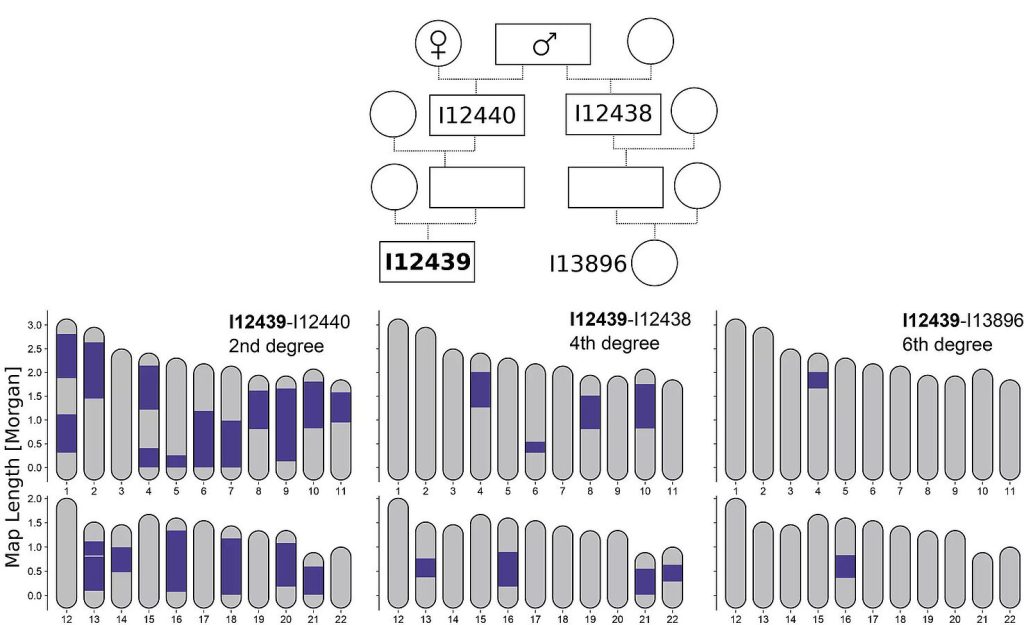
A new method of genetic analysis makes it possible to determine family relationships of prehistoric and historical individuals up to the sixth degree. Methods used so far only managed this up to the third degree. This innovation will help scientists identify previously unknown connections between people and cultures of the past.
Scientists from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology in Leipzig, Germany, and the University of Harvard in the United States have developed a new tool that allows them to identify the relatives of prehistoric and historic individuals up to the sixth degree.
If two persons are biologically related, they share long stretches of DNA that they co-inherited from their recent common ancestor. These almost identically shared stretches of genomes are called IBD (“Identity by Descent”) segments. Up to the sixth-degree relatives – such as second to third cousins would be, or a great great great great grandparent – the two relatives even share multiple IBD segments. Personal genomics companies such as 23andme or Ancestry detect those segments routinely in DNA of their customers, and use this signal to distinctively reveal biological relatives in their databases.
In a new study, researchers have now developed a powerful new tool named “ancIBD” to extract these IBD segments also in genomes of humans who lived hundreds, thousands, or even tens of thousands of years in the past. The critical challenge was that such ancient genomes are often very degraded and therefore of much worse quality than modern DNA, so the authors had to come up with an innovative trick to fill in gaps in ancient genomes using modern reference DNA panels.
This advance unlocked completely new ways to analyze ancient DNA data. “By precisely measuring the regions of shared genome we can now detect pairs of up to sixth-degree relatives also in ancient genomes, while previous aDNA methods using genomic average similarities were limited to detecting only up to third-degree relatives,“ explains Yilei Huang, a first author of the study and PhD researcher at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Researchers identified hundreds of new pairs of relatives
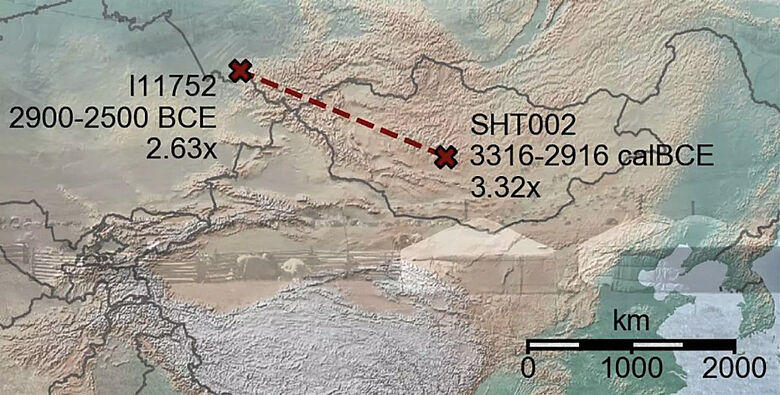
The authors then applied their new tool to a dataset of 4,248 previously published ancient genomes from across Eurasia and the last 50,000 years and were able to identify hundreds of previously undetected pairs of relatives. In some fascinating cases, the two relatives were buried a large distance apart, which directly revealed the mobility of past people. In one such case, the authors detected a pair of two Early Bronze Age nomads from Central Asia who lived ca. 5,000 years ago and were fifth-degree relatives who were buried ca. 1,500 kilometers apart from each other. These individuals, or their immediate ancestors, must have moved hundreds of kilometers between being born and being buried.
The new tool allowed the authors to also investigate even more distant relatives with unprecedented precision. Not all such relatives beyond the tenth degree share long IBD, but the authors could measure the average rate of sharing long DNA between groups of ancient people. These signals revealed previously unknown connections. “We found exciting links between ancient cultures, and the signal of long shared segments allowed us for the first time to specifically demonstrate close relationships between important ancient cultures, sometimes over vast spaces over the order of only a few hundred years,” says Harald Ringbauer from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, the lead researcher of this study.
Gene flow from the Eurasian Steppes
Among other things, the authors revealed fascinating new details about a massive gene flow from the Eurasian steppe that began around 5,000 years ago. The first Europeans with substantial steppe ancestry, associated with Corded Pottery, an archaeological culture that then spread from Central Europe to Scandinavia and present-day Russia, share many long IBD segments with the Yamnaya herders of the Pontic-Caspian steppe. This suggests a distinct genetic bottleneck event and a biological connection between these groups of populations that dates back only a few hundred years.
The authors also found elevated sharing of long IBD segments between Corded Ware individuals and East European people associated with the Globular Amphora culture (GAC) from Poland and Ukraine, who were not yet carrying Steppe-like ancestry. “These IBD links appear for all Corded Ware groups across Central Europe to Russia, indicating that individuals related to GAC contexts must have had a major demographic impact early on in the genetic admixtures giving rise to various Corded Ware groups,” says Ringbauer.
The new method to screen ancient DNA for parental relatedness gives researchers a versatile new computational tool. Looking forward, the field of ancient DNA is quickly developing, with thousands of ancient genomes being produced every year. By revealing close and distant biological relatives, the new tool will allow researchers to shed new light on the lives of our ancestors, both on the small scale, relevant to understanding the life stories of people and their relatives, and on the macroscale, relevant to large-scale cultural-historical events.
Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology
DOI: 10.1038/s41588-023-01582-w
Cover image: © Ringbauer & Huang et al., Nature Genetics