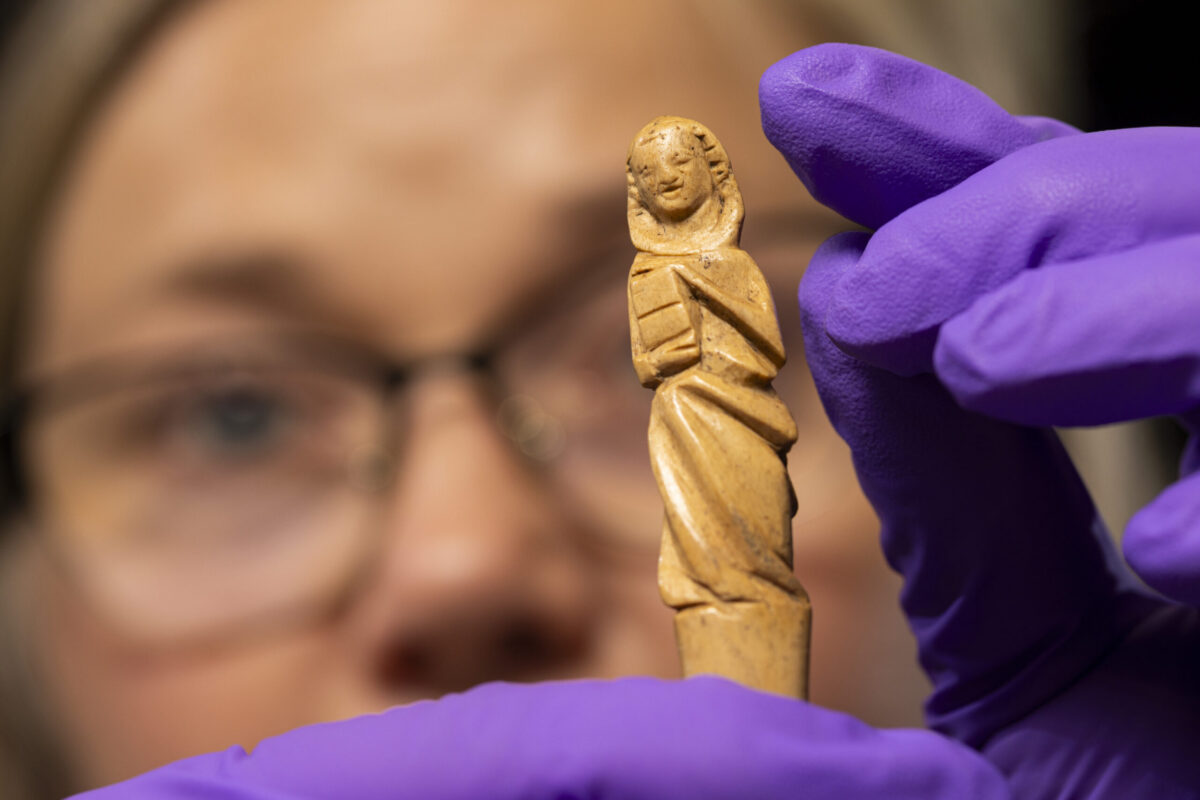
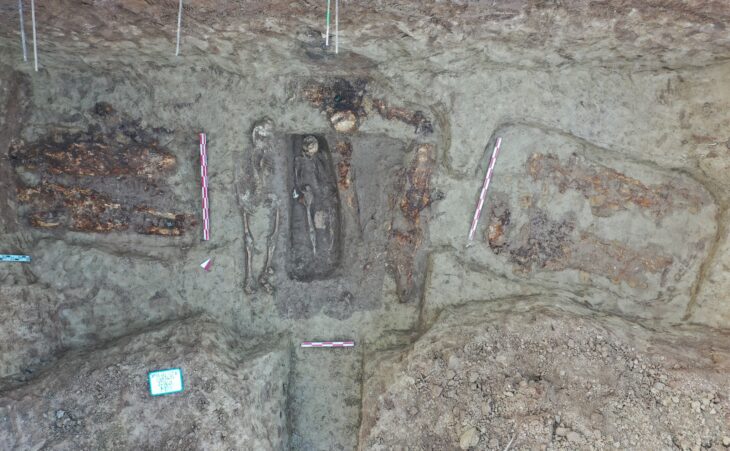
A rare medieval hair-styling implement has been uncovered during excavations at Eilean Donan Castle in the Scottish Highlands, offering an unprecedented glimpse into grooming practices and daily life in one of Scotland’s most iconic fortresses. The artifact, known as a gravoir, has now been acquired by National Museums Scotland, joining what experts describe as one of the most important collections of medieval material culture in the United Kingdom.
