Archaeologists from Freie Universität Berlin together with an international team have uncovered fortified prehistoric settlements in a remote region of Siberia.
The results of their research reveal that hunter-gatherers in Siberia constructed complex defense structures around their settlements already 8000 years ago.
This discovery reshapes our understanding of early human societies, challenging the notion that people only began to build permanent settlements with monumental architecture and complex social structures with the advent of agriculture.
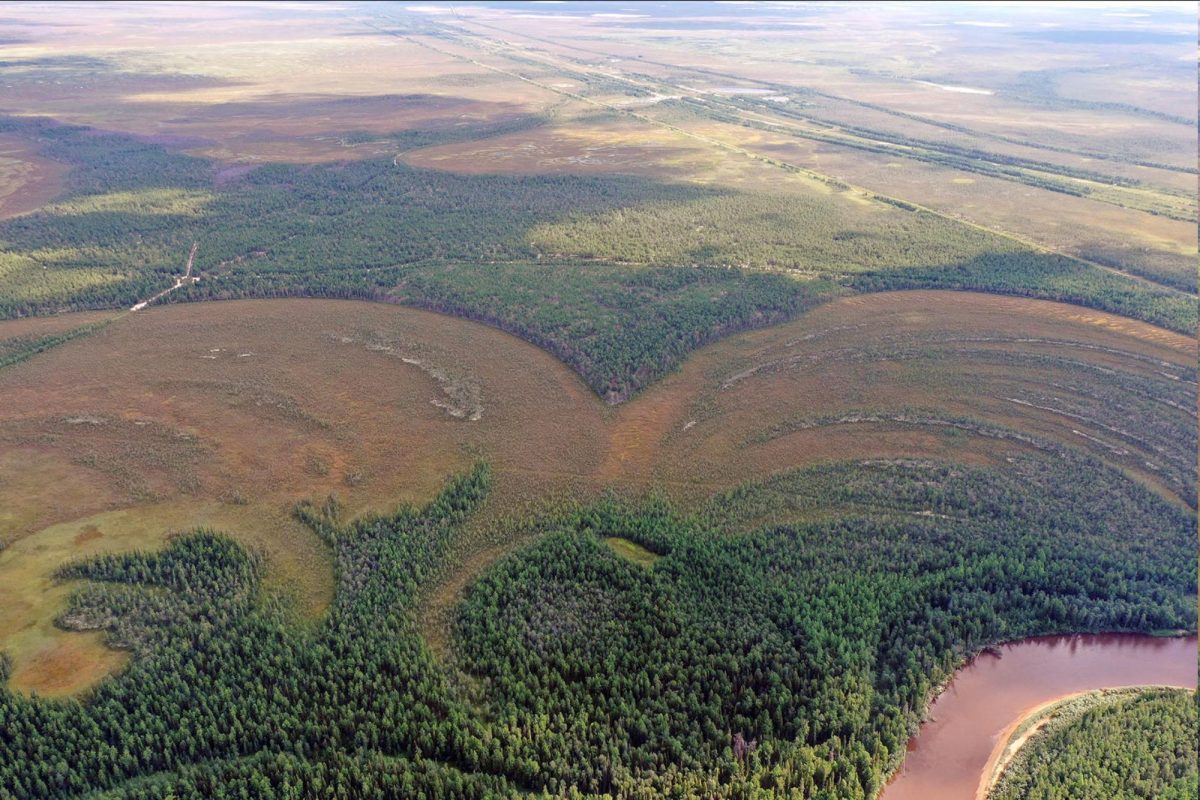
The investigation centered on the fortified settlement of Amnya, acknowledged as the northernmost Stone Age fort in Eurasia, where the team of researchers conducted fieldwork in 2019. The group was led by Professor Henny Piezonka, an archaeologist at Freie Universität Berlin, and Dr. Natalia Chairkina, an archaeologist in Yekaterinburg, Russia. Among the team’s members were German and Russian researchers from Berlin, Kiel, and Yekaterinburg.
