing excavations on a structure consisting of several business premises that covers an area of around 170 square meters.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
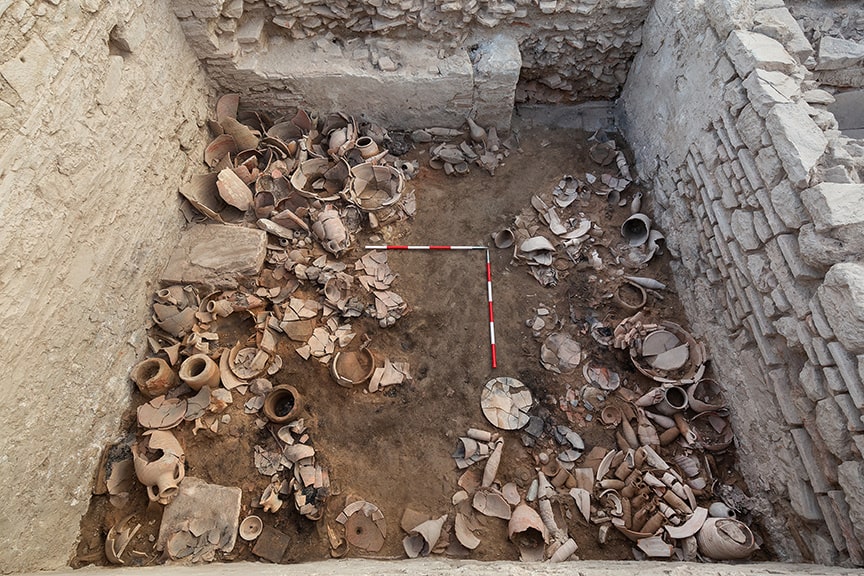

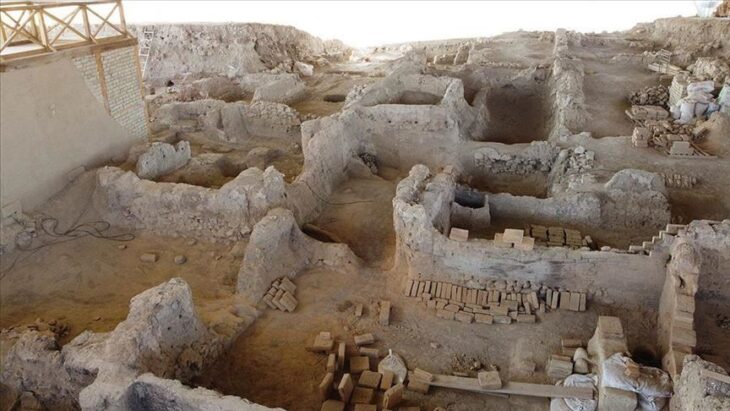
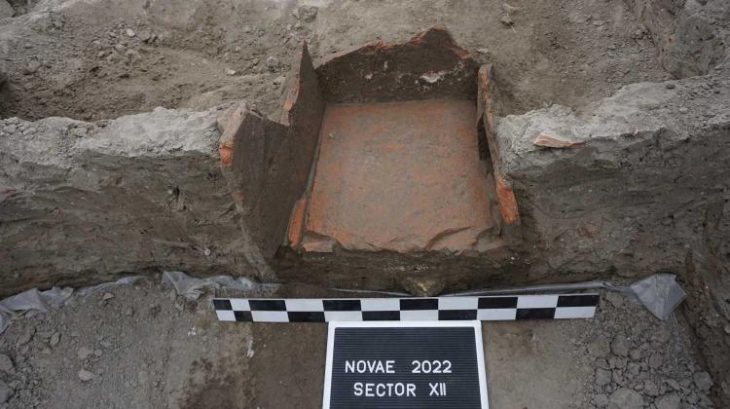
The researchers dug up filling material meters high and eventually arrived at a fire layer about half a meter thick. Sealed by this, a unique snapshot of life at the time was preserved at a depth of about 3.5 meters.
