One of, the world’s oldest and largest library, the other was born 100 years later as a rival to it. The interesting existence of these two unique libraries and the culture wars between them.
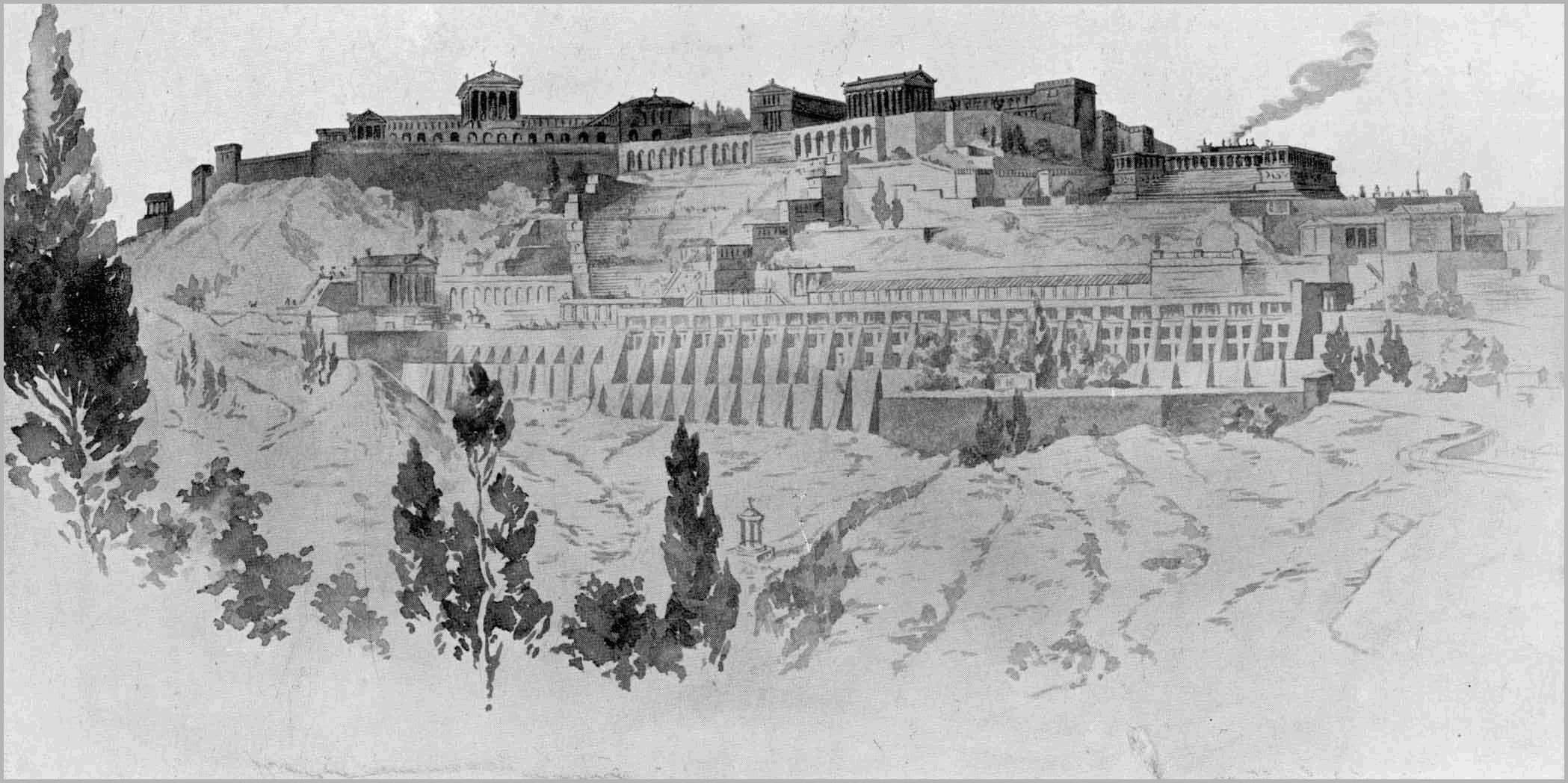
The Library of Alexandria was a library with the largest collection of Antiquity with 900,000 manuscripts. BC. 3 It was founded by the Ptolemaic dynasty in the Egyptian city of Alexandria at the beginning of the century. It was built as part of the research institute known as the Alexandria Museum.
