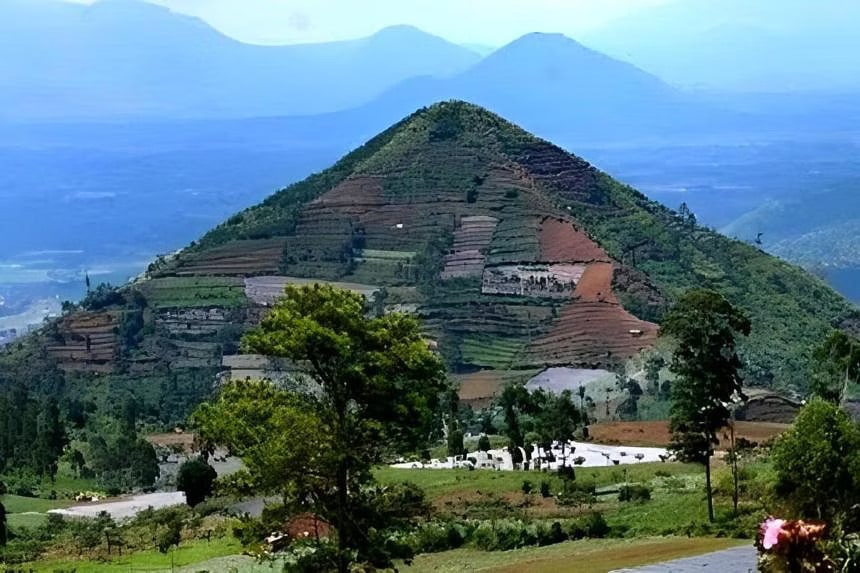
Gunung Padang, a colossal megalithic structure nestled in the lush landscapes of West Java, Indonesia, could be the world’s oldest pyramid. Recent research suggests that this ancient site may predate Egypt’s famous pyramids and is even older than the stone wonders of Türkiye’s Göbekli Tepe.
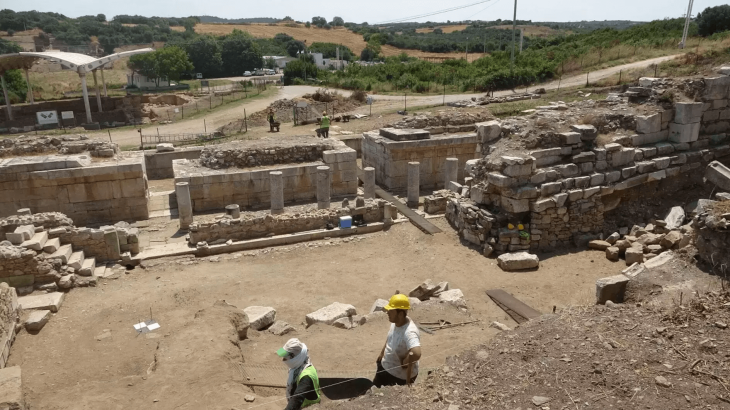
A team of archaeologists, geophysicists, geologists, and paleontologists affiliated with multiple institutions in Indonesia has found evidence showing that Gunung Padang is the oldest known pyramid in the world.
The group describes their multi-year study of the cultural heritage site in their article published in the interdisciplinary archeology journal Archaeological Prospection in October.
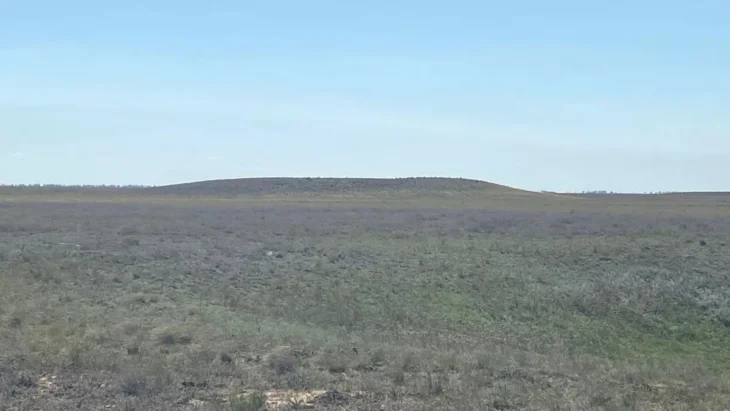
Gunung Padang, also known as the “mountain of enlightenment”, sits at the top of an extinct volcano and is considered a sacred site by locals. In 1998, Gunung Padang was declared a national cultural heritage site.