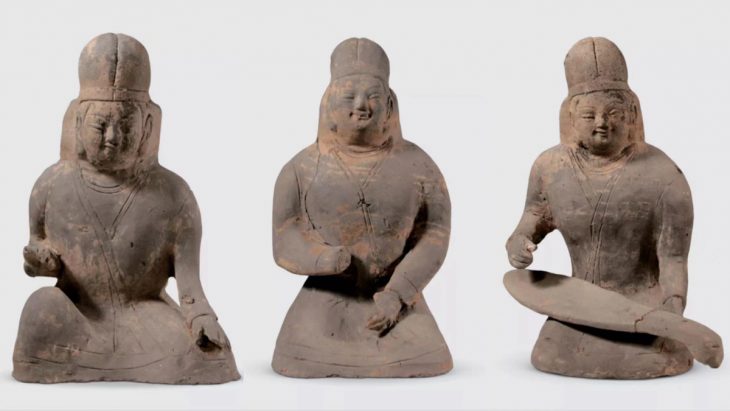
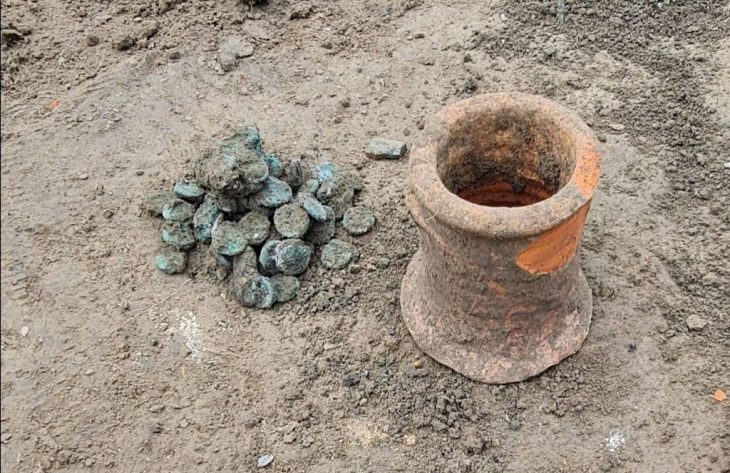
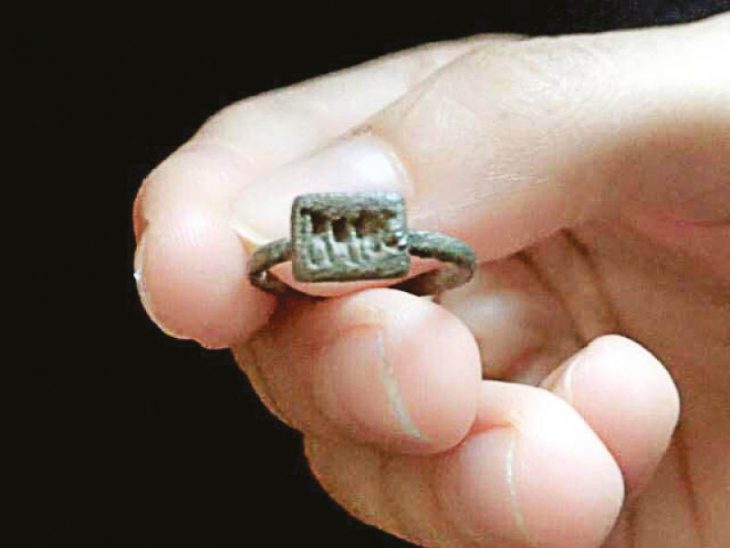
Individual rooms are preserved, containing thousands of pieces of ceramics, including whole bowls with the remains of seafood such as cockles or oysters, as well as amphorae filled with salted mackerel. Also found were thousands of barrels, including whole bowls of seafood remnants such as cockles or oysters, amphoras filled with salted mackerel, peach, almond, and olive kernels, charred pulses, with more than 700 copper coins and four matching gold coins and gold jewelry.
