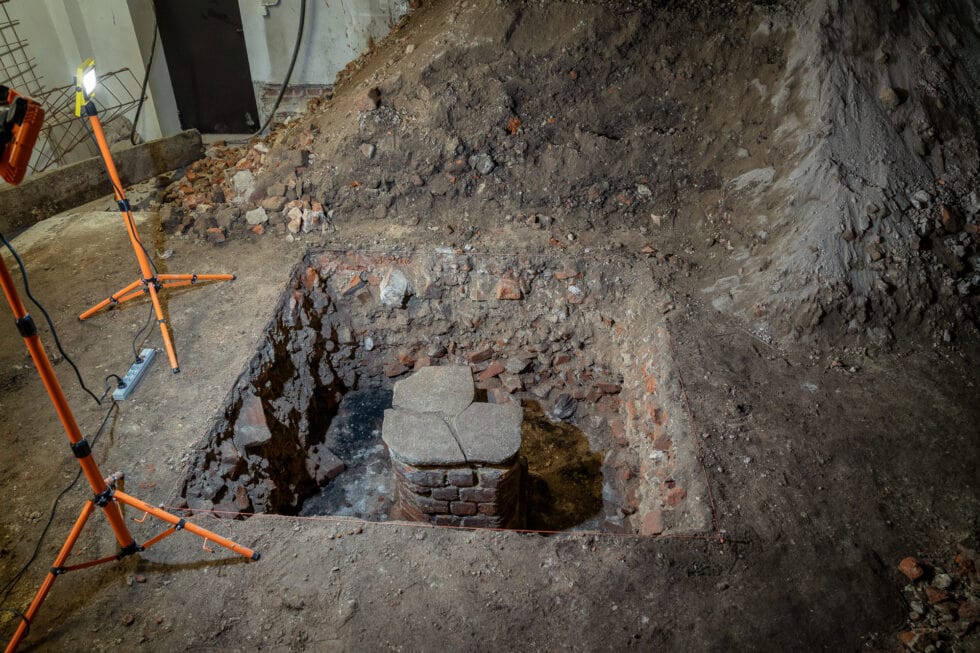
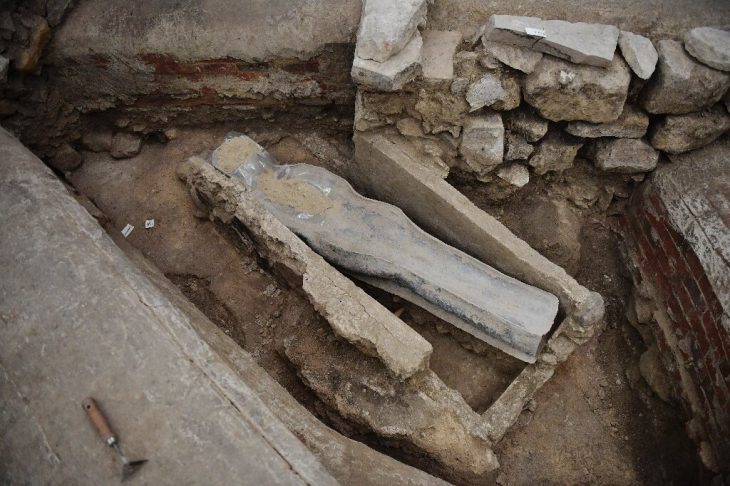
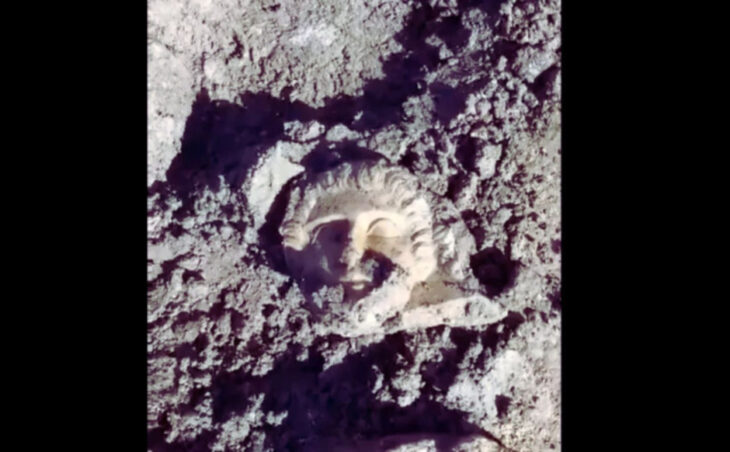
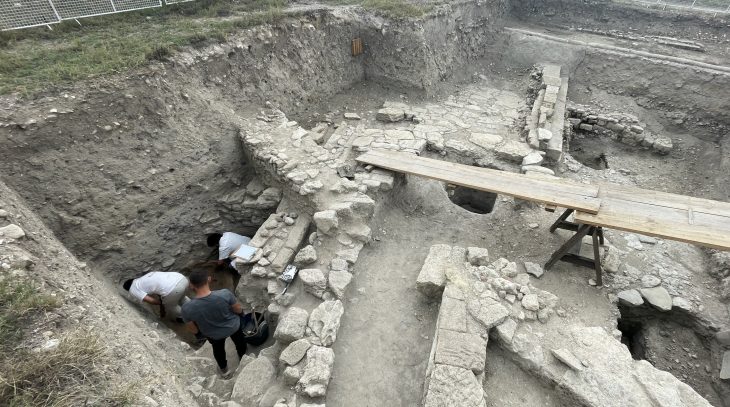
The remains of what is thought to be a sizeable 14th-century synagogue complex, including a mikvah, have been discovered during research linked to the renovation of the building that houses the Historical Institute of Wrocław University.