A Unique Discovery in the Highlands
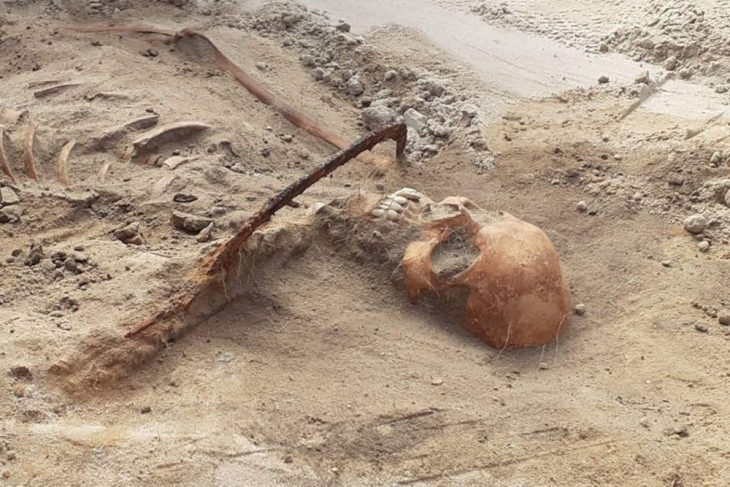
The gravoir, dated to the 13th century, was unearthed during excavations led by FAS Heritage. Although the castle is one of Scotland’s most photographed landmarks—featured in films such as Highlander and The World Is Not Enough—its medieval heyday has long remained poorly understood. The discovery of the gravoir, alongside hundreds of other artifacts, now paints a vivid picture of life within the fortress when it was a hub of Highland Gaelic lordship.
What makes the find exceptional is both its rarity and its craftsmanship. Only two other examples of gravoirs are known in the UK, and this is the first to be found in Scotland. Typically carved from imported ivory, the Eilean Donan piece was instead fashioned from local red deer antler. It features an incised figure wearing a hood and holding a book—imagery associated with continental fashions of the medieval elite.
Dr. Alice Blackwell, Senior Curator of Medieval Archaeology and History at National Museums Scotland, emphasized the significance:
“This remarkable gravoir shows us how elite inhabitants of Eilean Donan were engaging with fashions on the continent. Yet the assemblage reveals a much broader picture of 13th- and 14th-century life. It allows us to imagine how the full social spectrum of people inside the castle walls spent their days—whether styling their hair, toiling in a smithy, or making toys for children.”
