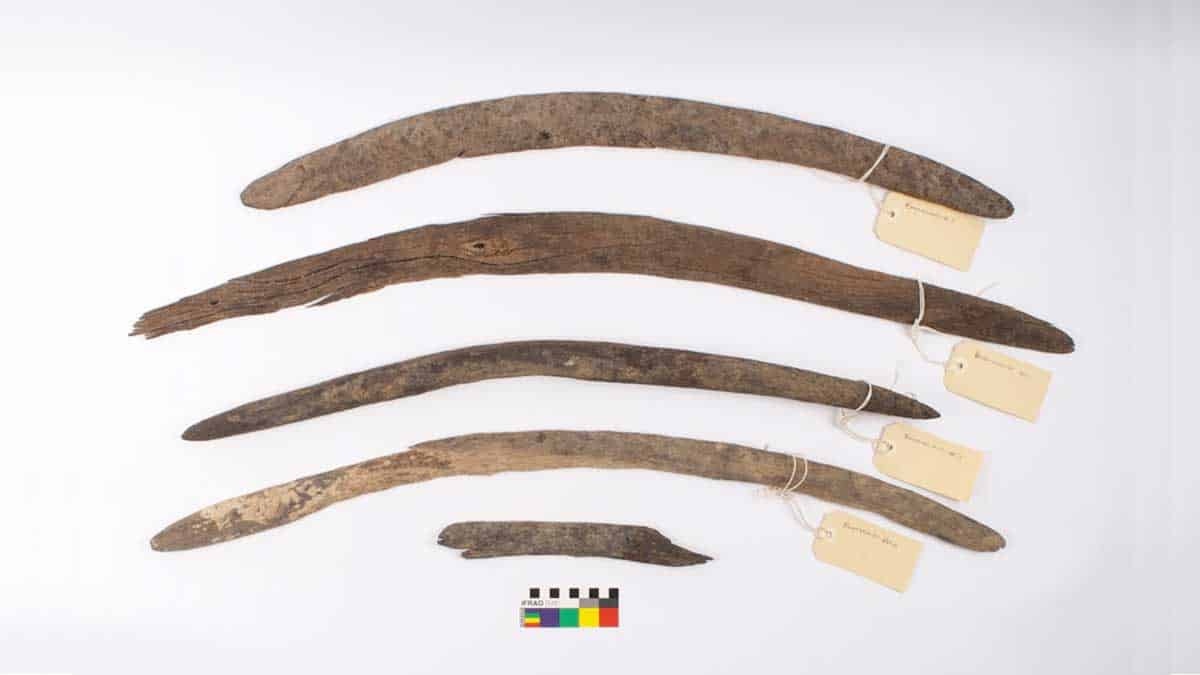
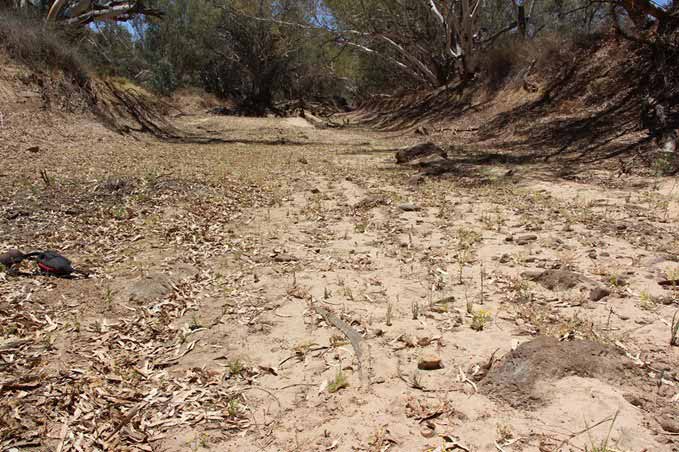
The drying waters of the Cooper Creek river have revealed extremely rare 4 boomerangs that have been partially buried.
The first was discovered by Katheryn Litherland from the Yandruwandha Yawarrawarrka traditional landowner’s group, who was cleaning up rubbish on a dry river bed. The other three boomerangs and fragments were found within a few weeks, several miles away from each other.
The boomerangs have now been dated thanks to an investigation led by the Yandruwandha Yawarrawarrka Traditional Landowners Corporation in partnership with Australian Heritage Services, Flinders University, and the Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO). It has been determined that boomerangs were utilized from AD 1650 to AD 1830.
According to a recent investigation of the artifacts — four entire boomerangs and a piece of another — Aboriginal Australians utilized them for a range of functions, including hunting, digging, fuelling fires, and maybe even ceremonial and hand-to-hand fighting.
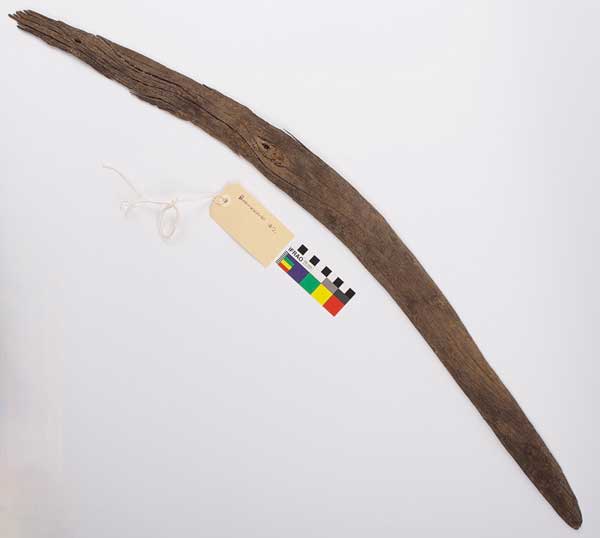

Boomerangs are famous today for flying away and then back toward the thrower; but that may have been an accidental discovery due to their aerodynamic cross-sections, researchers said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The largest of the newly discovered boomerangs would have been roughly 40 inches (1 meter) long when finished and would have been much too heavy to be utilized as a projectile. “It is therefore probable that this artifact’s main use was in close fighting,” the researchers wrote in a study published online Nov. 3 in the journal Australian Archaeology.
The new collection’s oldest boomerang, dating from around 1656, is also one of the finest maintained. The researchers discovered that it, too, was probably too heavy to be thrown very far.
“The wooden artifact was therefore much more multi-purpose in function and could have been used as a digging stick, infighting and for hunting game,” the researchers wrote in the study. It was significantly charred at both ends, which indicated it had probably also been used to stoke fires.

According to Amy Roberts, an archaeologist and anthropologist at Flinders University in Adelaide, the artifacts provide a unique peek into what life was like for the southern continent’s Indigenous inhabitants.
Amy Roberts said that “non-returning” boomerangs are more useful and more common.
“I think it’s just a stereotype that a boomerang returns and that it’s the smaller, symmetrical-looking one, when in fact it’s a really broad class of objects,” Roberts said. “Many would have some aerodynamic properties, but a lot of them didn’t return.”
According to ethnographic research, Aboriginal men preserved several varieties of boomerangs in their camps for various purposes, including ornamental ones for dances and celebrations. The Cooper Creek boomerangs, on the other hand, aren’t adorned with carvings or show evidence of being painted, according to Roberts.
Cover Photo: The collection of four boomerangs was analyzed by archaeologists and Traditional Owners. Photo: Yandruwandha Yawarrawarrka Traditional Landowners Aboriginal Corporation / Flinders University