The researchers developed a neural network that can take a single 2D photo of a three-dimensional object and produce a digital reconstruction in three dimensions. Particularly for artifacts that are hidden, too delicate for traditional 3D modeling, or too fragile to be excavated, this method may revolutionize digital preservation.
In a sense, scientists created a 21st-century stereoscope. Last month, at the 32nd edition of the ACM Multimedia conference, the team presented their proof-of-concept.
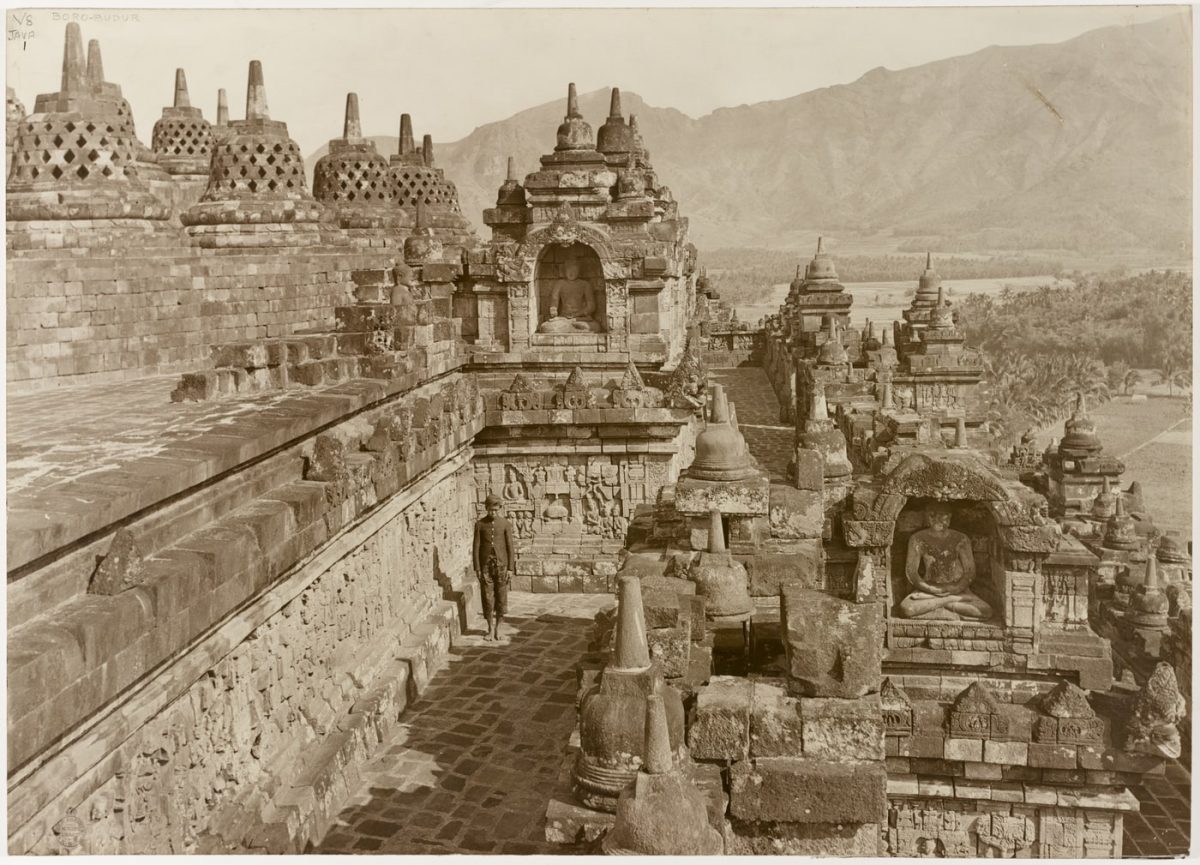
A research team at Ritsumeikan University led by Professor Satoshi Tanaka along with Dr. Jiao Pan, from the University of Science and Technology Beijing, used a 134-year-old photograph from the Borobudur Temple in Indonesia to demonstrate the incredible work this neural network can perform.
The largest Buddhist temple in the world, Borobudur is covered in 2,672 relief panels. Built in the 9th century CE, it was eventually abandoned, only to be discovered centuries later by Dutch archeologists.
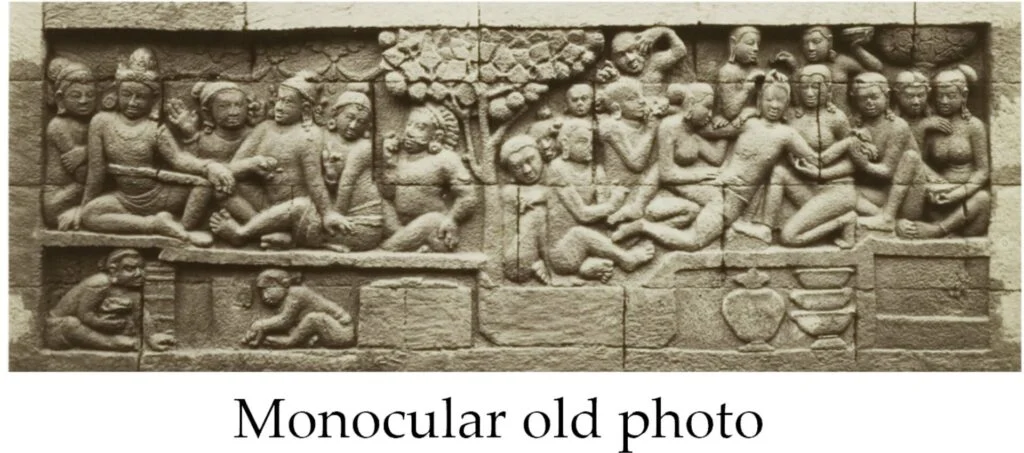

