A groundbreaking archaeological discovery in Croatia is being hailed as one of the most important medieval numismatic finds ever recorded in Europe. During ongoing research at the Batina site in the Baranja region, a place primarily associated with Iron Age settlements and the Roman frontier system, archaeologists unexpectedly unearthed an exceptionally rare hoard of early medieval silver coins linked to the period of the First Crusade. Experts say the find could redefine current understanding of medieval circulation routes, economic history, and the movement of crusaders through Central and Southeastern Europe.
A Discovery That Should Not Have Happened at This Site
The Batina site is widely known for its rich layers from the Iron Age and the Roman frontier system. Archaeological work carried out since 2008 has largely focused on ancient fortifications, Roman military structures, and prehistoric cultural horizons. For this reason, archaeologists were not expecting any significant medieval material—let alone a major numismatic breakthrough.
Curator and archaeologist Domagoj Dujmić emphasized that the discovery occurred entirely by surprise. The research team was examining Roman-era deposits when they encountered objects that clearly did not belong to the ancient layers. “We did not expect to find anything medieval here, especially not silver coins of such rarity,” Dujmić explained. “Even in France, where these coins were minted, specimens of this type are extremely scarce due to the continent-wide silver shortage that defined this period.”
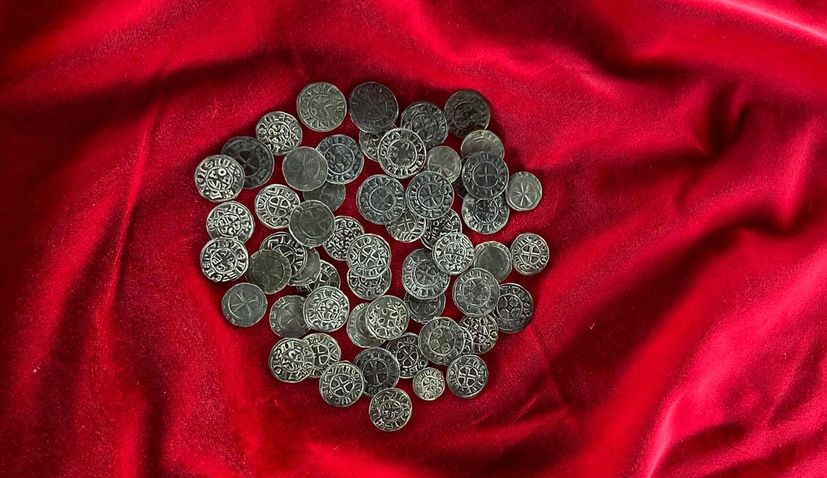
The hoard consists of 56 medieval French silver coins originating from Limoges, Toulouse, Albi, and the diocese of Le Puy. These coins were produced between the late 9th century and the mid-13th century, a time frame that intersects significantly with the era of the First Crusade (1096–1099). Their appearance in Croatia—far from their minting centers—reveals unexpected connections between Western European regions and the Danube basin.
Why These Silver Coins Are So Rare
The medieval period represented by these coins was marked by a severe silver crisis across Europe. Declining mining output, political instability, and disrupted trade routes caused widespread silver scarcity. As a result, minting operations in French territories produced far fewer coins than in earlier or later centuries. Many types survive today only in single or very limited examples.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
This is what makes the Croatian hoard so extraordinary: some of the pieces found at Batina represent over 10 percent of all known specimens of their type worldwide. In numismatic terms, such a concentration is nothing short of astonishing. It not only places Croatia on the map of significant medieval coin discoveries but elevates the find to one of the most important medieval numismatic discoveries ever documented in Europe.

A Possible Connection to Crusader Routes
Because the coins date from the era surrounding the First Crusade and come from regions deeply involved in crusader mobilization, scholars believe the hoard may be linked to the movement of crusaders or pilgrims traveling toward the Holy Land. Croatia’s geographic position made it a corridor for groups traveling through the Balkans toward Constantinople and the Levant. While historical texts mention large crusader armies taking well-known routes, countless smaller groups, families, or independent pilgrims likely traveled on less-documented paths.
The Batina discovery provides material evidence that Western European travelers may have passed through northern Croatia during the 11th and 12th centuries. The presence of French silver coins at a site dominated by Iron Age and Roman remains opens the possibility of mapping alternative medieval travel networks.
Transforming the Understanding of Medieval Europe
Beyond the immediate excitement surrounding the hoard, archaeologists believe this discovery could reshape broader historical interpretations of medieval trade, pilgrimage, and military logistics. Rare silver coins from the First Crusade era offer valuable clues about economic conditions, long-distance currency circulation, and cross-cultural encounters.
Moreover, since the coins were found in a location not previously associated with medieval settlement or activity, they introduce new questions regarding how and why such valuable currency ended up in this particular part of Croatia. Were they intentionally hidden? Lost along a travel route? Buried for safekeeping during conflict? Ongoing analysis may reveal answers.
A Landmark for Croatian Archaeology
The Ministry of Culture and Media, which has supported excavations at Batina for over 15 years, praised the find as a testament to the scientific importance of long-term archaeological investment. Croatia’s archaeological heritage spans thousands of years, but medieval numismatic discoveries of this magnitude are exceedingly rare.
The Batina silver hoard now stands as a landmark achievement not only for Croatian archaeology but for medieval scholarship across Europe. As further studies examine the coins’ metallurgical composition, minting characteristics, and historical context, researchers expect the discovery to contribute significantly to the global understanding of the First Crusade era and the circulation of medieval silver coinage.
The importance of the discovery extends beyond academic circles, as the hoard is now available for public viewing at the Archaeological Museum in Osijek. Carefully conserved and displayed alongside contextual information about its origin and medieval significance, the rare First Crusade–era silver coins offer visitors a unique opportunity to witness one of Europe’s most remarkable numismatic finds. Museum officials emphasize that the exhibition has already attracted both national and international interest, further establishing Osijek as a key center for medieval archaeological research.
Cover Image Credit: Nina Obuljen Koržinek via Facebook