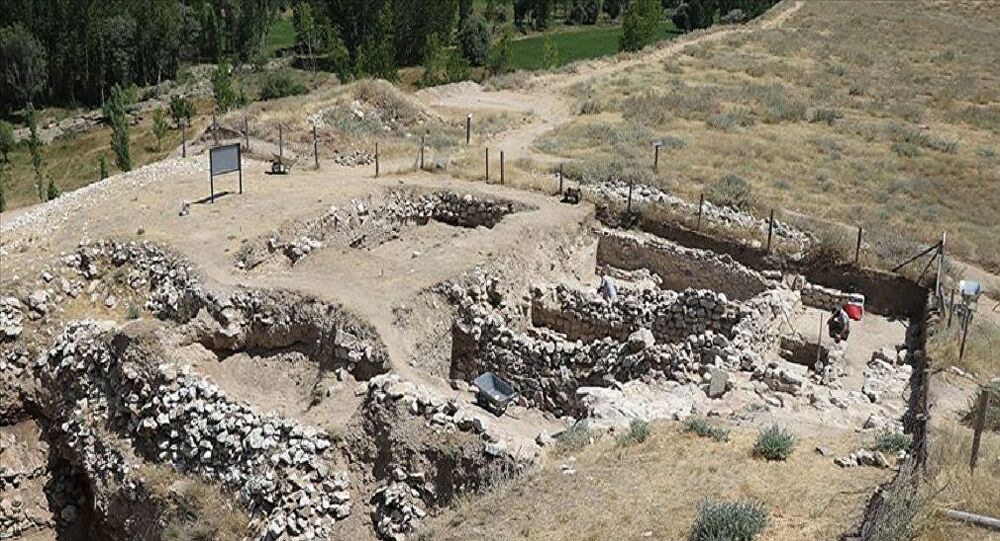
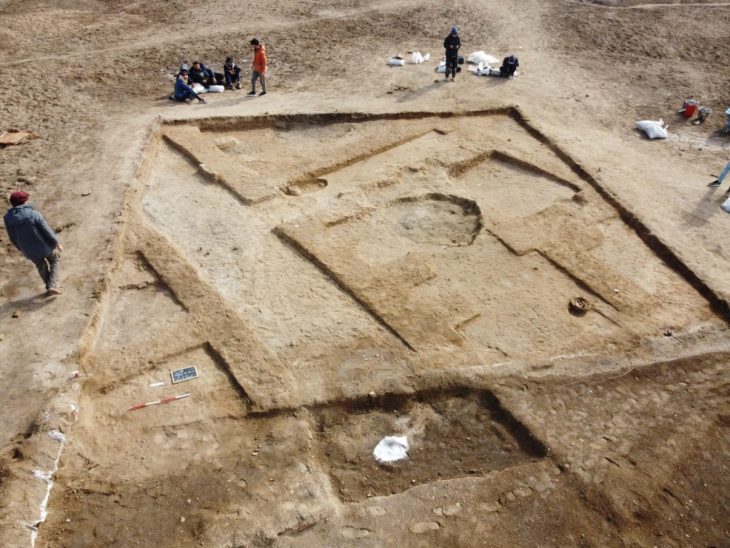
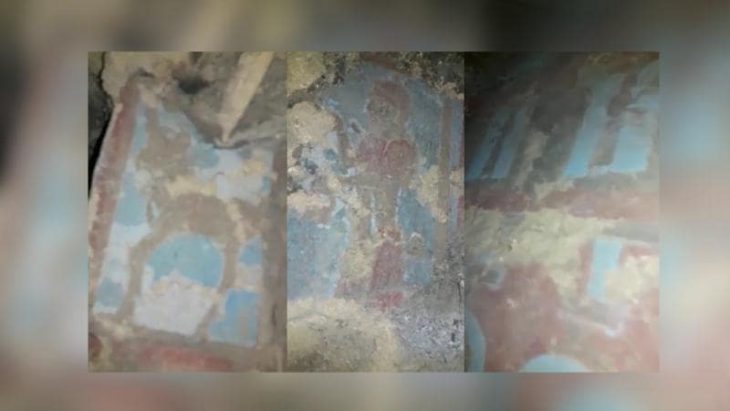
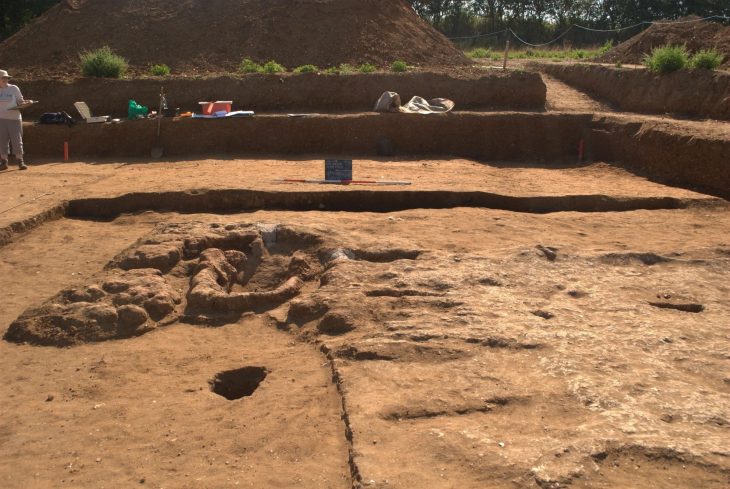
In the excavations of Porsuk Mound, which is an important Hittite settlement and where traces of settlement remains can be seen from the Neolithic age, iron age fortifications and plaster remains were unearthed
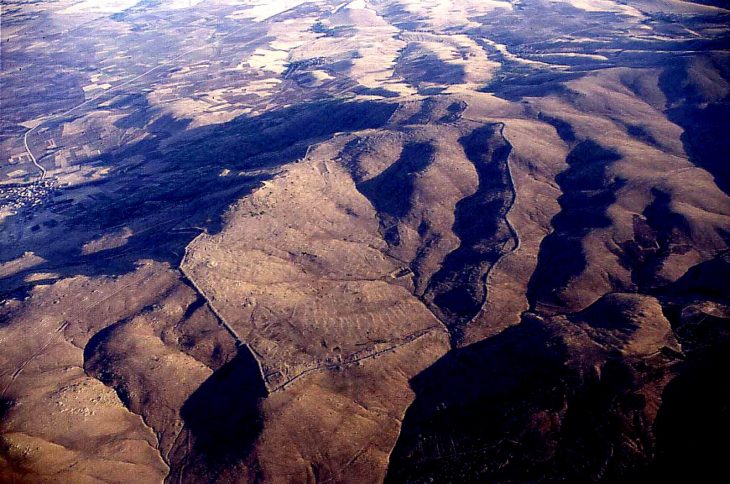
Porsuk Mound, also known as Zeyve Mound by the locals and located inside the borders of Porsuk Village in Ulukışla District of Niğde Province, is 55 kilometers from Niğde Province and 9 kilometers from Ulukışla District. It is possible to say that it is right in the heart of Anatolia.
During the excavations carried out by the French Archaeological Institute since 1968, new iron age walls and plaster remains were found this year. Excavations for the year 2021 at Porsuk Mound started in July.
Former Polytechnique Hauts De University Faculty Member of History and Classical Archeology Department Associate Professor Claire Barat, who is the head of the excavation, stated that they started the excavation work as of July, which they interrupted last year due to the Covid-19 epidemic, “This year, the Iron Age walls and the original We found plaster remains from the Iron Age,” she said.