The city of Wrocław referred to the discovery in the building’s basement as “sensational” in an article on its website. According to researchers, it might be one of the largest known medieval synagogue complexes in Europe.
The renovation of the building at ul. Szewska 49 in Wrocław, the seat of the Historical Institute of the University of Wrocław and previously, among other things, the palace of the Piasts of Legnica and Brest for about 300 years (15th-17th century), began in 2021.
In an article on its website, the University said that during the renovation work, which began in 2021, “large expanses of 14th-century walls began to emerge from under the plasterwork.”
After the walls were revealed, archaeologists began working on the site and determined that the unearthed structures resembled the typical layout of medieval European synagogues.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
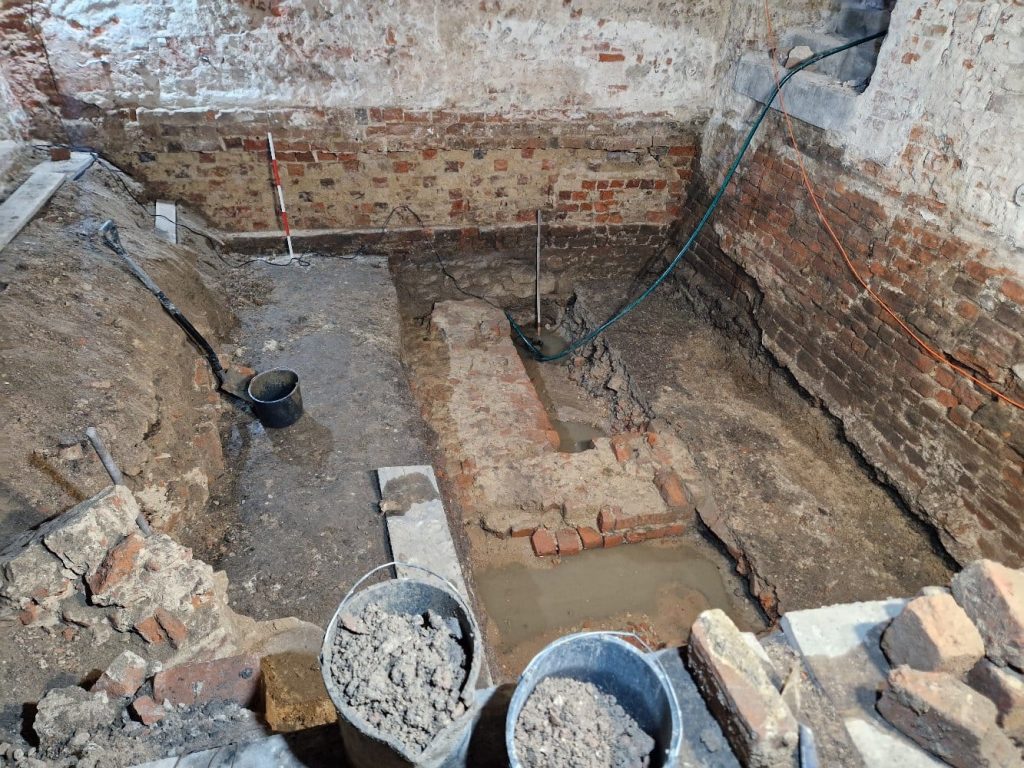

It quoted Prof. Małgorzata Chorowska, from the Wrocław University of Science and Technology, as saying that “it was precisely the fact that instead of the expected bourgeois tenement houses we had a synagogue, and above all its size, that was quite a surprise.”
