Archaeologists at Oxford uncover a perfectly preserved medieval reading stone alongside ancient halls, manuscripts, and artifacts that shed new light on centuries of scholarship.
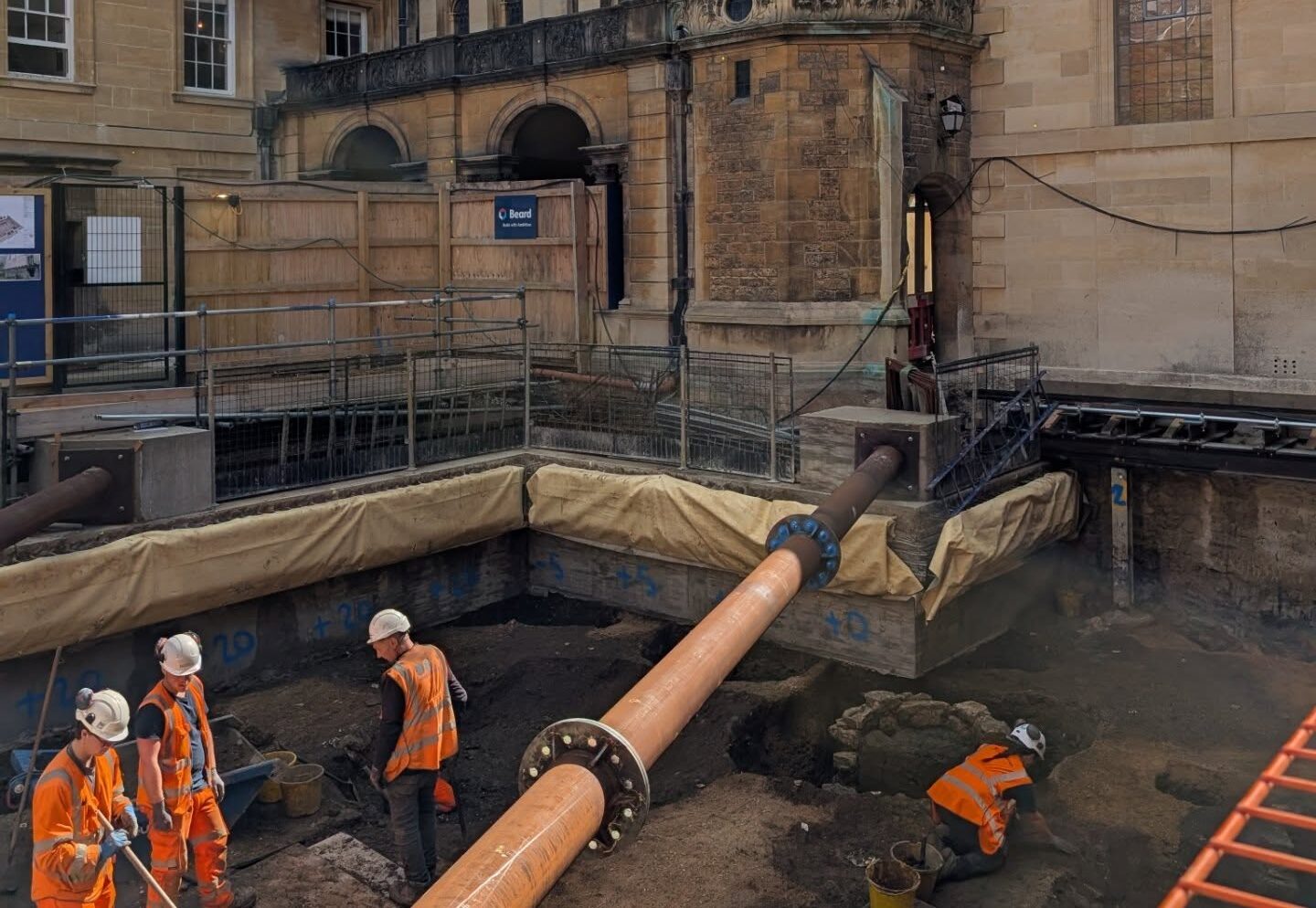
Archaeologists at Oxford University have unearthed a rare and perfectly preserved medieval reading stone, offering a striking glimpse into the intellectual life of scholars who studied at the institution more than seven centuries ago. The discovery was made during an extensive archaeological excavation beneath Hertford College, one of Oxford’s constituent colleges, where construction for a new library is currently underway.
