A breathtaking discovery in the southwestern English county of Wiltshire has captivated archaeologists and metal detecting enthusiasts alike. Two detectorists, Paul Gould and Chris Phillips, have unearthed a stunning gold and garnet raven’s head and an intricately designed gold band, both dating back approximately 1,400 years to the Anglo-Saxon period of the 7th century AD.
The Anglo-Saxon period (roughly AD 450-1066) is renowned for its intricate and striking metalwork. These metal adornments, often crafted using techniques such as casting, forging, soldering, and inlay, with high-status pieces frequently utilizing gold, silver, bronze, and iron, are not only aesthetically impressive but also offer significant insights into the social, religious, and cultural beliefs of the time. The remarkable finds in Wiltshire, the gold and garnet raven’s head and the gold band, offer a tantalizing glimpse into the artistry and symbolism of this era.
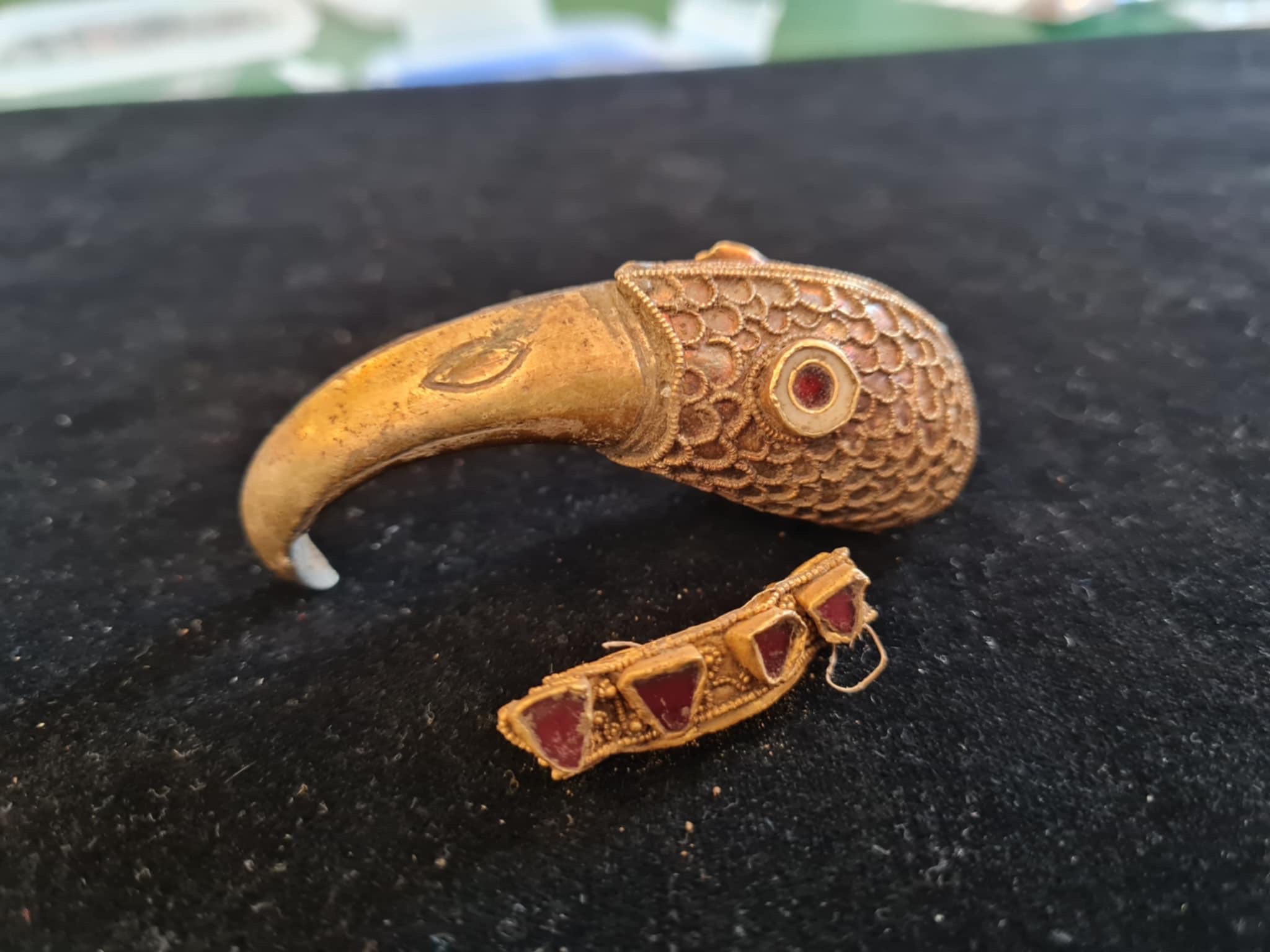
The raven’s head, weighing around 60 grams, is a masterpiece of early medieval craftsmanship. It features a striking garnet eye, with the opposite eye socket now missing its gem. Delicate gold spheres meticulously outline the “feather” portions of the head, which are further adorned with garnet inlays set against a distinctive waffle-patterned foil backing – a hallmark technique in Anglo-Saxon artistry.