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
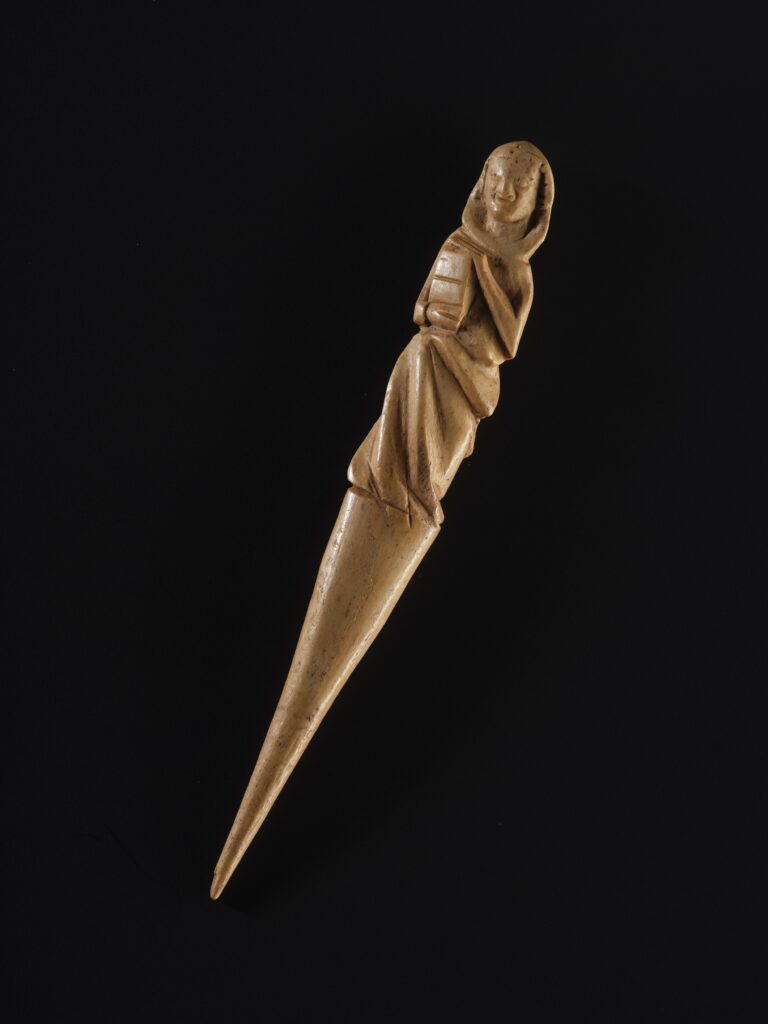

Medieval Life Beyond Politics and War
The acquisition includes a wide array of objects linked not just to warfare and lordship, but to music, craftsmanship, and leisure. Among the 80 boxes of material transferred to the National Museums Collection Centre in Edinburgh are brooches, dress pins, and crucibles used for melting copper alloys, silver, and gold. Residues of precious metals within the crucibles indicate that jewelry and dress fittings were produced on site, highlighting the castle’s role as a center of skilled metalworking.
The collection also sheds light on entertainment and everyday diversions. Archaeologists recovered bone game pieces, some carved from recycled pottery, as well as an iron jaw harp—a small instrument held in the mouth and plucked to create a distinctive twanging sound. Children may have played with so-called “buzz bones,” animal bones drilled with holes and spun on leather thongs to produce a buzzing noise. Together, these finds illustrate how both adults and children within the castle walls enjoyed leisure activities alongside their daily responsibilities.
A Strategic and Symbolic Stronghold
Eilean Donan Castle occupies a dramatic position where three sea lochs—Loch Duich, Loch Long, and Loch Alsh—converge, making it a vital stronghold in medieval Scotland. During the 13th and 14th centuries, it stood at the gateway to the Isle of Skye and became a seat of Gaelic power.
However, its prominence declined after the 15th century. By 1650, records described the castle as poorly maintained, and by 1714 it was roofless and derelict. In 1719, Jacobite forces briefly used Eilean Donan as a supply base, but it was bombarded and destroyed by British warships. The site remained a ruin until the early 20th century, when a restoration project transformed it into the romantic landmark familiar to today’s visitors.
Miranda van Lynden, Head Trustee at The Conchra Charitable Trust, which owns Eilean Donan, explained:
“Eilean Donan represents the very essence of a Scottish castle and its image is recognised around the world. However, we knew surprisingly little about life here at the height of its power. These excavations have revealed stories that connect the site to a much broader cultural and social history.”
