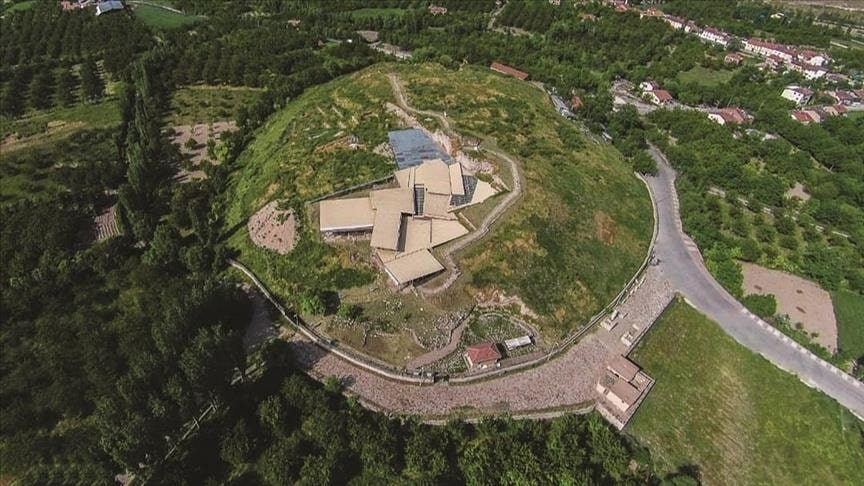
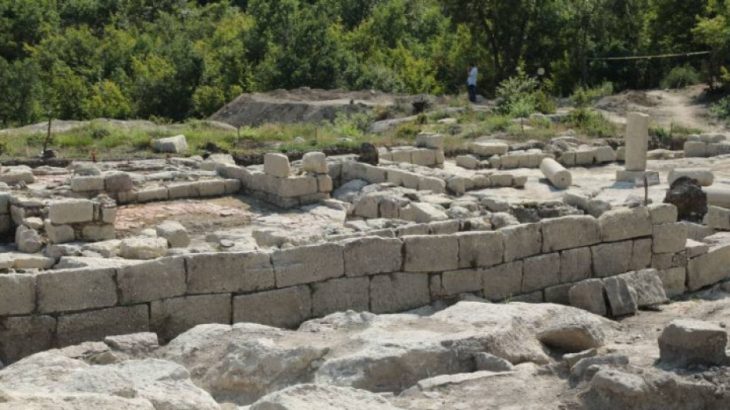
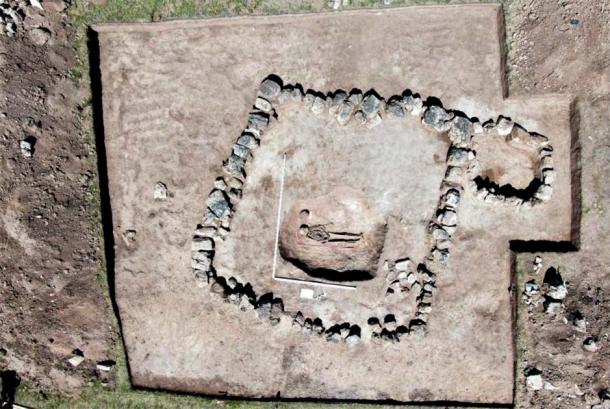
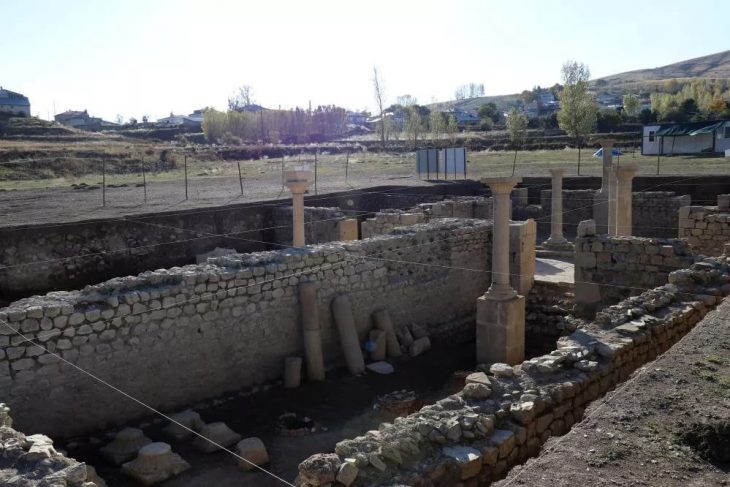
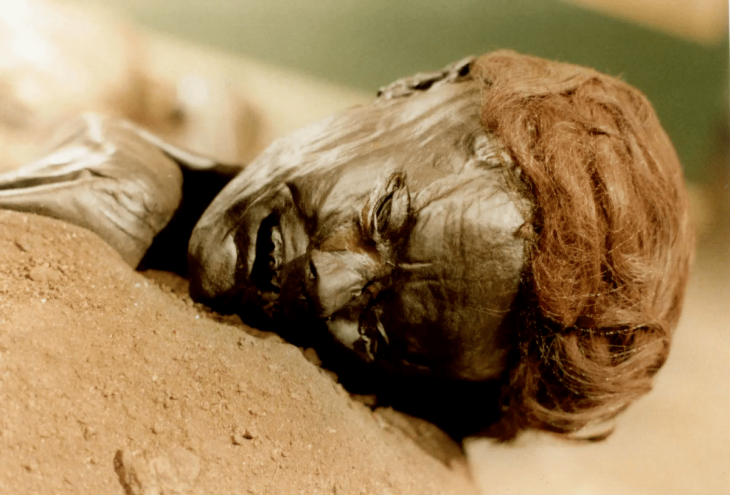
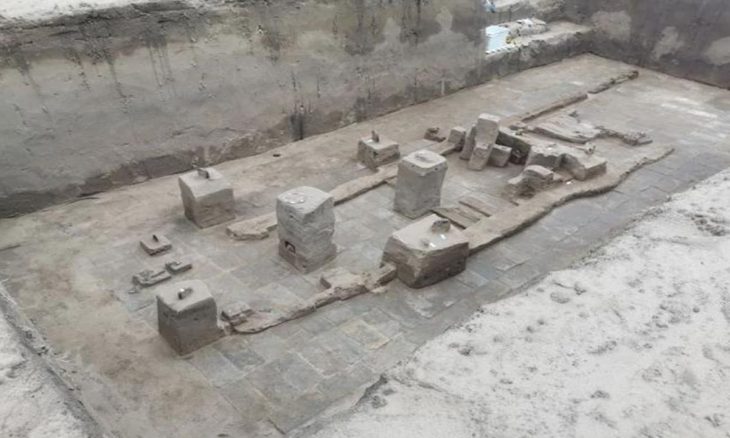
The tale of Turkey’s fascinating 7,000-year-old Arslantepe Mound, an ancient building in Malatya, eastern Turkey that was just added to the UNESCO World Cultural Heritage Permanent List, is told in a new documentary.
The bilingual Turkish-English documentary, according to Turkey’s Communications Directorate, highlights the country’s rich history and covers the process of bringing the ancient mound to light and adding it to the UNESCO World Heritage List.