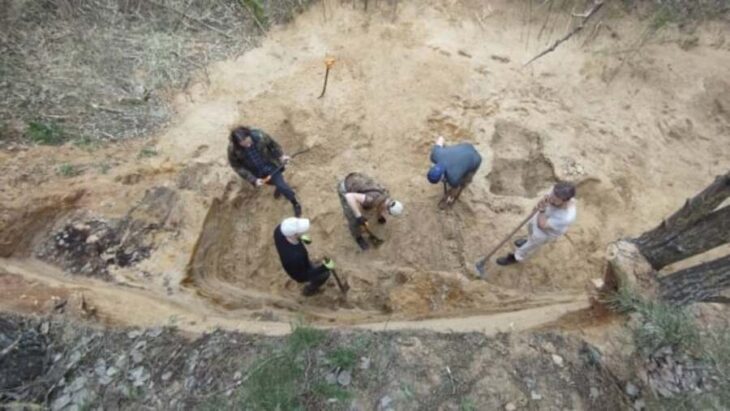
The excavation, led by Oxford Archaeology since 2024, revealed remnants of three early academic halls — Hart Hall, Black Hall, and Catte Hall — dating back to the 13th century. Among the collection of medieval artifacts recovered from the site, including book clasps, styli, animal bones, and trade tokens, the most remarkable find was the reading stone, an object once essential for the careful study of illuminated manuscripts.

A Window Into Medieval Study
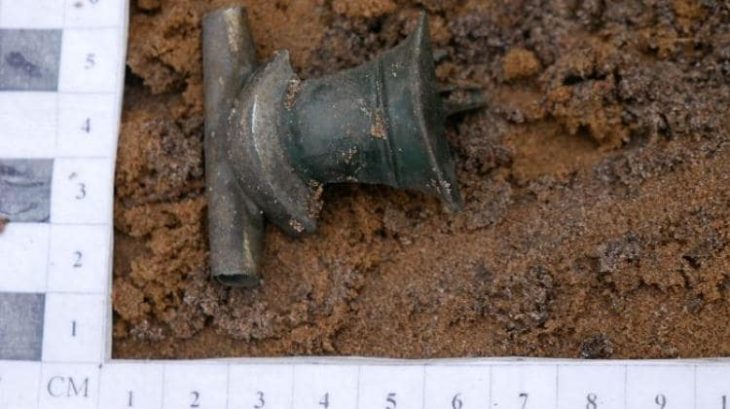
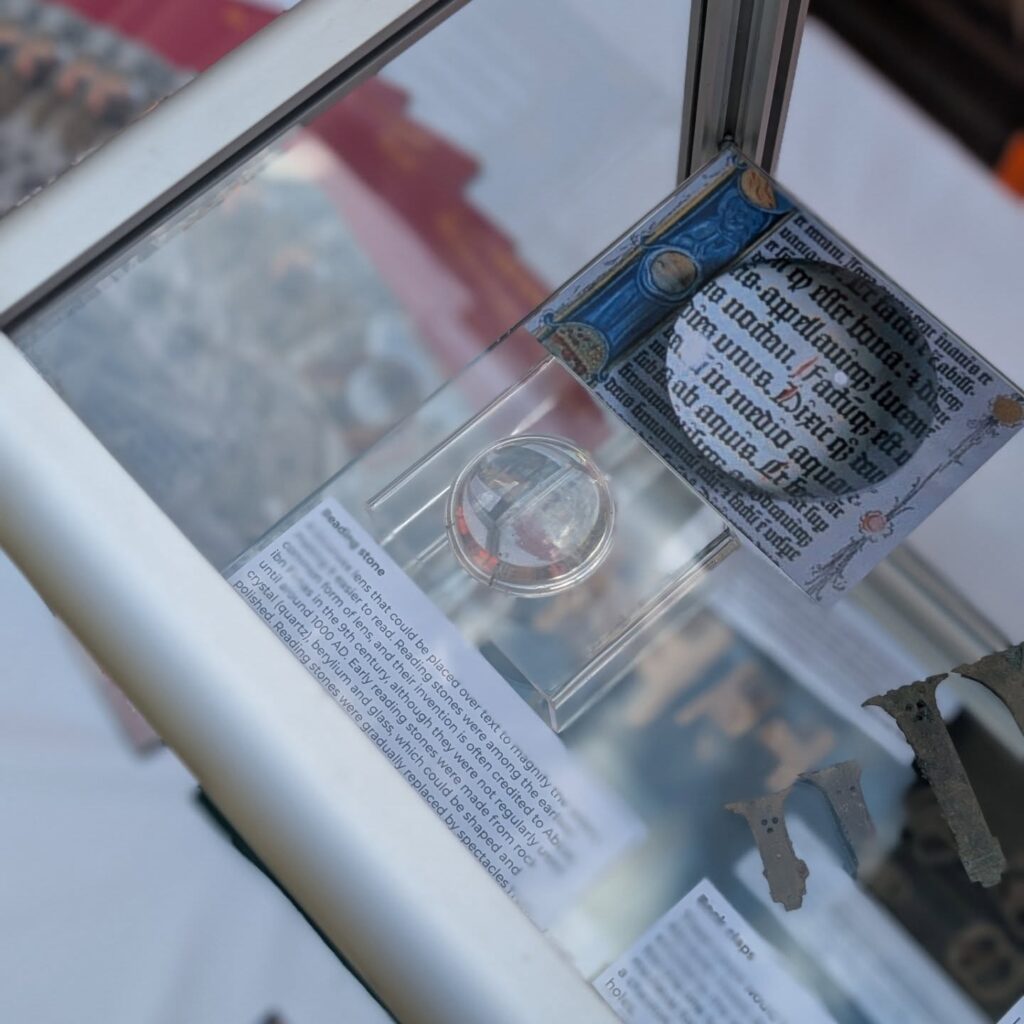
The reading stone, likely made from rock crystal or glass, functioned as an early magnifying lens. Medieval scholars would place it directly over handwritten texts to enlarge the script and ease the strain of long hours spent reading by candlelight. According to Ben Ford, Senior Project Manager at Oxford Archaeology, the stone is “an exceptional find — not only because it is so intact, but because, unlike many archaeological artifacts, it can still be used for the purpose for which it was made.”
Ford added that the discovery is “particularly fitting” given that it emerged during the creation of a new library — a modern space rising above centuries-old evidence of book-making and scholarly pursuits. “The continuity between the medieval and modern traditions of study at Oxford is truly remarkable,” he said.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Unearthing Oxford’s Hidden Academic Past
Excavations beneath Hertford College have exposed not only architectural remnants of Oxford’s early halls but also the material culture of student life spanning from the Norman Conquest (1066) through the 19th century. Archaeologists identified refuse pits filled with animal bones, oyster shells, and fish remains imported from London’s River Thames, some 50 miles away — suggesting a surprising degree of trade and connection between Oxford and the capital.