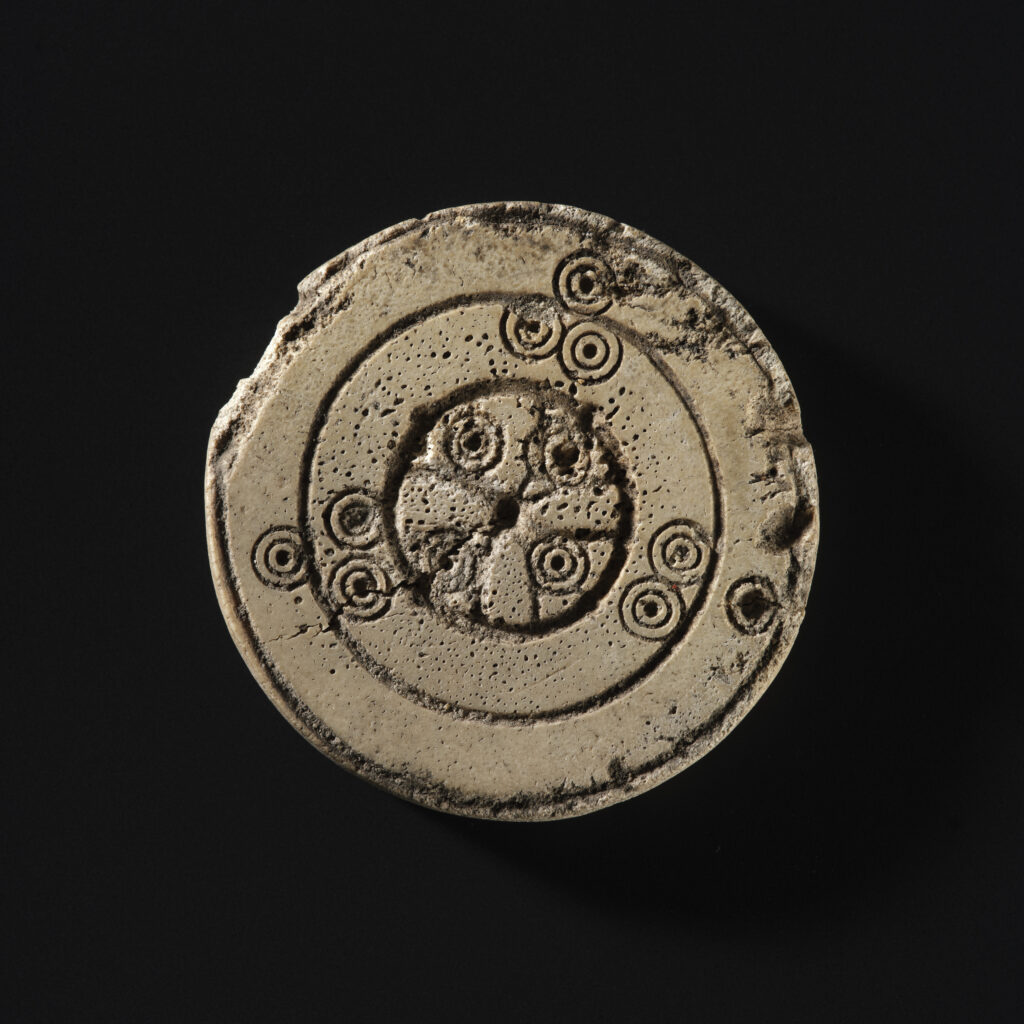

A Window into Medieval Scotland
The Eilean Donan assemblage is not only a treasure trove for researchers but also a reminder that castles were more than just military bastions. They were vibrant communities where politics intersected with culture, craftsmanship, and domestic life. The discovery of the gravoir highlights how even remote Highland lordships were connected to wider European fashions and trends.
For archaeologists and historians, the collection now housed in Edinburgh will provide years of research potential, from studying medieval metallurgy to reconstructing the social fabric of castle life. For the public, it enriches the story of a monument already famous for its picturesque silhouette and cinematic appearances, anchoring its romantic image in tangible human history.
As Dr. Blackwell noted, these finds allow us to see beyond the battlements:
“It’s a privileged glimpse into life in medieval Scotland that we don’t often get.”
Cover Image Credit: Dr Alice Blackwell with the gravoir. Duncan McGlynn – National Museums Scotland