In their latest research, scientists have come across a treatment practice in a mummy from 4000 years ago, as written in ancient Egyptian medical papyri. This treatment has been recorded as the first gynecological treatment to date.
Scientists from the Universities of Granada and Jaén examined the physical evidence found in the mummified remains of a woman who suffered severe trauma in the pelvis and link them to a treatment described in Egyptian medical papyri of the time.
During the Qubbet al-Hawa Project, led by the University of Jaén (UJA) in Aswan (Egypt), in which scientists from the University of Granada (UGR) participated, researchers reported on a woman living in ancient Egypt who on a woman who died approximately in 1878-1797 BC and They found evidence of the oldest gynecological treatment in the record.
During the 2017 archaeological excavations in Qubbet al-Hawa on the west bank of the Nile River, Andalusian researchers found a vertical shaft dug into the rock in tomb number QH34, which also opened the door to a burial chamber with ten sturdy skeletons.
Mummification techniques were not very effective in this region in upper Egypt. However, individuals buried there often belonged to the upper classes of society, which meant special attention should be paid to them. These particular mummies were wrapped in thick linen strips and very well preserved.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Professor Miguel Botella said, “mummies had grave gifts with different types of necklaces and masks on their faces, placed in two interlocking rectangular sarcophagi. It had hieroglyphic inscriptions, but it was badly damaged by the termite infestation. “she said.
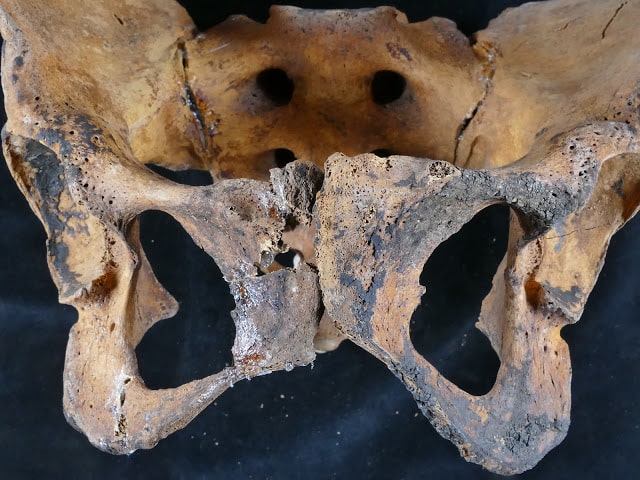
One of the mummies excavated by the team of anthropologists was perhaps the last mummy buried in the room. In the remains of the outer coffin belonged to a high social class woman, whose name was Sattgen. This woman, named Sattgeni A, is this name widely used among the upper classes of the region, so it can be thought that an adverb is added.
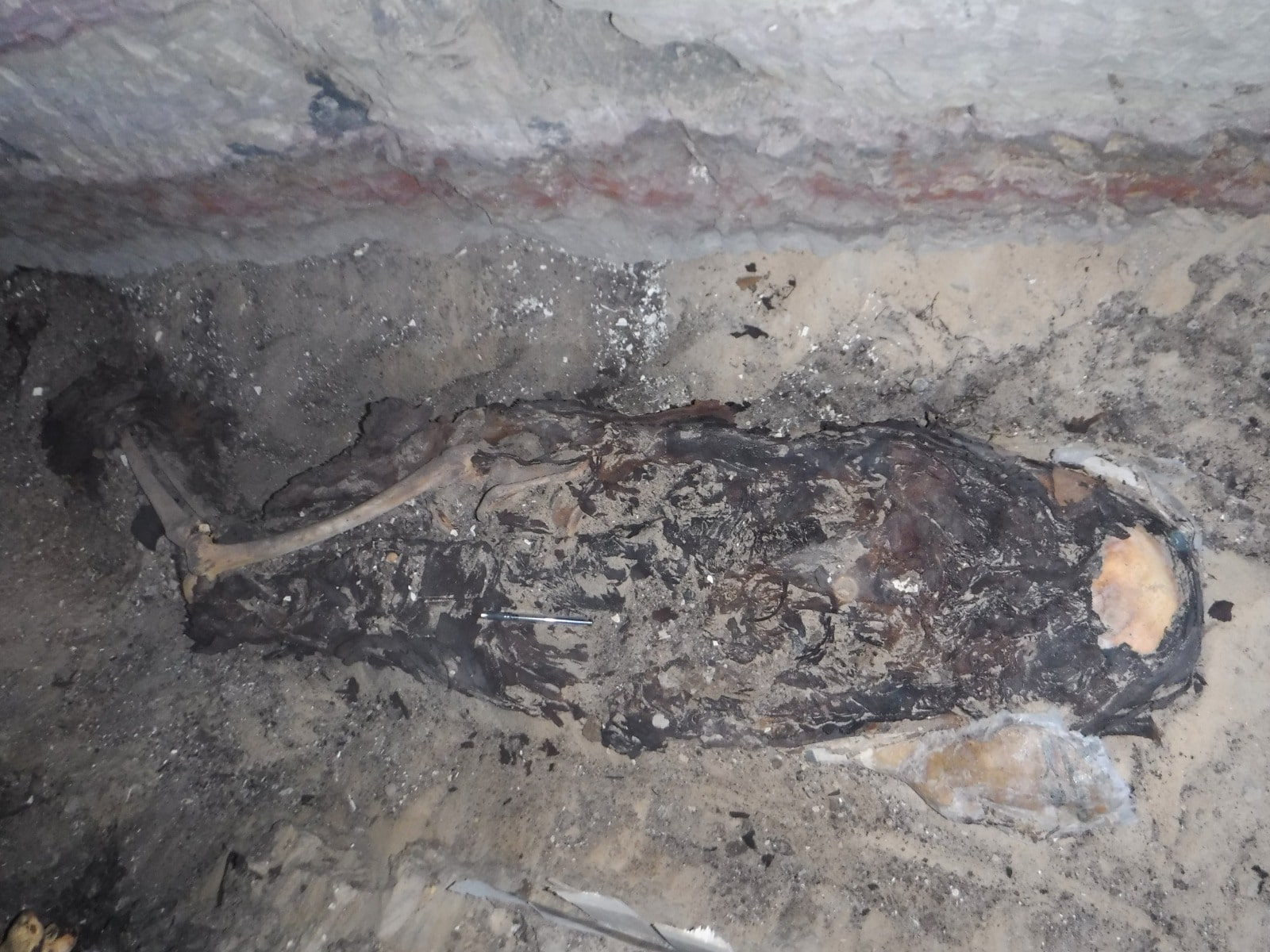
The researchers found a ceramic bowl with signs of use, containing burnt organic debris, between her bandaged legs, in the lower part of the pelvis, and under the linen dressings. Analysis of the skeletal remains was carried out by a team of anthropologists from the UGR (coordinated by Professor Botella) and confirmed that the woman had survived a severe fracture in her pelvis, possibly due to a fall that caused severe pain.
As written in medical papyri that describe the solutions for gynecological problems, it is highly likely that the woman will be treated with fumigation to relieve these pains.
UJA Egyptologist and Qubbet al-Hawa Project manager Dr. Alejandro Jimenez,”The most interesting feature of the discovery made by researchers from the University of Jaén is not only the documentation of palliative gynecological treatment that is quite unique in Egyptian archeology, but also that this type of fumigation therapy is defined in the contemporary medical literature.
But until now, no evidence could not be found to prove that such a treatment was actually applied” saying he expressed the importance of the research conducted.
If our article caught your attention, you can read the entire article at https://www.degruyter.com/view/journals/zaes/147/2/article-p171.xml