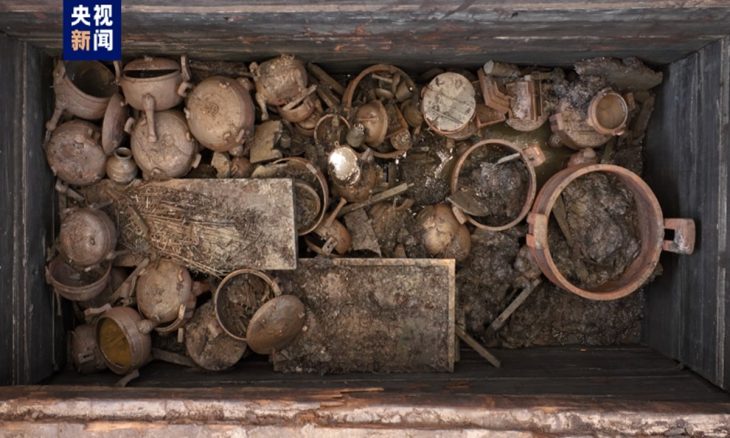
The documentary delves into the historical context of the aristocracy’s rise to power and the formation of the first state structure, as well as notable artifacts found from the mound.
The documentary will be aired on state broadcaster TRT Belgesel (documentary channel) and posted on the directorate’s social media accounts.
About the documentary, directorate head Fahrettin Altun said that over the course of millennia, Turkey’s vast Anatolian region has been home to countless civilizations and peoples.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
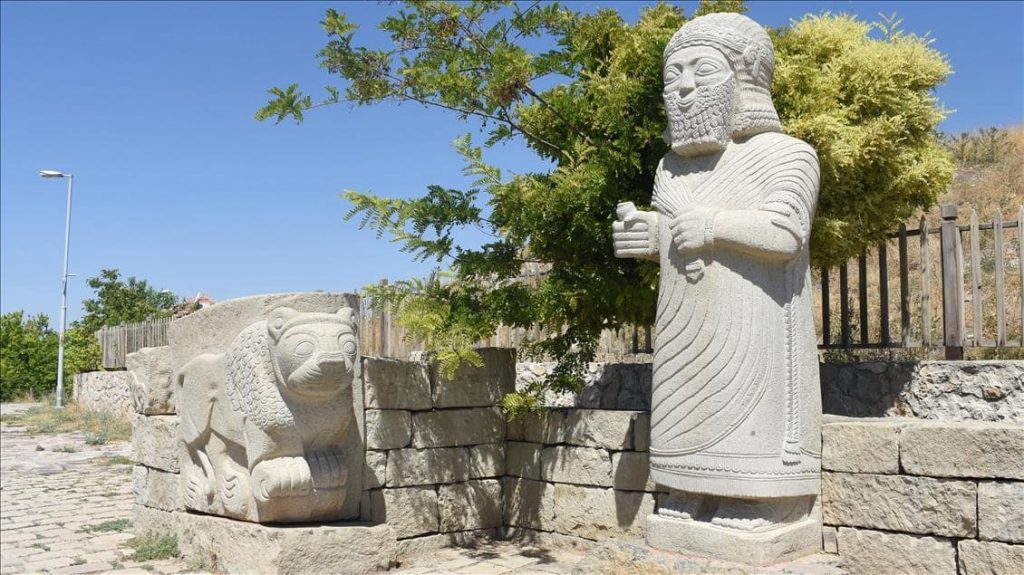

“With our documentary, we aim to introduce Arslantepe Mound to the whole world, to boost its profile and awareness, and to contribute to Turkey’s cultural tourism,” Altun said, stressing that Anatolia’s rich ancient history makes it deserving of the title “humanity’s ancient heritage.”
– Weapons, combat, early state
This July, the ancient mound was added to the UNESCO World Heritage List. The site was occupied from at least the sixth millennium BC until the late Roman era, said UNESCO, citing archaeological evidence.
“The earliest layers of the Early Uruk period are characterized by adobe houses from the first half of the 4th millennium BCE.”
“The site illustrates the processes which led to the emergence of a State society in the Near East and a sophisticated bureaucratic system that predates writing,” the UN agency added.
“Exceptional metal objects and weapons have been excavated at the site, among them the earliest swords were so far known in the world, which suggests the beginning of forms of organized combat as the prerogative of an elite, who exhibited them as instruments of their new political power.”