It is one of the most important works created in human history. As it is known, Alexander the Great founded the city of Alexandria. After the death of Alexander, Ptolemy I, son of Lagus, one of their commanders, declared his kingdom in Egypt.
The capital of this new state was the city of Alexandria, and the new king would completely repair and develop this city and make it the most famous capital of the period. Unlike other kings, Ptolemy he had wanted to live in peace rather than expand his country’s borders. He was fond of art and science.
The most important work he created in Alexandria was the museum and the library attached to the museum. A beautiful place, especially around the palace, was chosen for its establishment. In the museum there was a sample of animals and plants in all countries known of that period. There was also a botanical garden and an observatory. An anatomy hall was opened to examine the human body through autopsy. On this science site, houses were built for physics, chemistry, medicine, astronomy, mathematics, philosophy, literature, and physiology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Undoubtedly, the most important part of the museum was its library. The director of the library was authorized to receive any written work he could find. Every book that came to Egypt would definitely be brought to the library. Here, a copy is made and the copy was given to its owner, and the original book would stay in the library. Officers sent abroad for different books would buy and bring books they found in other countries. Thus, all kinds of works that were scattered and doomed to disappear were gathered in a safe place.
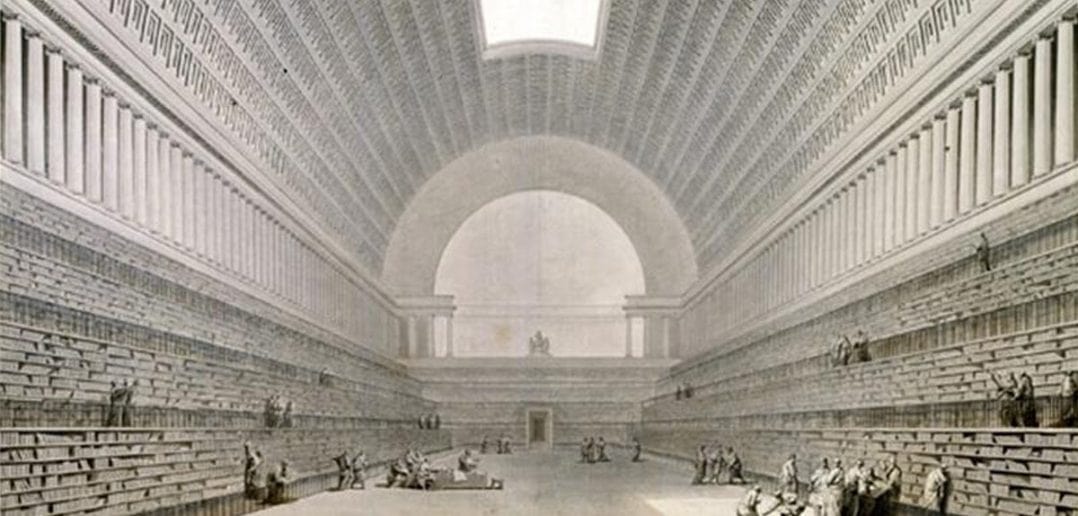
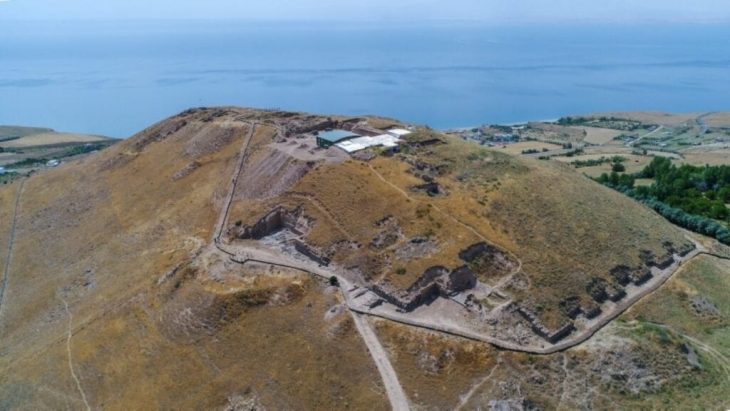
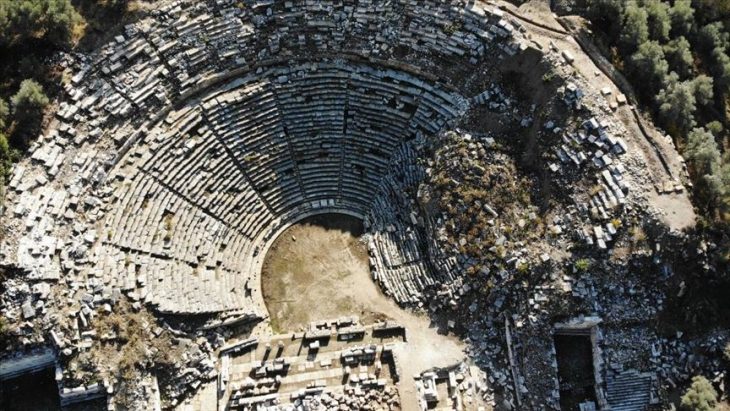
Pergamon Library (Bergama-İzmir) was established almost a hundred years after the library of Alexandria. Pergamon, built by Eumenes II (the end of the 3rd century) and located at the northern end of the Acropolis, has become one of the most important libraries of the ancient world.
