Archaeologists in Hungary have made a remarkable discovery: a rare Avar-period saber has been unearthed near the city of Székesfehérvár. The find, which experts say sheds new light on the region’s significance during the early medieval era, was made possible through satellite-based archaeological research.
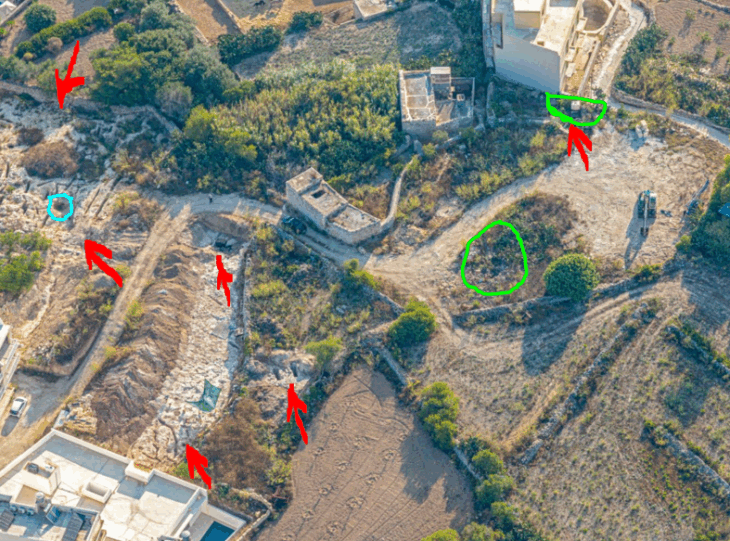
The excavation is part of the “Cemeteries from Space” program, a project led by the Hungarian National Museum and the King Stephen Museum. Using satellite imagery, archaeologists can detect hidden burial grounds by observing crop marks. In areas where the soil was once disturbed by grave digging, crops tend to grow greener and denser because the looser soil retains water better. This allows researchers to pinpoint not only the locations of cemeteries but even individual grave sites, especially those dug deeper than one meter — a hallmark of certain historical periods such as the Migration Era.