The relief, found on the ground level of the famed Borobudur Temple a UNESCO World Heritage site, depicts a group of people in traditional attire set against a backdrop of trees and ancient architecture. It was only known by a black-and-white photo that was taken in the 19th century while the relief was exposed during reconstruction work. It was then covered over by reinforcement walls.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The recent team’s neural network managed to reconstruct one of those now-hidden reliefs using an old black-and-white photo from 134 years ago.
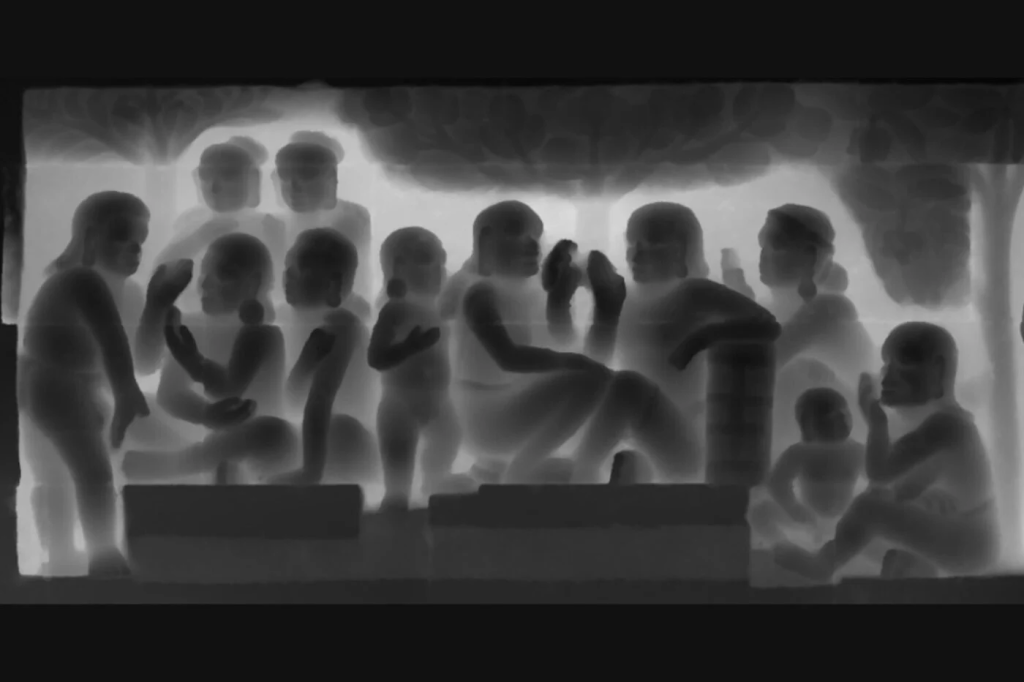

Although earlier reconstructions had been attempted, they were unable to capture the finer details of the reliefs. These three-dimensional reliefs contain detail from the carvings closest to the viewer and farthest from the viewer, and prior reconstruction attempts flattened out the details at these varying depths, resulting in the loss of those details due to the compression of depth values. Based on the computed curvature changes in the 3D space, the team created a map of the lost characteristics, which they called “soft edges.”
“Our multi-task neural network successfully reconstructed these hidden sections of Borobudur’s ground-level reliefs from surviving old photographs. Through computer visualization and virtual reality, our research now allows virtual exploration of these unseen treasures,” says Prof. Tanaka.
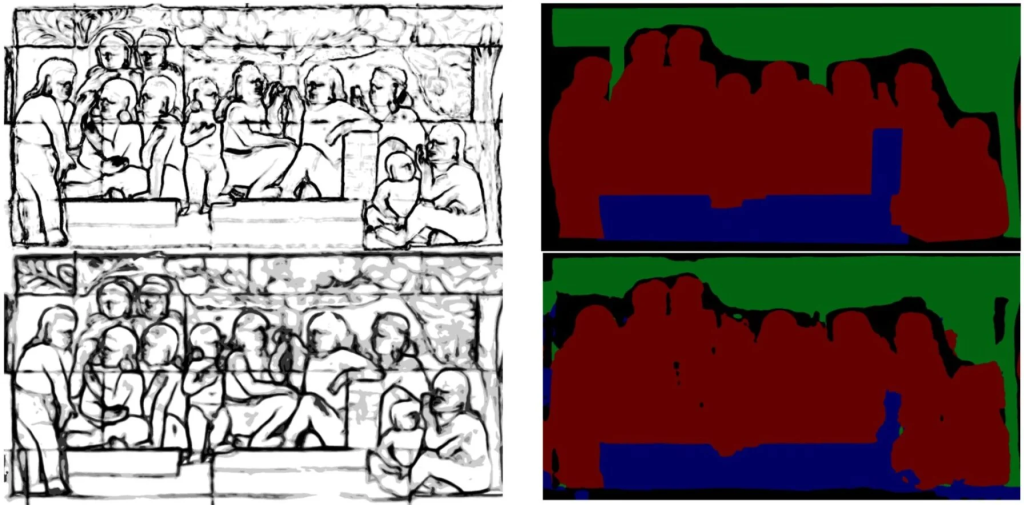

By enhancing the depth estimation, particularly around soft edges, they were able to produce images that more accurately represent the original reliefs. The technique is a breakthrough, as 3D scanning and photogrammetry can only record reliefs in their current state, whereas 3D digital restoration returns us to the original.
“Our technology holds vast potential for preserving and sharing cultural heritage,” shares Prof. Tanaka. “It opens new opportunities not only for archeologists but also for immersive virtual experiences through VR and metaverse technologies, preserving global heritage for future generations.”
Cover Image Credit: Terrace on the temple of Borobudur 1913. Wikipedia Commons