A project of the Cluster of Excellence ROOTS uses archaeological raw material finds for network analyses from the Middle Stone Age to antiquity.
Who knows whom? Who has which desires and needs? The answers to these questions are worth a lot of money for the advertising industry today. With the help of huge amounts of data and artificial intelligence, internet companies can answer them more and more precisely. Similar methods, but with the aim of better understanding the networks and relationships of prehistoric and early historical people, are used in the “Big Exchange” project, which a team of archaeologists from seven countries led by Kiel University presents in the journal Antiquity.
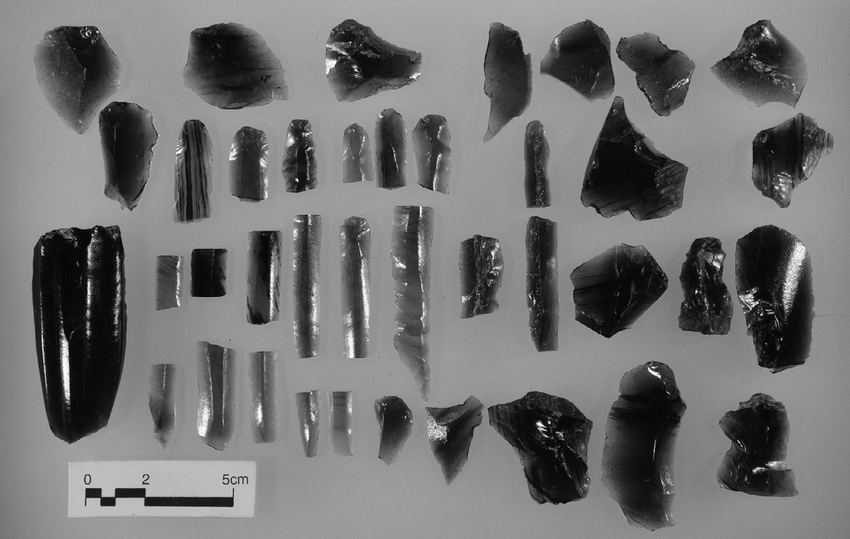
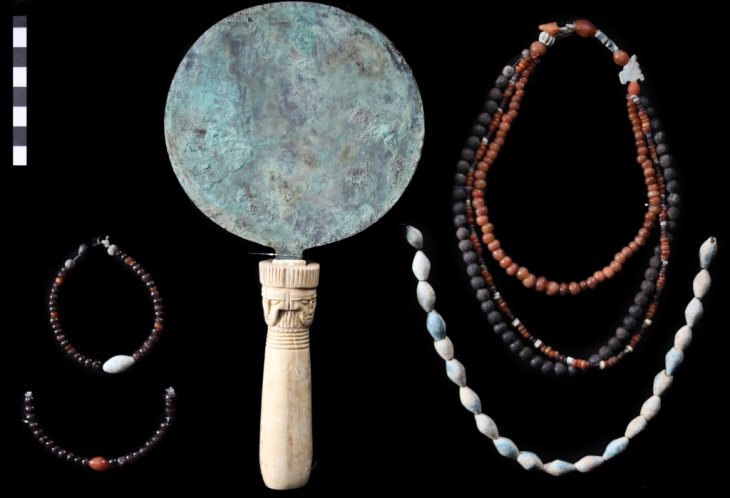
Archeology finds no direct imprints of relationships in the ground, but uncovers raw materials such as flint, obsidian, jade, ivory and various metals, which have often traveled long distances from their source to the site of discovery. These materials serve as traces of past relationships between people and allow us to study networks in the past. Dr Tim Kerig, project manager and archaeologist in the ROOTS Cluster of Excellence at the CAU Kiel, explains: “With the help of network analyzes and AI, we can better understand the relationships between people in the past.”
The analysis of early networks based on raw material finds and the associated raw material sources is nothing new. Archaeology has already been using this possibility for about 50 years. These studies have provided valuable insights into the past, but due to the high level of effort and specialization, they have often been limited to a specific raw material.
Dr. Johanna Hilpert, an archaeologist at the Institute for Prehistory and Protohistory and postdoc at the CAU Kiel data campus, explains: “Thanks to digitalization, we can now carry out more complex analyzes that include several raw materials at the same time.” The “Big Exchange” project aims to include all available raw materials and their find and place of origin in the evaluations for the period from the Mesolithic to antiquity. This is only possible with the help of network analysis and AI.

More than 6000 sites with millions of finds recorded
Only recently has digitisation enabled more complex analyses with multiple raw materials at the same time. “The approach of our project ‘Big Exchange’ is now to include all recordable raw materials, their find locations and places of origin in the analyses for the period from the Middle Stone Age to antiquity. This can only be done by means of network analysis and with AI,” emphasises Dr. Hilpert.
So far, the project has already recorded more than 6000 sites with millions of individual finds from Western Europe to Central Asia. The network analyses made possible by this data allow statements to be made about how the simultaneous distribution of various goods is related to the more or less restricted access of the respective people to raw materials. This also concerns fundamental questions about social inequality and various power relations.
At the same time, the project is a social experiment. “It is not just about feeding datasets into appropriate databases and having them analysed automatically. We want to have archaeologists on board for every dataset,” Dr. Kerig emphasises. Archaeological datasets vary widely, he says, and some are only available in analogue form. “That is why it is important to involve colleagues who know the underlying excavations or surveys in the analysis. We do not just want to analyse prehistoric networks, but we also want to build scientific networks and link archaeology with data science.”
Call for Collaboration
The authors are already presenting a first result of the project in Antiquity. The Linear Pottery culture is the first farming culture in Central Europe. For a long time, its northwestern characteristics were considered typical for its epoch. However, when considering recent excavations, the network analysis of “Big Exchange” shows that the product mix of the northwestern Linear Pottery is rather a very special case. “We will probably experience even more surprises like this when we systematically analyse the available data,” says Dr. Kerig.
The authors also see their article as a call to colleagues to participate in “Big Exchange” and contribute their own data sets. “The more participation, the better we can understand past relationship and network dynamics,” concludes Tim Kerig.