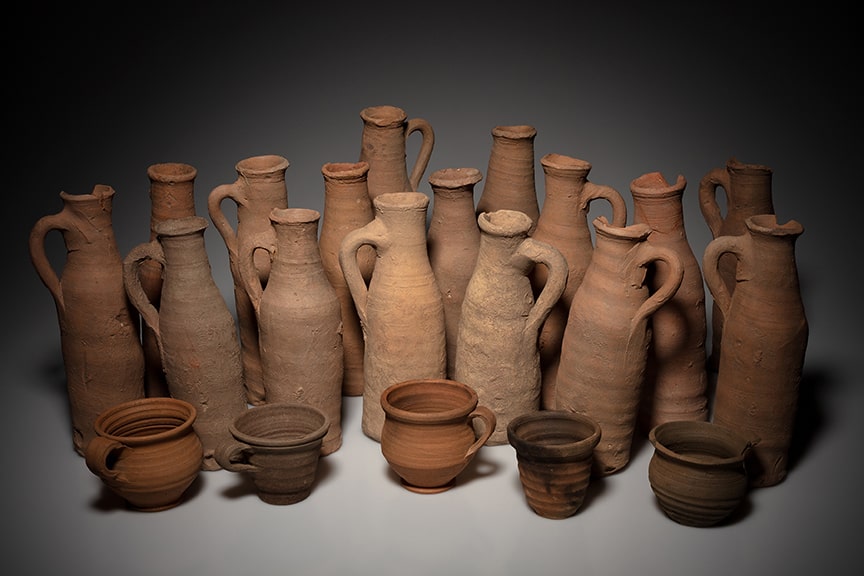

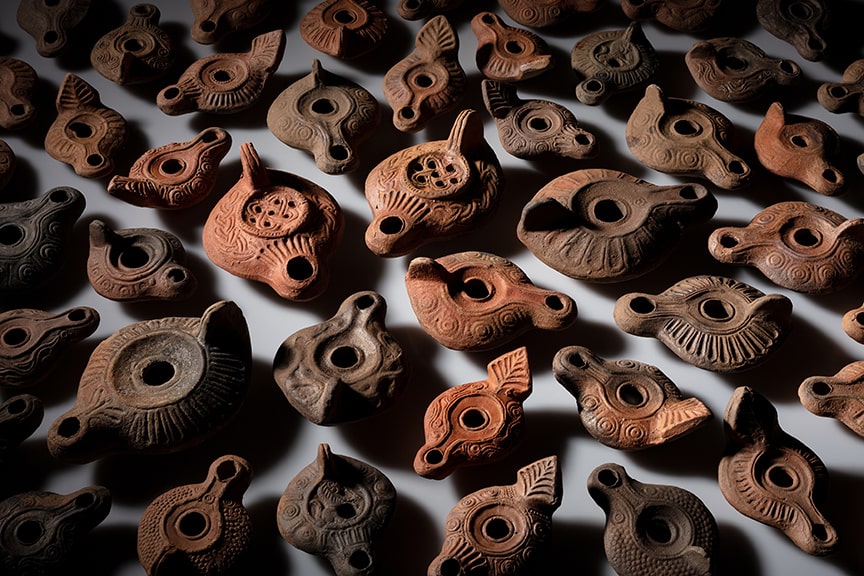
Based on the finds, it was also possible to reconstruct the earlier use of the rooms. So it is a cooking shop, a storage room, a tavern, a workshop with an adjoining sales room, and a shop for lamps and Christian pilgrim souvenirs (indicated by the discovery of around 600 small pilgrim bottles that were sold to Christian pilgrims).
However, coin dating indicates that the bustling trade and craft industry abruptly ended in the year 614/15 beneath the half-meter thick layer of fire. The scientists surmise a military conflict because there are no signs of an earthquake, such as shifted walls or vaulted floors. The numerous spearheads and arrowheads discovered also attest to this. The causes of this were unknown prior to this.
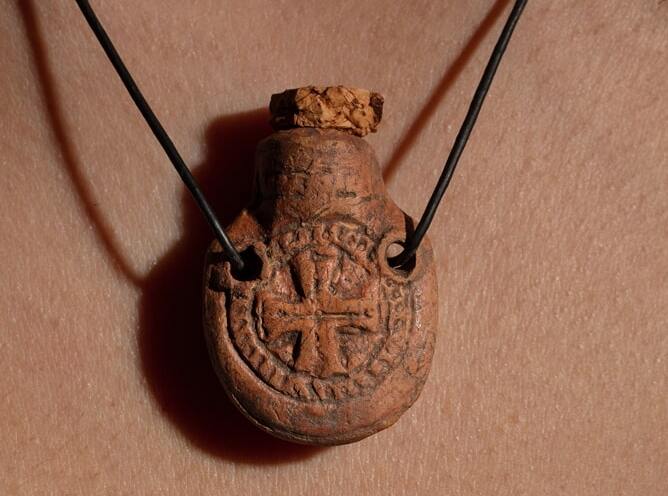

Based on the new finds, “this turning point in the history of the city of Ephesus will probably have to be associated with the Byzantine–Sasanian War”.
Cover Photo: OeAW-OeAI/Niki Gail