It was made by the Attalos dynasty by trying to liken the library of Alexandria. It contained around 200,000 texts written on “Pergaminus” parchments, instead of the Egyptian papyrus used in Alexandria.
The use of parchment caused great jealousy among the Alexandrians, who controlled the Papyrus flow. After all, they were one another’s arch-rivals in the cultural sphere.
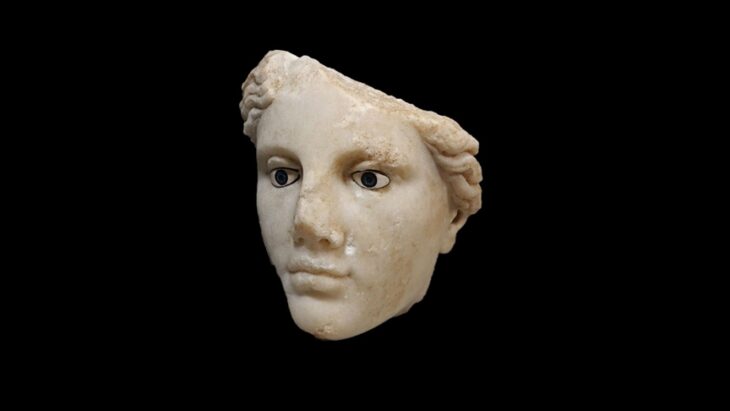
In the library of Alexandria, names such as mathematics scholar Euclides, mechanical scientist Archimedes, medical scientist Heterofilos, astronomer Eratosthenes, Ptolemy worked here. However, the Pergamon library was also invited to the palace by Peripatoscu and Platonist scientists during the time of Pergamon King Attalos I, especially Antigonos of Karystos, Krates of Mallos, historian Cleanthes and the mathematician Apollonios of Perga. Among these summoned people, Krates from Mallos, who is known for making criticisms of Homer’s poems, must have been appointed as the head of the library. As a matter of fact, according to the sources we received information on this subject, Krates established the grammar school in Pergamon and interpreted Homer as allegorically, unlike the one in the Library of Alexandria.

Galenos (AD 130-200) from Pergamon also mentioned that the Library of Alexandria and the Pergamon Library were competing with each other in obtaining manuscripts, and as a result of their behavior, fake manuscripts emerged due to the high demand in the book market.
In fact, this competition between Alexandria and Pergamon Library has reached such an advanced level; An embargo was placed on the papyrus exported from Egypt to Pergamon, and the Kings of Pergamon gave importance to the production of parchment (pergament) in order to provide the necessary writing material by using animal skins.
As a last word, although the winner of this beautiful race is not known, it is obvious that Pergamon was the winner of the parchment paper. Parchment is derived from the Latin Charta Pergamena, meaning Pergamon Paper, and it has passed to all languages from here. But an important issue that needs to be corrected here is that Parchment was actually produced and used in Anatolia before that.
Source: Üreten, H.” Antikçağ Anadolu’sunda Bir Kültür Merkezi Pergamon – Kraliyet- Kütüphanesi” Türk Kütüphaneciliği 22, 4 (2008), s: 435-450
https://tr.wikipedia.org/wiki/%C4%B0skenderiye_K%C3%BCt%C3%BCphanesi