Prior to the Historical Institute, 49 Szewska Street had housed a palace of the Legnica-Brzeg branch of the Piast dynasty for 300 years from the 15th to 17th century.
On the basis of earlier historical and architectural research conducted under Chorowska, there is a “high probability that the remains of a 14th-century synagogue integrated into the walls of the later city palace have just been discovered,” the University of Wrocław published in a statement.
The statement also noted that despite many years of archaeological research of buildings demolished to their foundations, “until the ongoing renovation of the building at 49 Szewska Street, it was not possible to determine the location or find any material remains of the oldest synagogues in Wrocław.”
“The building at 49 Szewska Street is a valuable and very interesting monument, and if the presumption of a synagogue is correct, then we are potentially dealing with the best-preserved relics of one of the oldest, if not the oldest, brick building of its kind in Poland,” Mateusz Goliński of the Historical Institute’s department of Polish and general history was quoted as saying.
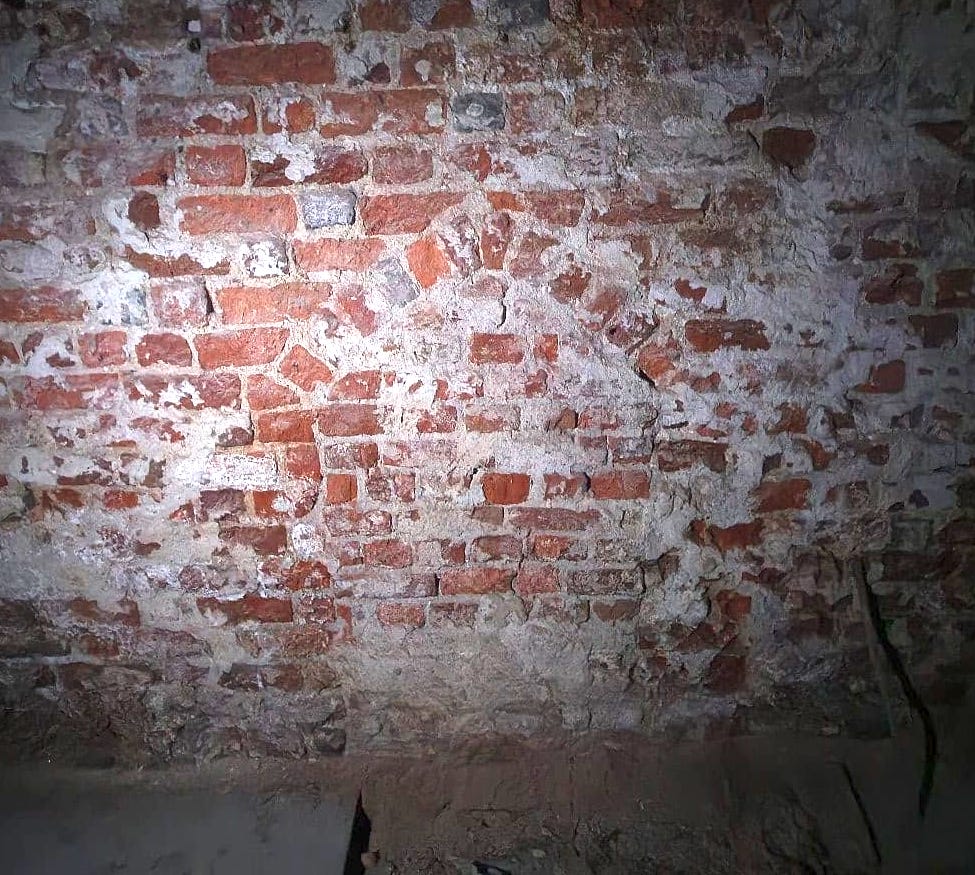

Europe we can suggest that we are dealing with the remains of a synagogue of the first Jewish community in Wrocław,” wrote researchers Prof. Małgorzata Chorowska, Prof. Mateusz Goliński, and architect Mariusz Caban in an article published in the Journal of Heritage Conservation.
Wrocław’s Jewish history dates back to the 12th century, when the city was a major trade center along the Amber Road. The city once boasted one of the largest Jewish communities in East Central Europe. The largest synagogue in the city, then known as Breslau and a part of Nazi Germany, was destroyed by fire during the Kristallnacht pogrom in 1938.
Research of the site, which began in 2021, is still ongoing to determine whether the Wrocław synagogue complex is one of the largest in Europe from the first half of the 14th century.