A Hidden Cemetery Revealed
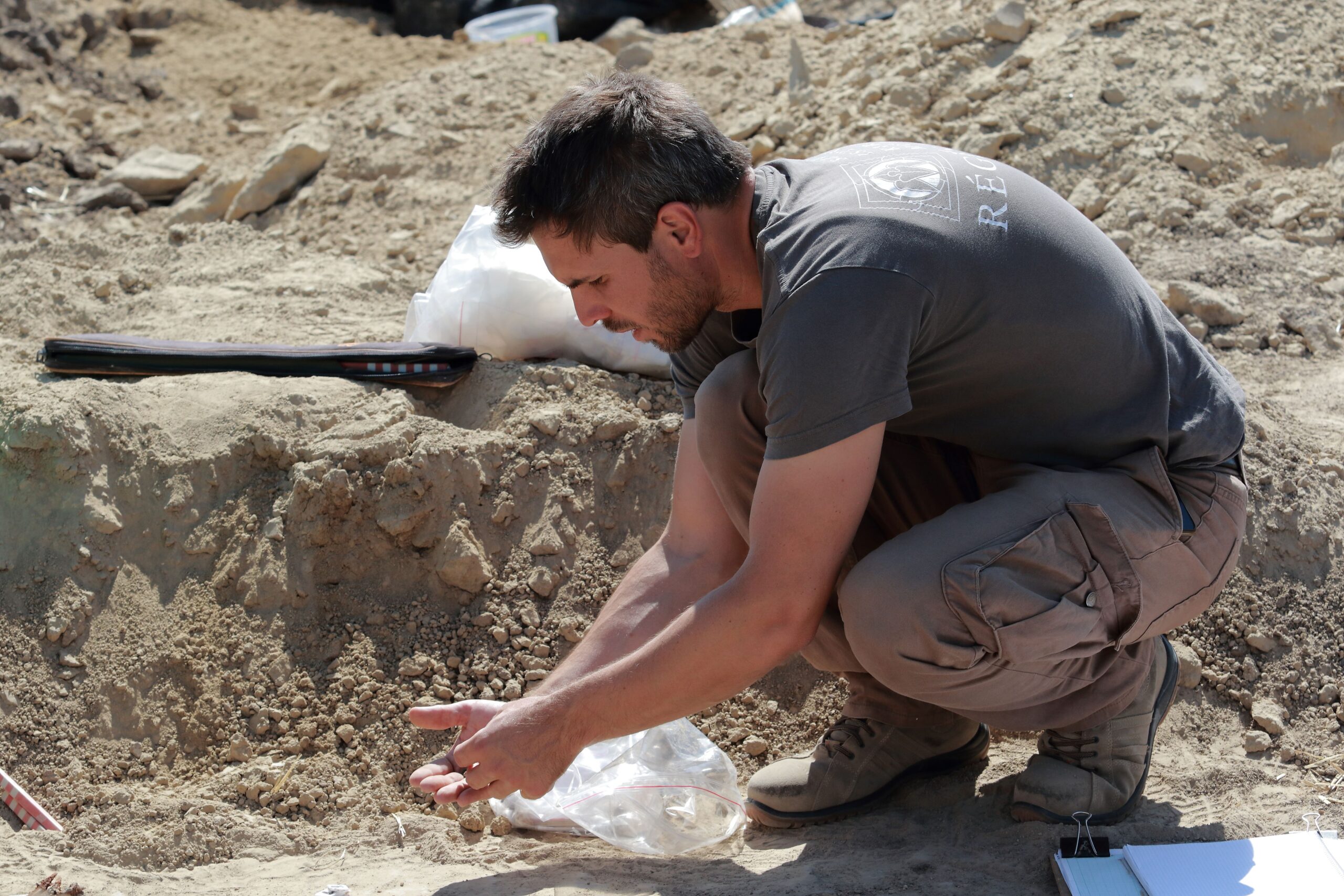
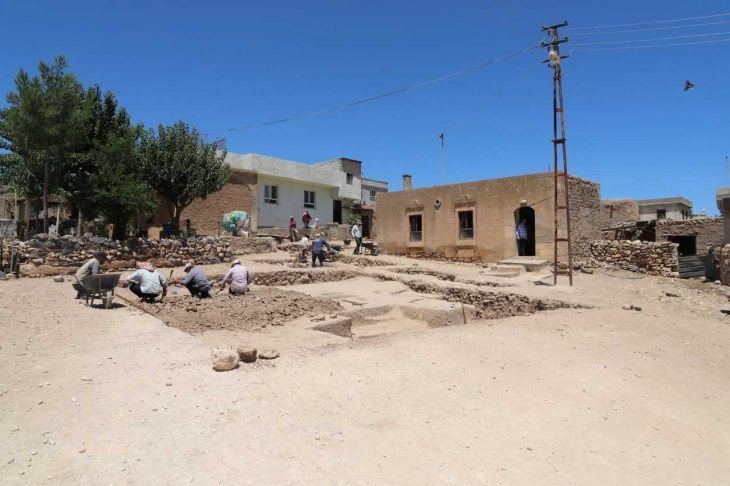
Guided by these satellite photographs, archaeologist Frigyes Szücsi and his team began excavations along the border between Székesfehérvár and Aba, on private farmland. The imagery indicated the presence of a large cemetery containing 400–500 graves, as well as a smaller burial ground a few hundred meters away.
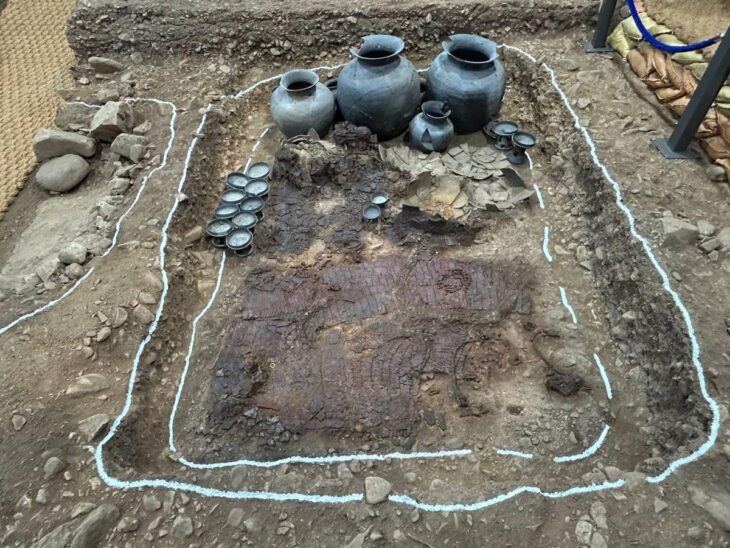
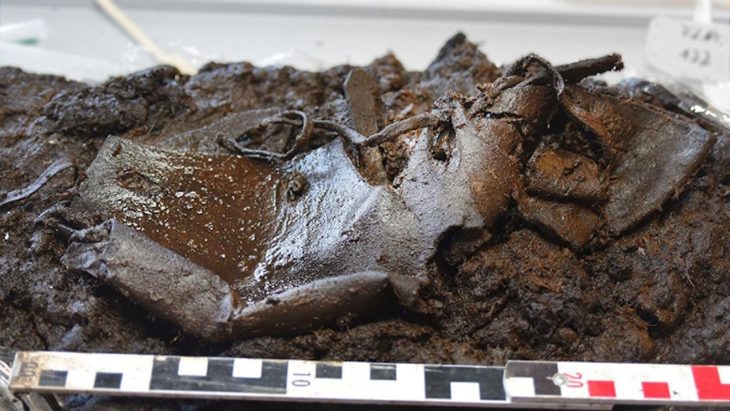
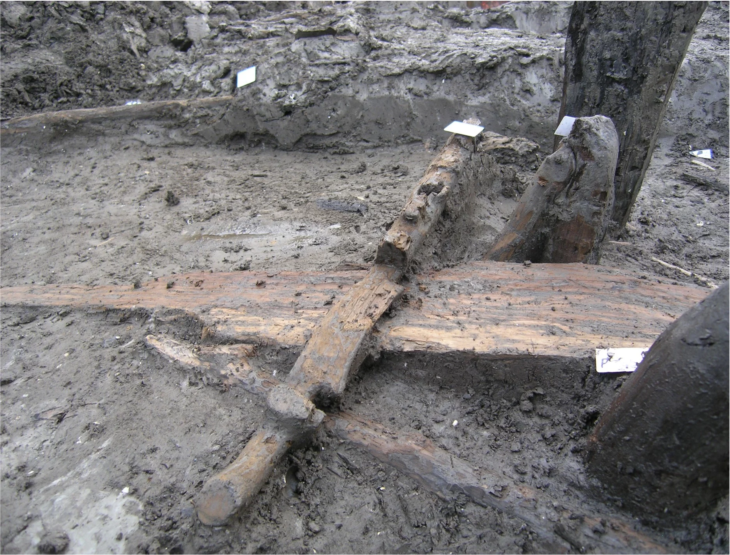
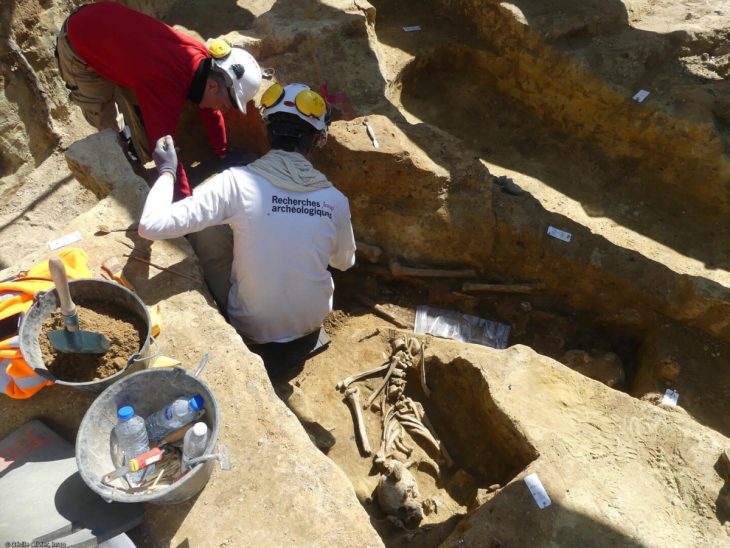
So far, two graves from the larger cemetery have been carefully opened. Based on the artifacts uncovered, they date to the Middle Avar period (7th–8th century). On August 25, as the excavation neared completion, the team made an unexpected discovery: the outline of a saber emerging from the soil.
An Exceptional Find
Szücsi explained that sabers are extremely rare in Avar graves, particularly in Fejér County. The last comparable discovery in the region occurred in 1979, when the late archaeologist Gyula Fülöp unearthed a similar find at Kajászó-Újmajor.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
In most Avar-era graves, archaeologists typically find spears, bows, and other weapons. The presence of a saber, however, is a powerful status marker. According to Szücsi, “The sword itself already indicates that a person of higher rank was buried here.” The grave also contained gilded bronze hair ornaments and a pressed bronze belt fitting, both of which further suggest that the deceased was of elevated social standing.