Experts at the British Museum, where the artifacts are currently undergoing careful cleaning and analysis, note the exceptional quality and detail of the piece. Small pins discovered inside the raven’s head suggest it may have once been attached to another significant object, possibly the terminal of a drinking horn, reminiscent of similar adornments found in the famed Sutton Hoo burial.
Adding to the significance of the discovery is a gold band or ring, studded with tiny gold beads and triangular garnets held in place by delicate gold filigree. While its exact purpose remains under investigation, it could have served as a piece of personal jewelry or formed part of a larger, more elaborate artifact, perhaps even connected to the same object as the raven’s head.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
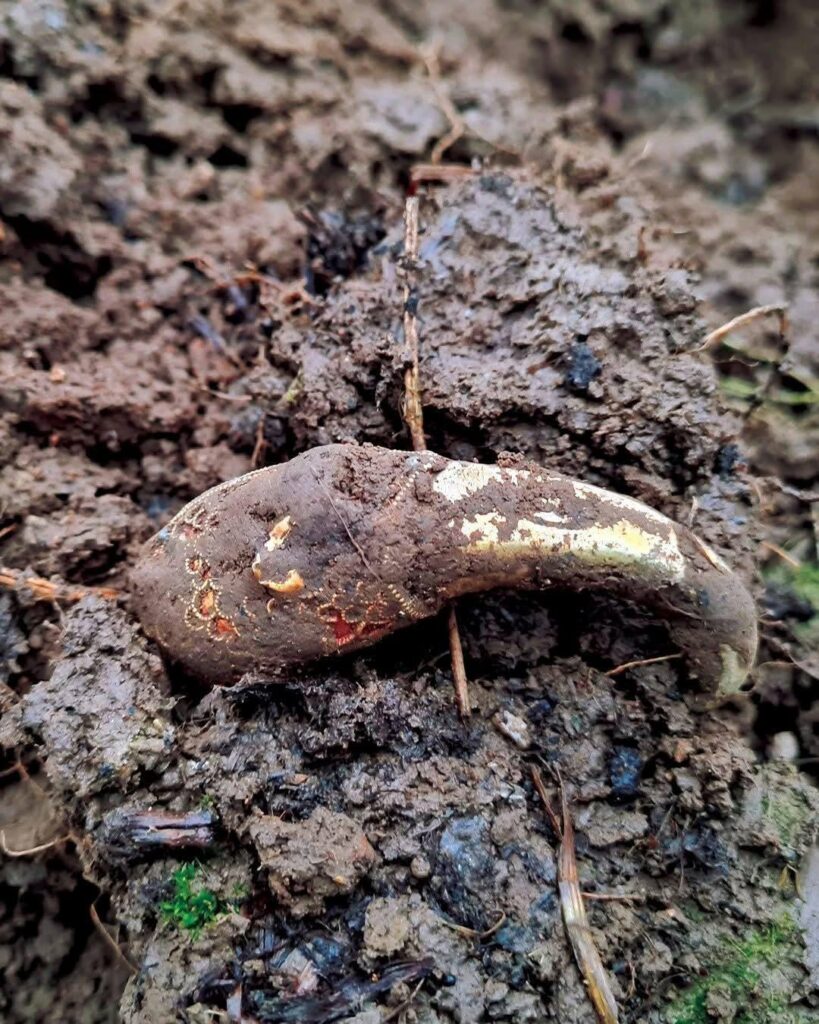

The symbolism of the raven head is particularly intriguing. In Germanic and Viking Age cultures, ravens were often associated with darkness, death, and the Norse god Odin. However, the precise meaning and function of this specific gold and garnet representation remain open to scholarly interpretation. Similar, though not identical, bird-like jewelry has been found in significant Anglo-Saxon hoards like Sutton Hoo and Staffordshire, often featuring distinctive garnet-inlaid eyes and beak shapes, underscoring a potential cultural significance of such imagery.
Following the initial discovery in January, the find site has become a focal point for further investigation. Archaeological surveys, including geophysical analysis, have indicated the presence of additional buried materials. Excitement is building for a planned full excavation of the site in the summer of 2026, which promises to shed more light on the context of these remarkable finds and potentially uncover further treasures from this important historical period.
The detectorists, adhering to best practices, promptly reported their finds to the landowner and the local Finds Liaison Officer under the Portable Antiquities Scheme. This scheme encourages the reporting of archaeological discoveries by the public, contributing significantly to the understanding of British history.
The unearthed artifacts will now undergo the formal “treasure process,” as outlined by the UK’s Treasure Act, which governs the handling of precious metal artifacts over 300 years old.
Chris Phillips, visibly moved by the discovery, described it as a “find of a lifetime.” His fellow detectorist, Paul Gould, who initially unearthed the gold band, echoed this sentiment.
Their remarkable finds not only highlight the potential for significant archaeological discoveries through responsible metal detecting but also underscore the rich and complex history that lies beneath the fields of England. The ongoing investigation promises to unveil more secrets from this fascinating period, potentially rewriting our understanding of Anglo-Saxon artistry and culture in the region.
Cover Image Credit: Minelab Metal Detectors -Facebook