Led by geologist Danny Hilman Natawidjaja and his team at Indonesia’s National Research and Innovation Agency, the new research suggests that Gunung Padang dates back to the last Ice Age, around 25,000 to 14,000 years ago.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
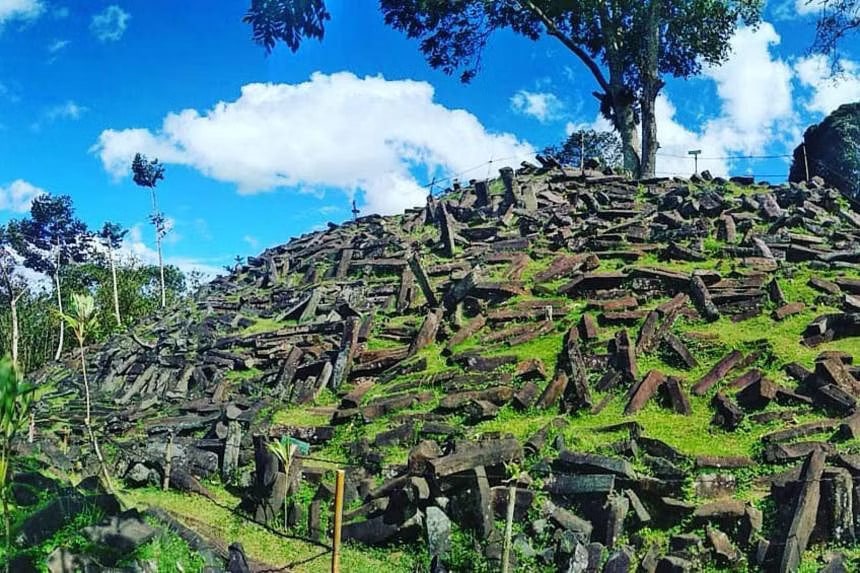

The oldest construction of the pyramid likely “originated as a natural lava hill before being sculpted and then architecturally enveloped”, according to the team. This makes Gunung Padang at least 16,000 years old.
The pyramid was finished between 2,000 BC and 1,100 BC, according to the study.
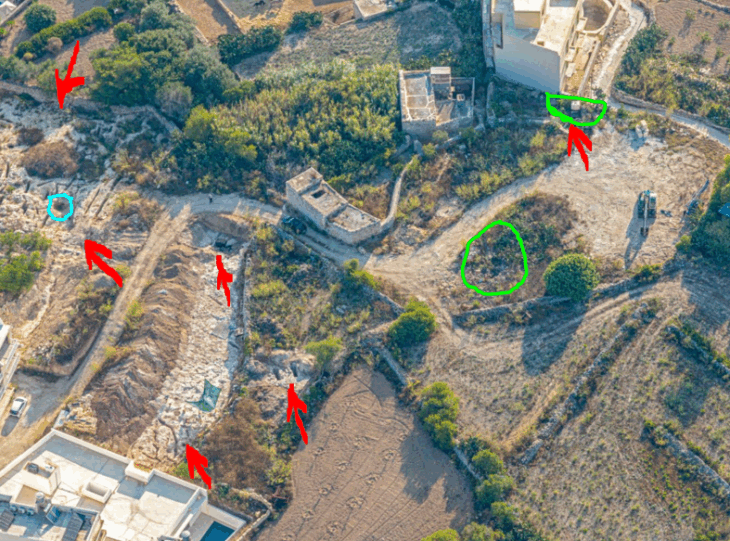
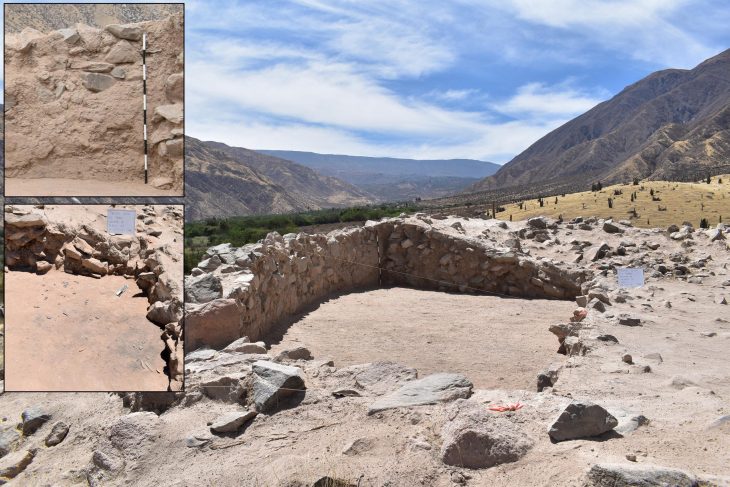
More specifically, the researchers discovered evidence of several efforts that, when combined over time, resulted in a completed structure. The first was sculpted lava, in which builders carved shapes into the top of a small, dead volcano. Another group added a layer of bricks and rock columns several thousand years later, sometime between 7900 and 6100 BCE. Another group later added a dirt layer to part of the hill, covering some of the earlier work. Then, between 2000 and 1100 BCE, another group added additional topsoil, stone terracing, and other elements.