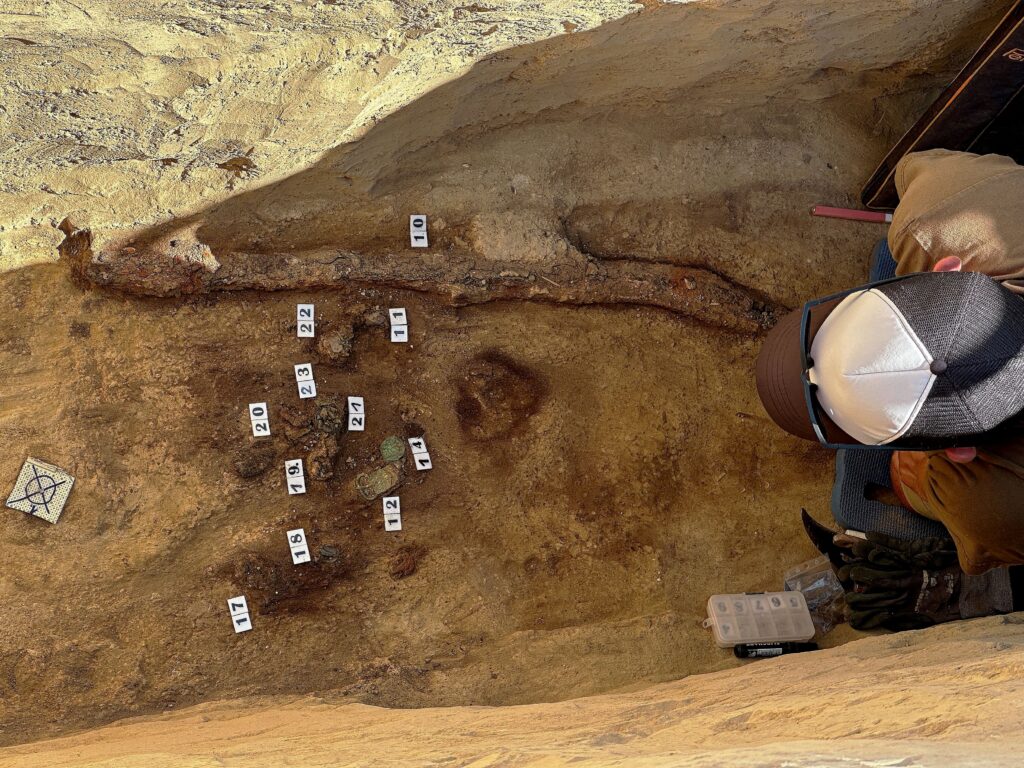

Preserving the Saber
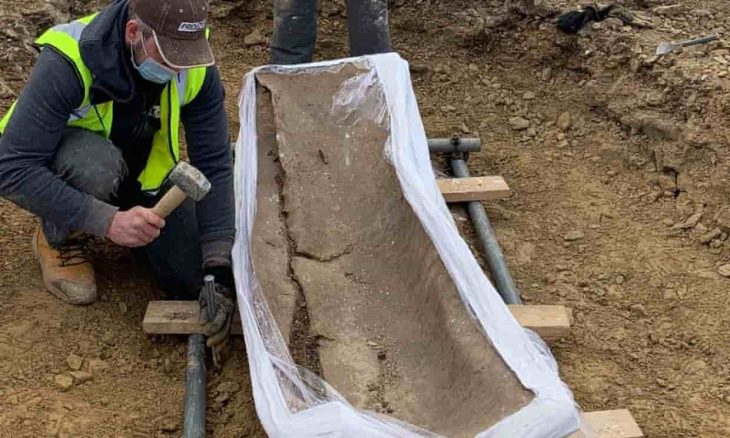
Extracting the saber presented significant challenges. After centuries underground, the corroded metal is extremely fragile and risks disintegrating if removed carelessly. To protect it, the weapon was lifted in a custom-made wooden frame, crafted by volunteer carpenter László Teker. The soil surrounding the sword will remain intact until specialists in a restoration laboratory can stabilize and conserve the artifact.
This step is critical because metals buried beneath farmland often suffer from heavy chemical damage due to modern agricultural treatments. Without careful conservation, the saber could be lost forever.
Wider Historical Significance
Fejér County is now emerging as a hotspot for Avar-period archaeology. Szücsi revealed that around 80 additional sites have already been photographed from space but remain unexcavated. Even partial investigations of these sites could confirm their Avar origins, opening up new avenues for scientific study.
Historian György Szabados, who visited the site, emphasized the importance of the discovery for understanding Hungary’s early medieval history. “The progress of archaeological research demonstrates that Fejér County was already a significant area 1,400 years ago,” he noted. “The large number of Avar cemeteries supports this conclusion.”
A Glimpse Into the Avar Past
The Avars, a nomadic people of Central Asian origin, settled in the Carpathian Basin in the late 6th century and established a powerful khaganate that lasted until the 9th century. Weapons, ornaments, and burial customs provide crucial evidence of their social hierarchy and interactions with neighboring cultures.
This latest discovery — a saber belonging to a high-ranking individual — not only enriches Hungary’s archaeological record but also underscores how cutting-edge technology like satellite imaging is transforming the way ancient history is uncovered.
As research continues, the saber from Székesfehérvár may yet prove to be one of the most significant Avar finds in recent decades, offering a rare glimpse into the life, status, and martial traditions of an elite warrior from over a millennium ago.
Cover Image Credit: Szent István Király Múzeum