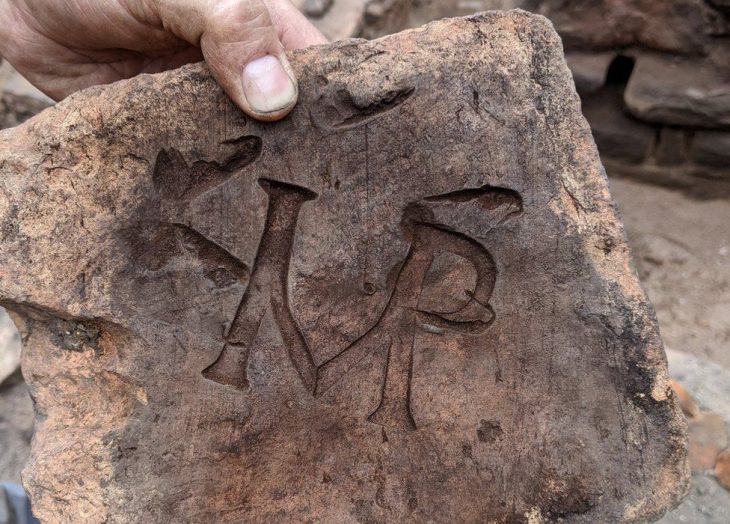Newly discovered clay seal may connect to a high-ranking official from King Josiah’s court, offering a rare, tangible link to the Bible’s historical narrative.
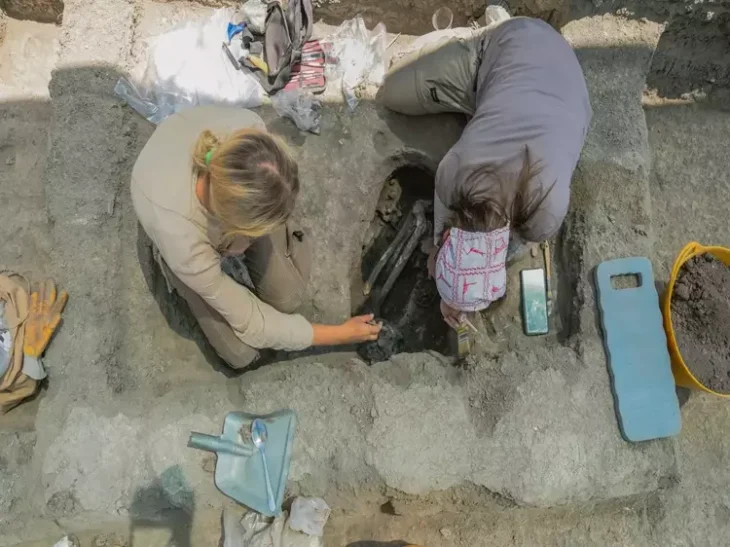
In a discovery that blends archaeology and ancient scripture, researchers at the Temple Mount Sifting Project have unearthed a 2,600-year-old clay seal (bulla) bearing the name “Yeda‛yah (son of) Asayahu” in ancient Paleo-Hebrew script. The exceptionally preserved artifact, dating back to the First Temple period, may have belonged to the son of a biblical official who served King Josiah of Judah — a potential breakthrough in linking material evidence with the biblical record.
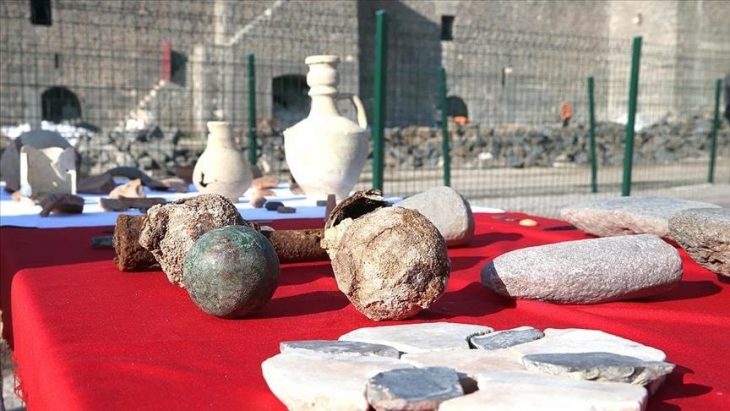
This minute clay seal was found amidst tons of earth sifted from the Temple Mount debris — soil that was removed from Jerusalem’s most sensitive religious site during unauthorized construction in the late 1990s. Archaeologist Mordechai Ehrlich made the find during routine examination of sorted material. At first mistaken for a bone fragment, the seal soon revealed its identity through a full inscription and an ancient fingerprint pressed into its back — possibly from the official who once used it.
“This is one of the most complete sealings we’ve discovered in over two decades,” said archaeologist Zachi Dvira, co-director of the Temple Mount Sifting Project. “Nearly every letter is legible. Finds like this, especially with such historical resonance, are incredibly rare.”
A Royal Connection?
The inscription reads: “Belonging to Yeda‛yah (son of) Asayahu.” The name “Asayahu” (a longer theophoric form of “Asaya”) appears in the Bible in connection with King Josiah’s court. Specifically, Asayahu is listed among the king’s senior emissaries dispatched to consult the prophetess Huldah after the discovery of a sacred scroll — likely Deuteronomy — during Temple renovations (2 Kings 22:12, 2 Chronicles 34:20).
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Experts believe the seal’s owner may well have been his son, Yeda‛yah, serving in an administrative role within the royal or Temple treasury. Given the clay bulla’s use as a sealing for storage vessels or bags—most likely those containing food supplies or sacred materials—its presence supports the theory of a high-ranking functionary operating in Jerusalem shortly before the Babylonian conquest in 586 BCE.
