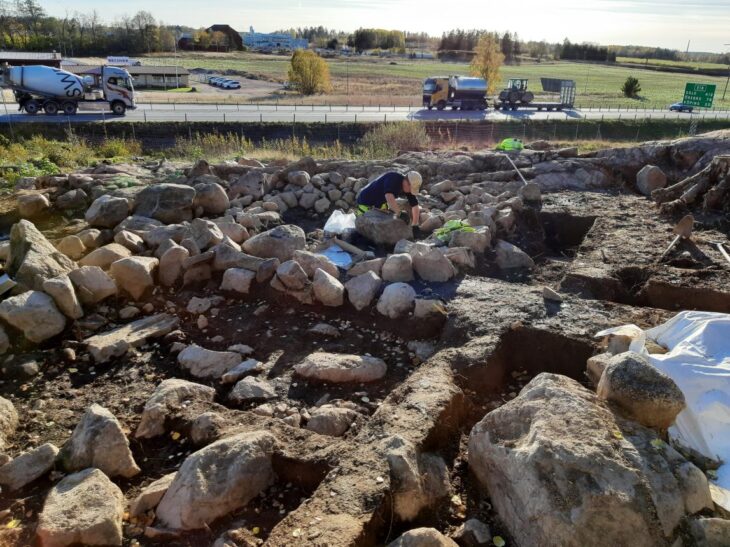
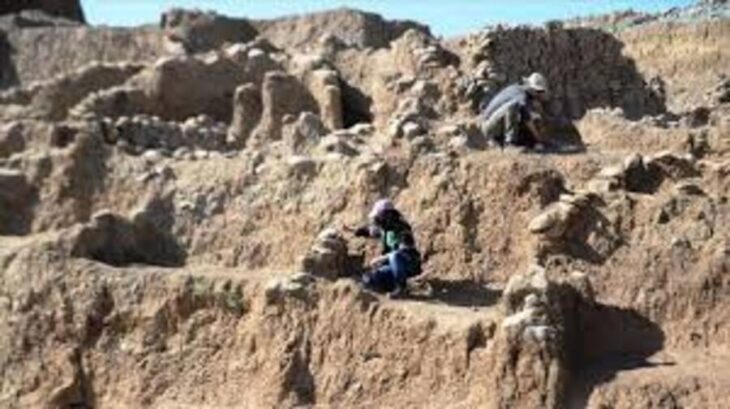
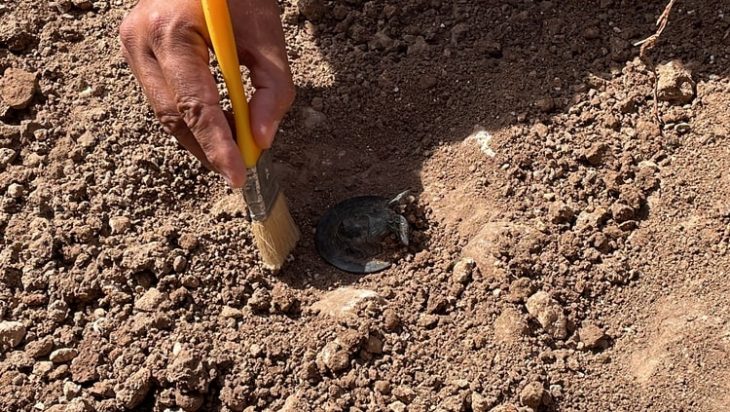
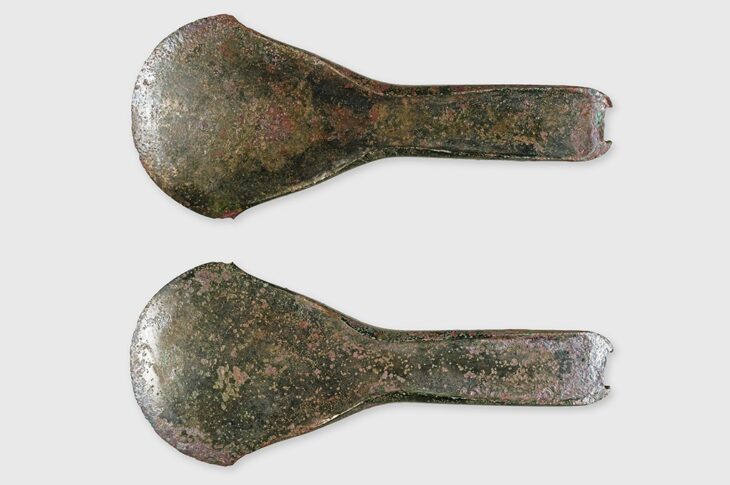
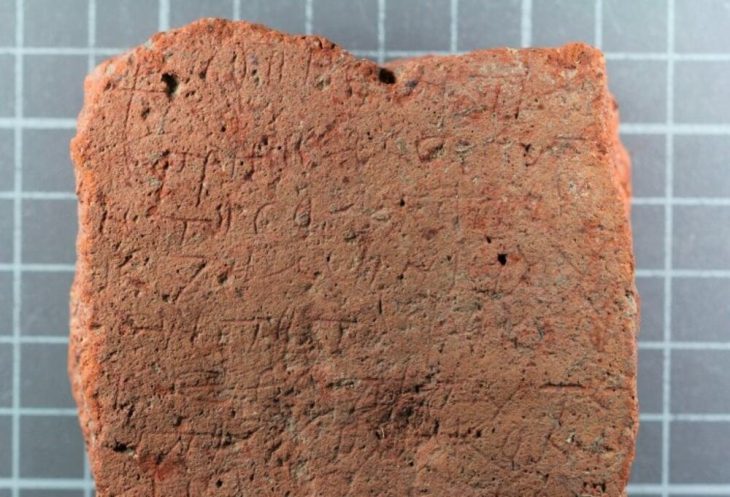
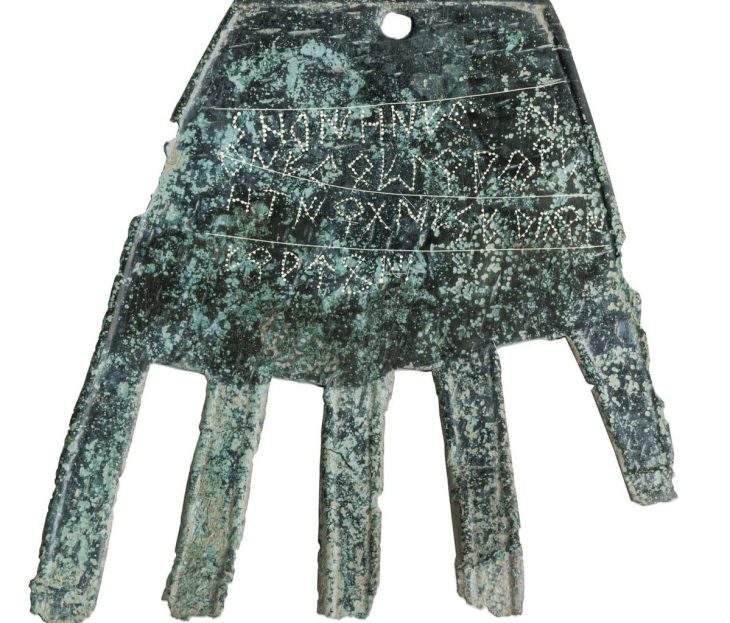
A sensational discovery was made in the Kogaly Valley, two hours from Almaty, Kazakhstan. For the first time in Kazakhstan, a rare type of Turko-Sughd coin has been discovered by researchers from the Tanbaly Reserve Museum.
The International Historical and Archaeological Expedition made this discovery during excavations in the Kogaly Valley, according to a press release from Kazakhstan’s Ministry of Culture and Information.
Turko-Sogdian coinage, issues of the khaqans of the Western Turkic khanate in Central Asia between the 6th and 8th centuries CE, so called because the Turkic rulers issued them with Sogdian inscriptions.
The number of known Turko-Sogdian coins increased significantly during the last decades of the 20th century thanks to excavations conducted in the medieval regions of Čāč, Čaḡāniān, and Otrār in modern Uzbekistan and Semirechye (south of Lake Balkhash) in modern Kyrgyzstan. However, prior research has not found any coins of this kind in Kazakhstan. Among these finds, there are new types with inscriptions, not only in Sogdian, but also in Bactrian, the language of Farghana, and Arabic.