Claire Barat, who gave information about the works to Abdullah Özkul from AA, reminded that during the excavations 2 years ago, there were 2,100-year-old houses, cellars, rooms, and storage containers from the Roman period.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
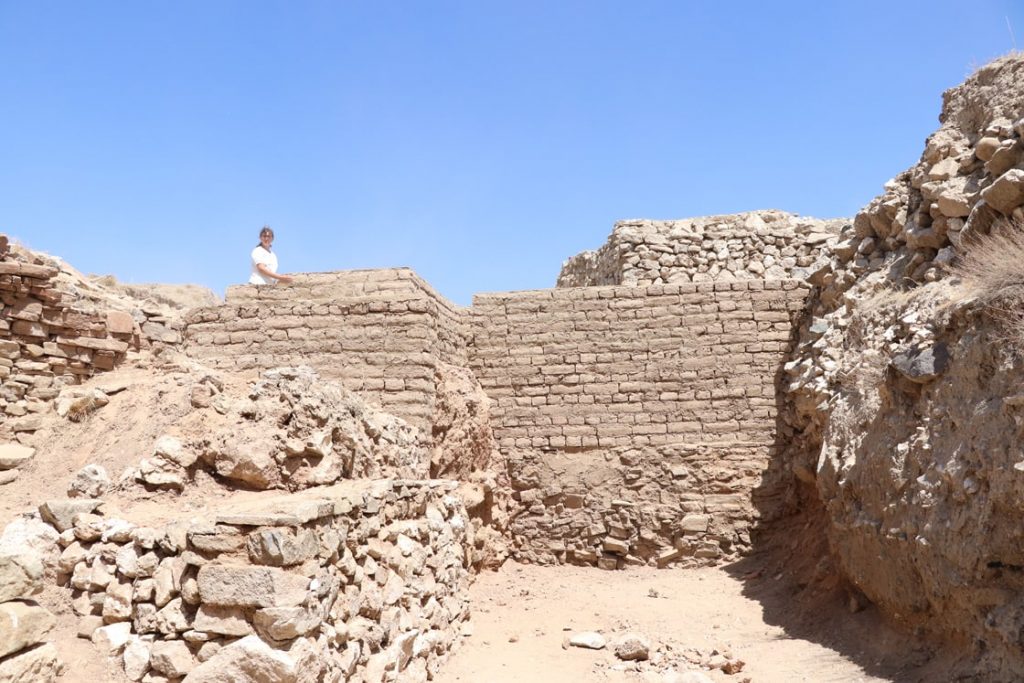

“This year we are excavating Roman houses and Iron Age walls. Porsuk-Zeyve Höyük is a very important protected area. There are Hittite walls, Iron Age walls, Hellenistic, Roman and Byzantine period artifacts. This year we found Iron Age walls and, crucially, the remains of original Iron Age plaster. Now we are doing emergency protection because there is a lot of wind and dust. It snows a lot in winter. Therefore, urgent work is needed.”
Noting that the mound is 4 hectares in size, Barat said, “There were walls and towers here. 2 years ago, we protected the tower and the walls. This year, we continue our conservation work. At the same time, there is a castle belonging to the Iron Age in our excavations,” she said.
Barat added that the original mudbricks in the mound should be preserved, and for this, they cooperated with the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, the Provincial Directorate of Culture and Tourism, the village headman of Porsuk, and the laboratory of the higher architecture school in Grenoble, France.

Porsuk Mound cultural layers
Located at the foot of the northern slopes of the Taurus Mountains, Porsuk Höyük has a strategic location in all periods. The fact that he controlled the Kilikia Gates, a narrow mountain pass on the Taurus Mountains from the Anatolian Plateau, further increased the importance of the region.
In addition, Porsuk Höyük has been the preferred region due to the volcanic mountain of Hasan Dağ (Melendiz Mountain), located 60 km north of Porsuk village, where the most important economic asset of the Neolithic period is the obsidian resources.
The layers unearthed in Porsuk Höyük, whose strategic location and economic values have hosted many civilizations, are as follows;
Old Hittite Kingdom Period, the founding of the city (Porsuk VI)
Hittite Empire Period, ca.14th century BC – 1200 BC (Porsuk V)
Early Iron Age, near phase, ca. 10-9 BC. centuries (Badger IV)
Middle Iron Age – Late Iron Age, Period of the Late Hittite Kingdoms, 8th-7th BC. centuries (Badger III)
Hellenistic Period, ca. 3rd-2nd BC. centuries (Badger II)
Roman Period, ca. 1st century BC – 3rd century AD (Porsuk I).