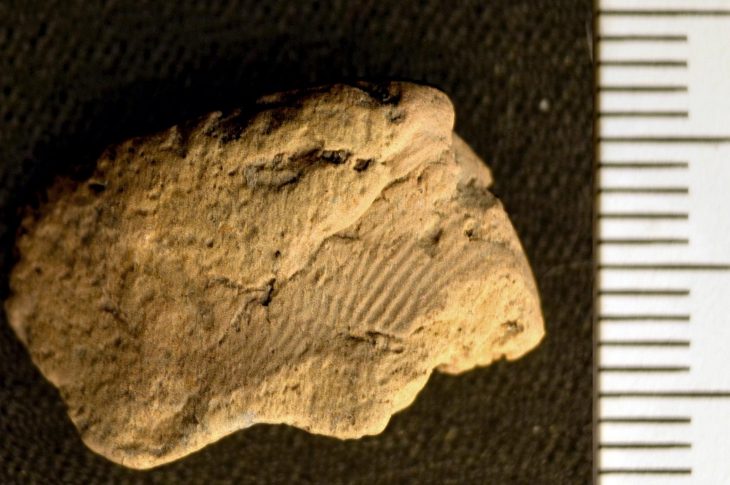
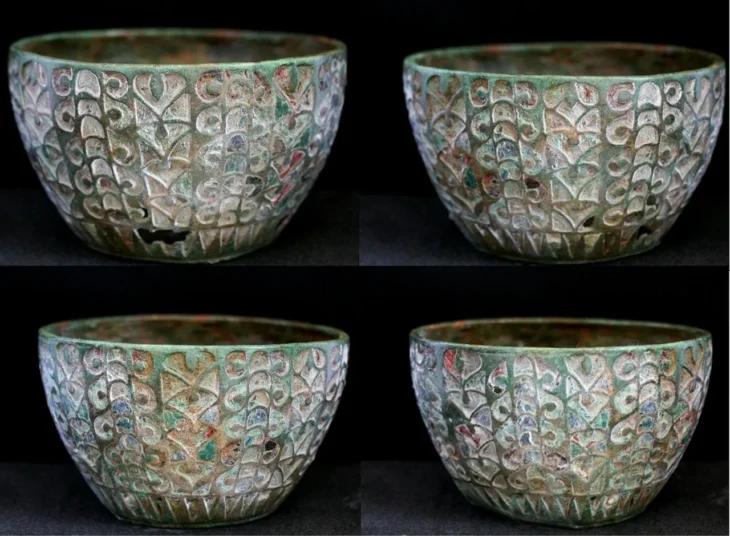
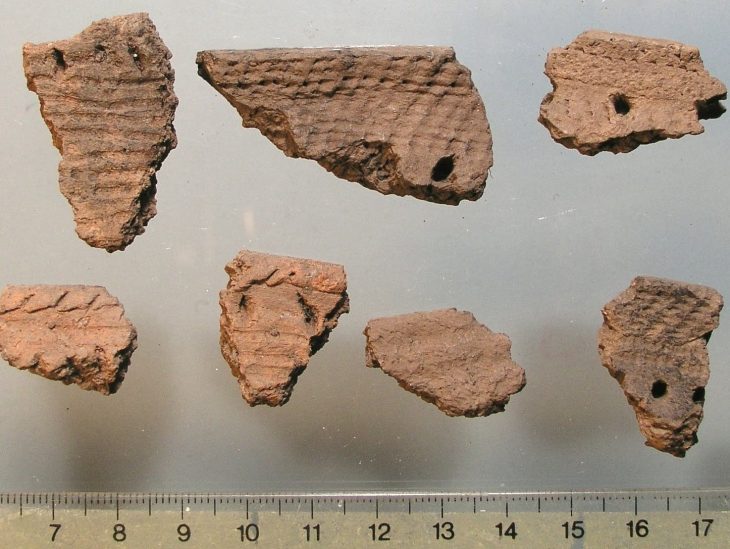
Tanja Schreiber, an archaeologist at the Institute of Prehistoric Archaeology in Berlin and co-author of the study explains, “Through detailed archaeological examinations at Amnya, we collected samples for radiocarbon dating, confirming the prehistoric age of the site and establishing it as the world’s oldest-known fort. Our new palaeobotanical and stratigraphical examinations reveal that inhabitants of Western Siberia led a sophisticated lifestyle based on the abundant resources of the taiga environment.” The prehistoric inhabitants caught fish from the Amnya River and hunted elk and reindeer using bone and stone-tipped spears. To preserve their surplus of fish oil and meat, they crafted elaborately decorated pottery.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
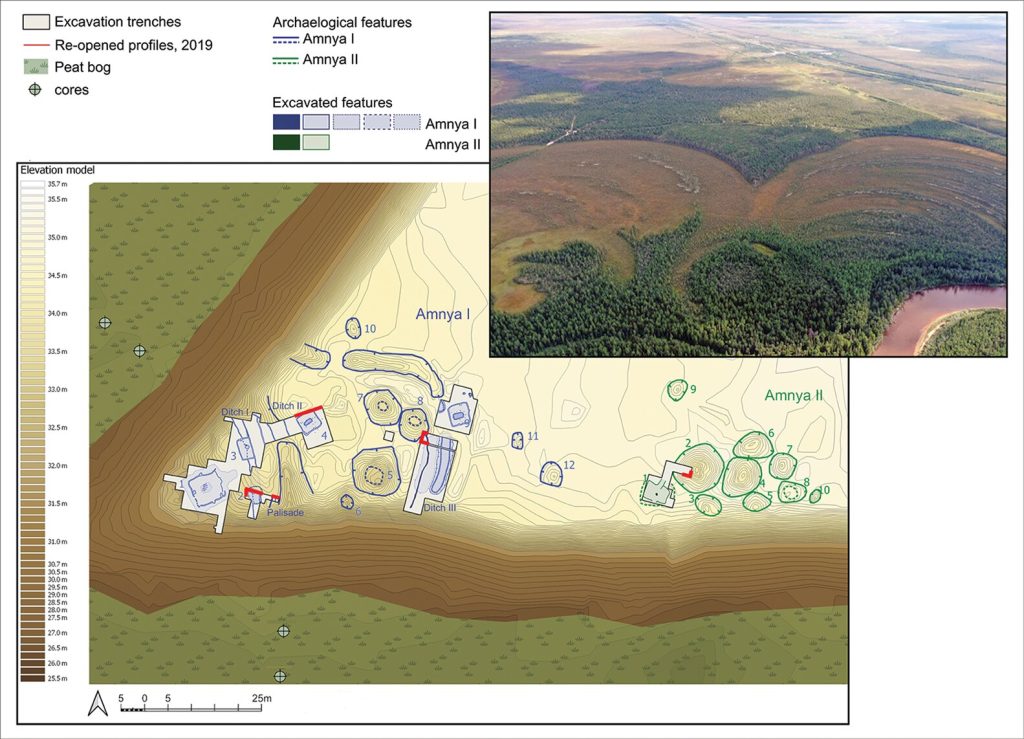
Approximately ten Stone Age fortified sites are known to date, with pit houses and surrounded by earthen walls and wooden palisades, suggesting advanced architectural and defensive capabilities. This discovery challenges the traditional view that permanent settlements, accompanied by defensive structures, only emerged with farming societies, thus disproving the notion that agriculture and animal husbandry were prerequisites for societal complexity. The Siberian findings, along with other global examples like Gobekli Tepe in Anatolia, contribute to a broader reassessment of evolutionist notions that suggest a linear development of societies from simple to complex.
In various parts of the world, from the Korean peninsula to Scandinavia, hunter-gatherer communities developed large settlements by drawing on aquatic resources. The abundance of natural resources in the Siberian taiga, such as annual fish runs and migrating herds, probably played a crucial role in the emergence of the hunter-gatherer forts. The fortified settlements overlooking rivers may have served as strategic locations to control and exploit productive fishing spots. The competitive nature arising from the storage of resources and increased populations is evident in these prehistoric constructions, overturning previous assumptions that competition and conflict were absent in hunter-gatherer societies.
The findings underscore the diversity of pathways that led to complex societal organizations, reflected in the emergence of monumental constructions such as the Siberian forts. They also highlight the significance of local environmental conditions in shaping the trajectories of human societies.
Research results published in the scientific journal “Antiquity.”
https://doi.org/10.15184/aqy.2023.164.
Cover Photo: The fortified settlement sits atop a section of land overlooking the bountiful Amnya River. Nikita Golovanov
