The coinage is not yet well studied, but it has been proposed to call them Old Turkic coins because all seem to be related to Turkic rule despite the various languages of their legends and countermarks.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
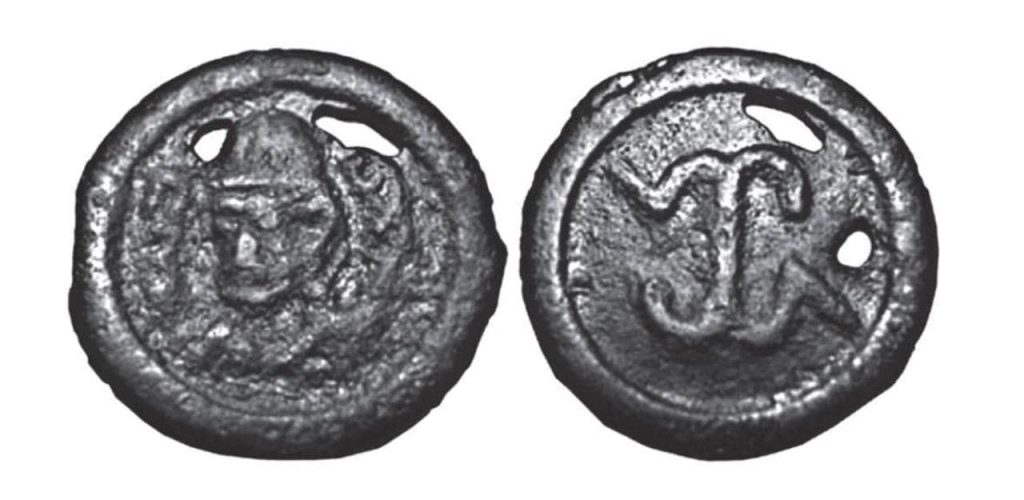

According to Turko-Sughd experts in early medieval numismatics, the found coin was in use from the mid-seventh century. The monuments of the Kogaly Valley studied by the expedition belong to the culture of the western Turks, who inhabited the lands of Zhetisu in the first half of the seventh to eighth centuries.
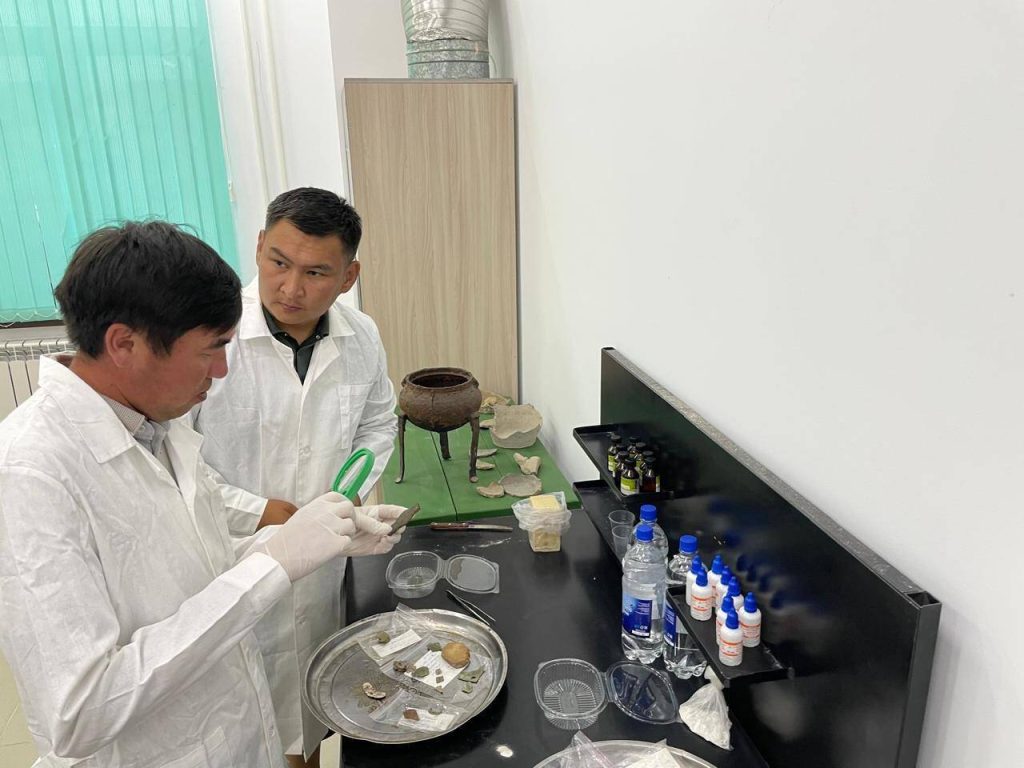
The first conservation efforts on this unique artifact are being carried out in the Tanbaly Science and Restoration Laboratory.