Other finds included medieval coins, trade tokens, combs, buckles, and even wooden bowling balls, hinting at recreational activities enjoyed by scholars of the era. Yet none captured public imagination quite like the reading stone, which remains fully functional despite centuries underground.

Bridging Past and Present Scholarship
Historians note that reading stones represent a pivotal moment in the evolution of reading technologies, predating the invention of spectacles by several centuries. Their use was common among monks, scribes, and university scholars who painstakingly copied and studied religious and philosophical texts. The Oxford specimen, preserved in extraordinary condition, provides rare physical evidence of academic life in a period when education was reserved for a privileged few.
“The reading stone connects us directly to the minds and hands of medieval scholars,” said Dr. Eleanor Markham, a historian of medieval education not involved with the excavation. “It embodies the transition from oral learning to textual scholarship — a fundamental shift that shaped modern academia.”
Oxford’s Continuing Legacy of Discovery
The Hertford College excavation is one of several high-profile archaeological projects in the United Kingdom this year. As the new library rises above the ancient halls, university officials plan to display selected artifacts — including the reading stone — in a forthcoming public exhibition celebrating Oxford’s academic heritage.
From its medieval origins to its present role as a global research powerhouse, Oxford University continues to bridge past and present. And now, thanks to the light refracted through a crystal lens once held by a 13th-century scholar, the story of learning itself has come sharply back into focus.
Cover Image Credit: Hertford College via Facebook