The study challenges conventional beliefs by highlighting the advanced masonry capabilities exhibited by the builders of Gunung Padang. Contrary to expectations based on traditional hunter-gatherer cultures, the research reveals the existence of advanced construction practices during the last glacial period.
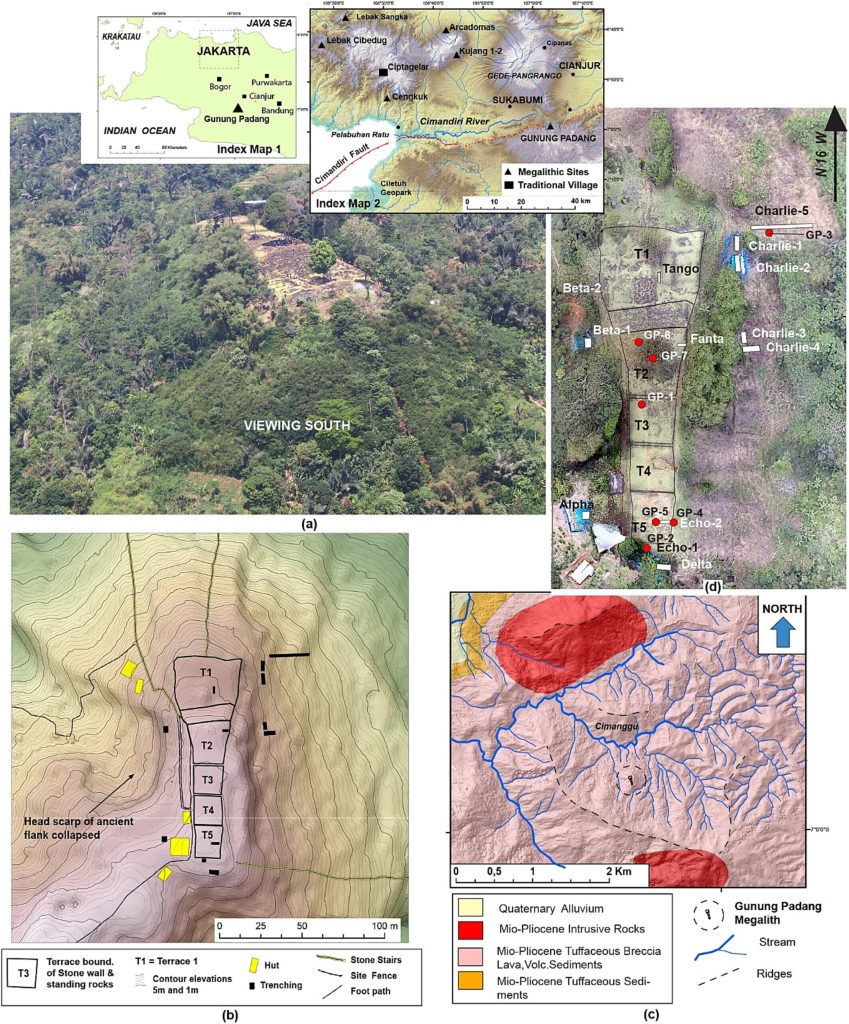
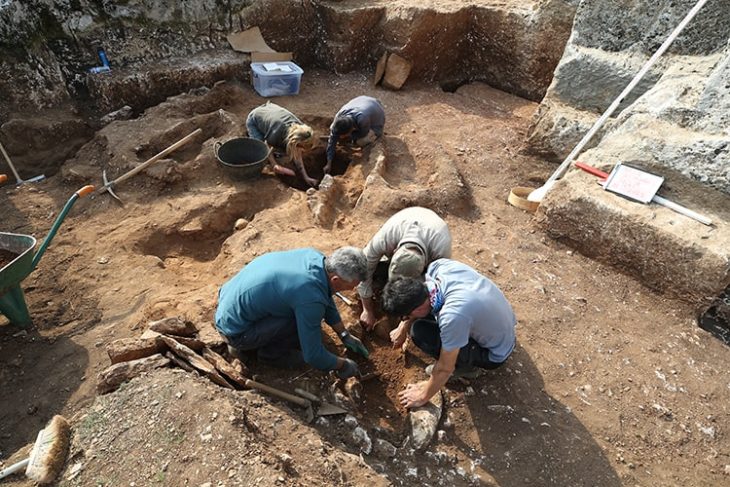
The research team conducted a long-term, scientific study of the structure for this new study. They studied the structure using seismic tomography, electrical resistivity tomography, and ground-penetrating radar from 2011 to 2015. They also drilled down into the hill and collected core samples, which allowed them to use radiocarbon dating techniques to determine the ages of the hill’s layers.
The research team has also found some evidence suggesting there might be some hollow parts inside the structure, suggesting possible hidden chambers. They plan to drill down to them and then lower a camera to see what might be in these areas.
“Gunung Padang stands as a remarkable testament, potentially being the oldest pyramid in the world,” said the researchers in the paper.
