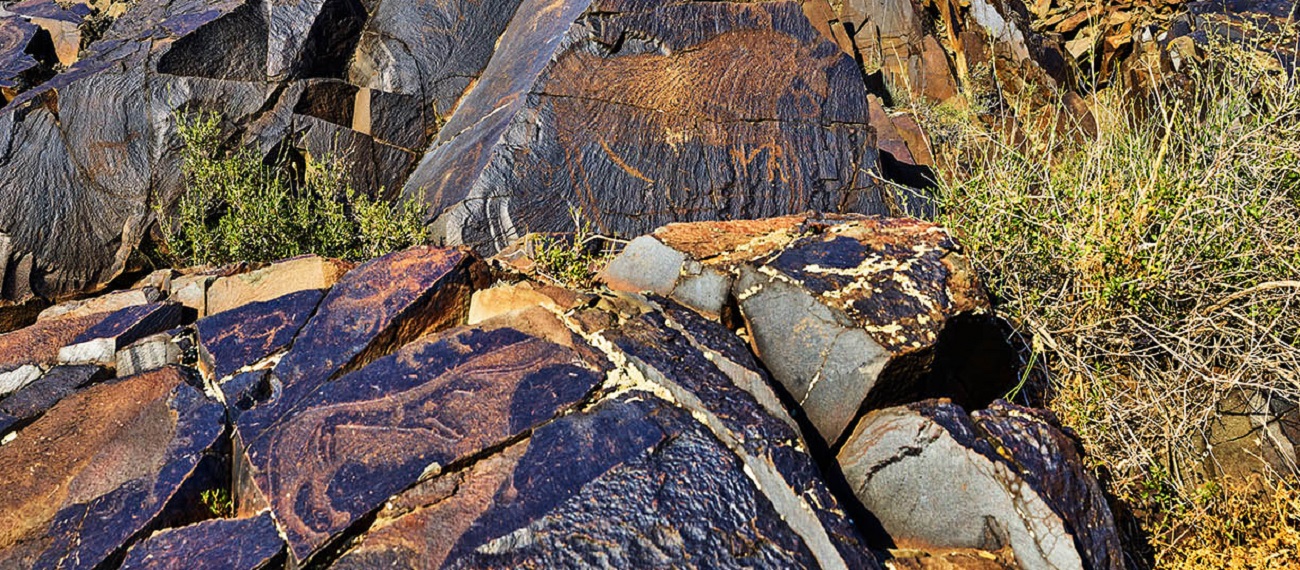
In 1957, Tanbaly petroglyphs were discovered in this area by an archaeological team led by Anna Georgievna Maksimova. In 2004, it was the first monument of rock art in Central Asia to be recognized as a World Heritage Site.

As a result of the archaeological investigations conducted by Luc Hermann and Boris Zheleznyakov, more than 6100 rock engravings in the cultural landscape of Akkainar, located between two important sites of rock art, Tamgaly, and Kulzhabasy, were documented. Over 800 of them were attributed to the ancient Turkic period.
A small group among them consists of tamgas, representing clan signs placed on hereditary property, including cattle. These tamgas are dated wider from the Early Turkic period to the beginning of the 20th century.
The archaeological excavations are still ongoing in the region.
Cover Photo: https://tanbaly.kz/