“This seal would not have belonged to a commoner,” said Dr. Anat Mendel-Geberovich, an expert in ancient Hebrew epigraphy who led the deciphering process. “It would have been used by someone in a position of authority — someone trusted to oversee valuable goods or sacred spaces.”
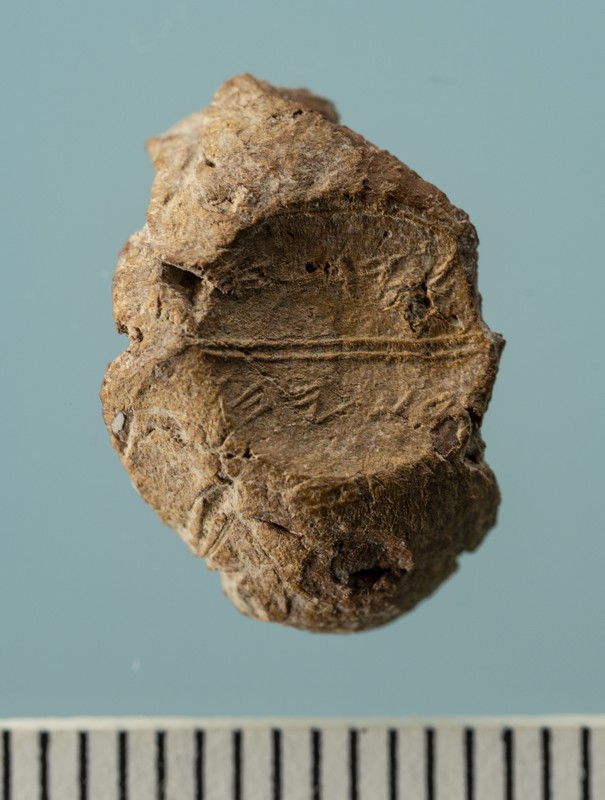

Traces of a Vanished Kingdom
The fingerprint preserved on the clay evokes an eerie sense of continuity. “You’re literally touching the trace of a person who lived in Jerusalem during one of its most pivotal periods — possibly even a figure mentioned in the Bible,” said Dvira. “It’s a silent message across 2,600 years.”
The find gains further significance as it was uncovered just days before Tisha B’Av — the Jewish day of mourning commemorating the destruction of both the First and Second Temples. Symbolically, the seal seems to echo across the centuries, a fragment of faith and history reclaimed from the ashes of loss.
Seals as Ancient Signatures
In ancient Judah, seals were more than tools — they were statements of identity, authority, and legitimacy. Typically affixed to cords tying storehouse jars or papyrus documents, bullae served both practical and symbolic purposes. They confirmed ownership and prevented tampering, functioning as the bureaucratic backbone of ancient governance.
Until recently, most bullae in circulation came from the antiquities market, lacking archaeological context. The Sifting Project, by contrast, has revolutionized the field by recovering thousands of finds from a controlled environment, using advanced imaging techniques like Reflectance Transformation Imaging (RTI) to enhance inscriptions without damaging artifacts.
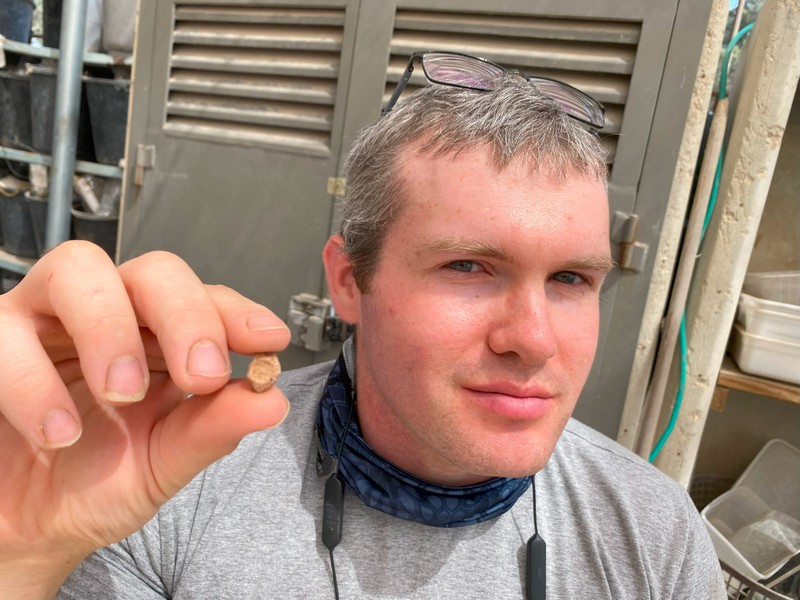

Reclaiming the Past, Piece by Piece
Launched in response to unsupervised excavation on the Temple Mount between 1996–1999, the Temple Mount Sifting Project has since yielded over half a million finds, including pottery, coins, jewelry, and burnt animal bones. More than 260,000 volunteers from around the world have participated in the effort, helping recover history one bucket of soil at a time.
“This find reminds us that beneath every shovelful of earth, a story waits to be told — one that bridges archaeology, faith, and heritage,” said Dvira.
While the fate of Yeda‛yah remains unknown, his clay seal—now carefully studied and documented—offers a poignant window into the world of ancient Jerusalem, where politics, religion, and prophecy intertwined. A peer-reviewed academic paper on the artifact is expected soon, adding another piece to the enduring puzzle of biblical history.
Temple Mount Sifting Project (TMSP)
Cover Image Credit: The Holyland Model of Jerusalem depicts Jerusalem during the late Second Temple period. The Temple Mount and Herod’s Temple are shown in the middle. View from the east. Public Domain