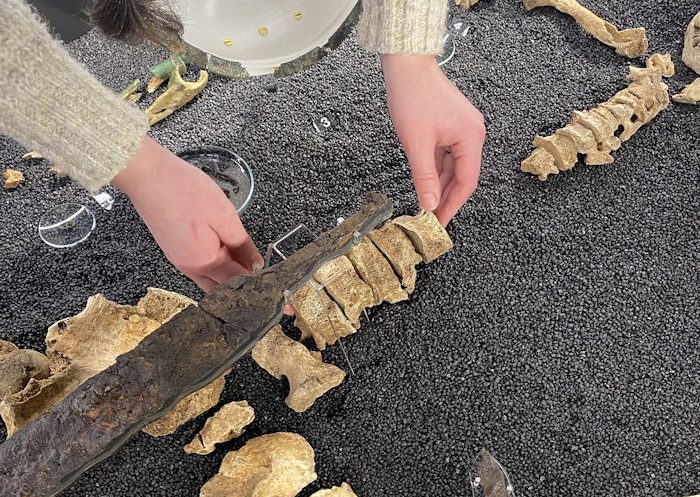
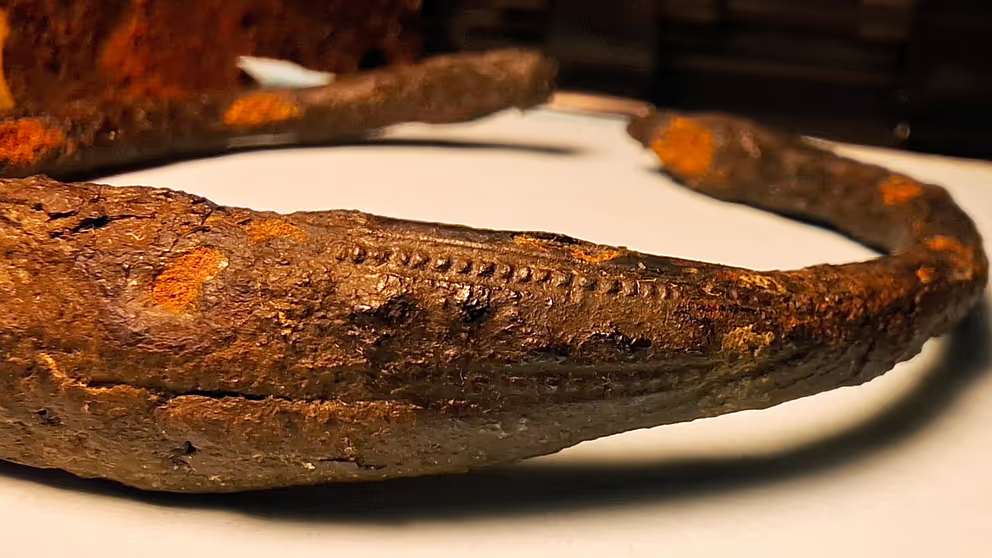Recently, two extraordinary archaeological finds have captivated the attention of historians and enthusiasts alike in Sweden. The first discovery, an exceptionally rare Viking armlet, was uncovered by a private individual in a wetland near Löt on the island of Öland.
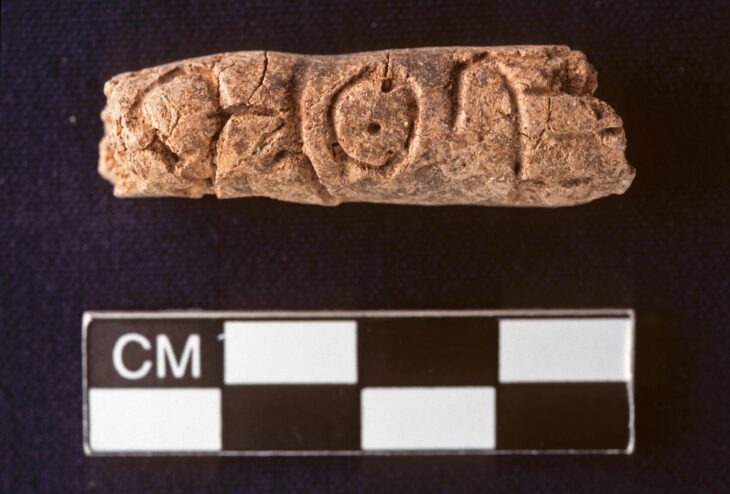
This armlet, dating back over 1,000 years, is notable for being crafted from iron, a material rarely used for such artifacts. According to Karl-Oskar Erlandsson from the County Administrative Board of Kalmar County, only three iron arm rings exist in the State Historical Museum’s collections, making this find particularly significant.
The armlet features intricate decorations, including animal heads at both ends and detailed rows of dots along its length. Its remarkable preservation is attributed to the oxygen-poor environment of the wetland, which has helped prevent corrosion. Erlandsson speculates that the wetland may have served as a sacrificial bog, suggesting the possibility of more artifacts waiting to be discovered in the area.
Plans are underway for a metal detector survey in the spring to explore the site further and determine whether the armlet was lost jewelry or part of a larger offering to the gods.

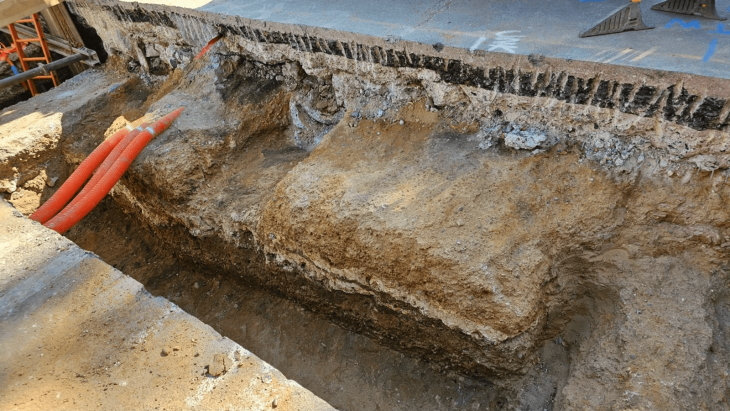
In a separate but equally fascinating discovery, a 2,000-year-old golden neck ring was found during excavation work in Trollhättan, Västra Götaland County. This exclusive neck ring, made of precious metal and adorned with gold wire and rings, was unearthed at a depth of about two meters. Niklas Ytterberg, an antiquarian from Västra Götaland County, described the find as highly unusual, noting that such jewelry was typically worn by the most powerful individuals of the time.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The neck ring, known as a torque, measures 23.5 centimeters at its widest point and weighs nearly a kilogram. Unlike similar artifacts found in the British-French region, which are usually solid bronze, this neck ring is believed to have been produced domestically in Scandinavia, showcasing the unique craftsmanship of the era.
Both discoveries highlight the rich archaeological heritage of Sweden and the importance of preserving these artifacts for future generations. The County Administrative Board plans to report these findings to the National Heritage Board, which will determine the next steps, including potential rewards for the finders and conservation measures.
As investigations continue, these remarkable finds promise to shed light on the cultural practices and craftsmanship of ancient Scandinavian societies, offering invaluable insights into their history and traditions.
Cover Image Credit: Länsstyrelsen Kalmar län (County Administrative Board of Kalmar County)