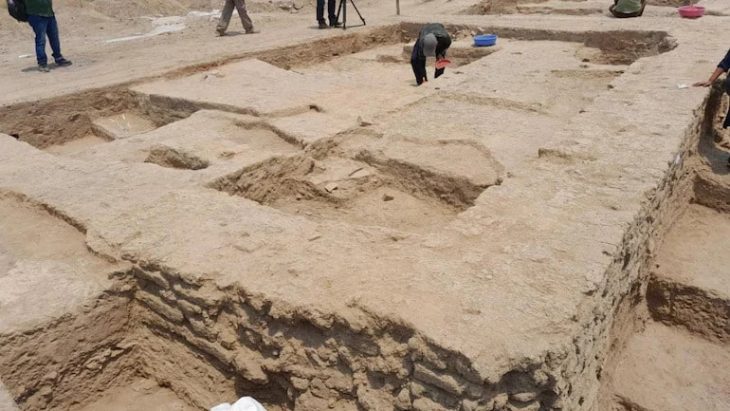
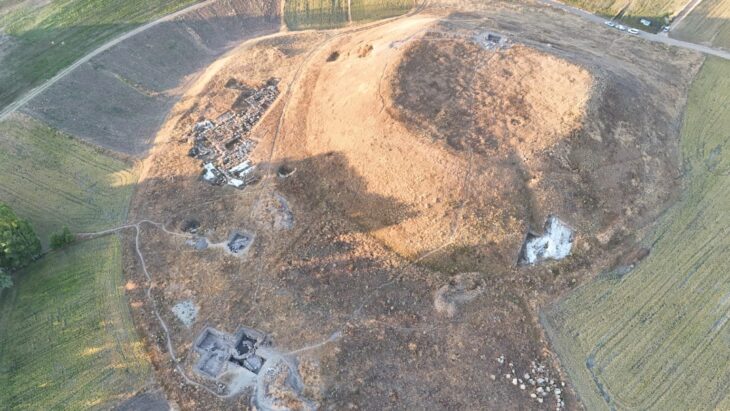
Rescue excavations along the planned D7 highway, between the towns of Knovíz and Slaný, approximately 40 kilometers northwest of Prague, have revealed a wealth of historical treasures spanning several millennia. Archaeologists from the Archaeological Centre Olomouc uncovered a total of 467 objects, ranging from Neolithic settlements to early modern artifacts, reflecting the rich and diverse history of the region. Among these discoveries, the grave of a young woman from the early Iron Age has captured particular attention.
The excavation, conducted along a 6.5-kilometer section of the future highway, identified 15 burial sites, with settlements spanning from the Neolithic period to modern times. “This area offers an extraordinary glimpse into thousands of years of human occupation,” says Michaela Bartoš Dvořáková, an archaeologist at the Archaeological Centre Olomouc.
A Woman of the La Tène Era
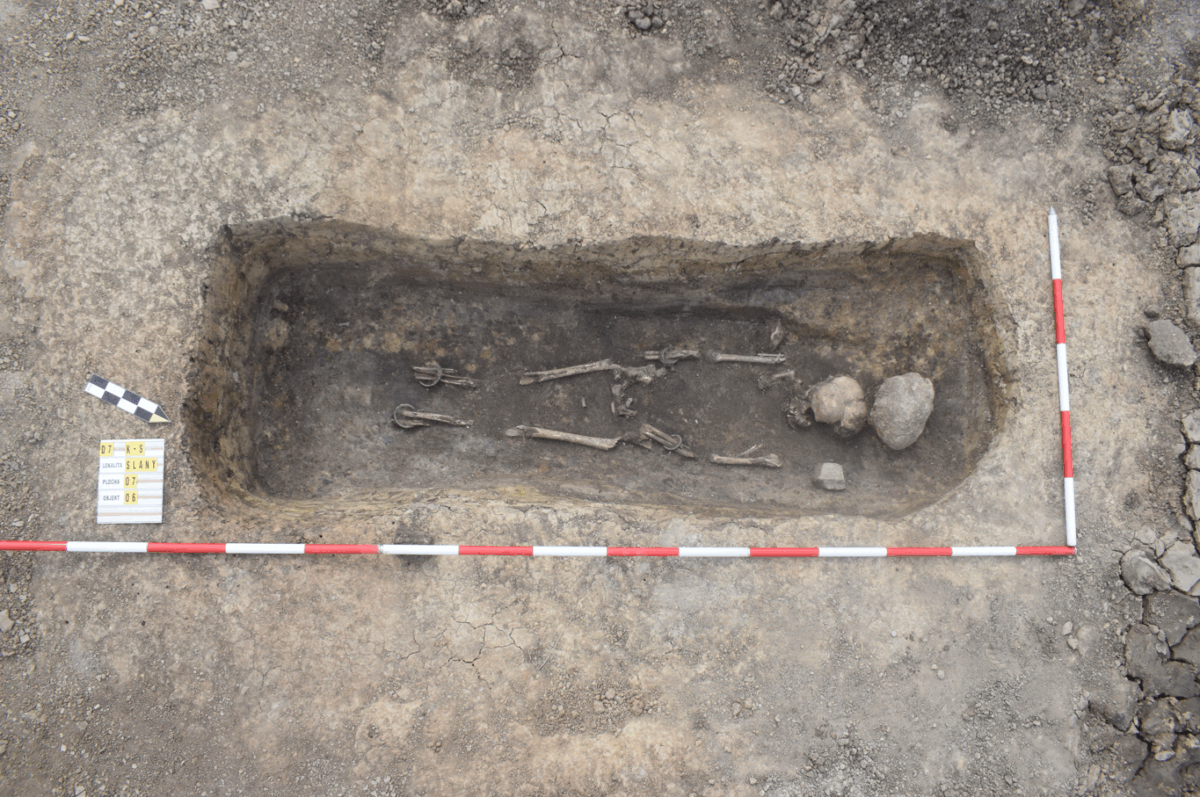
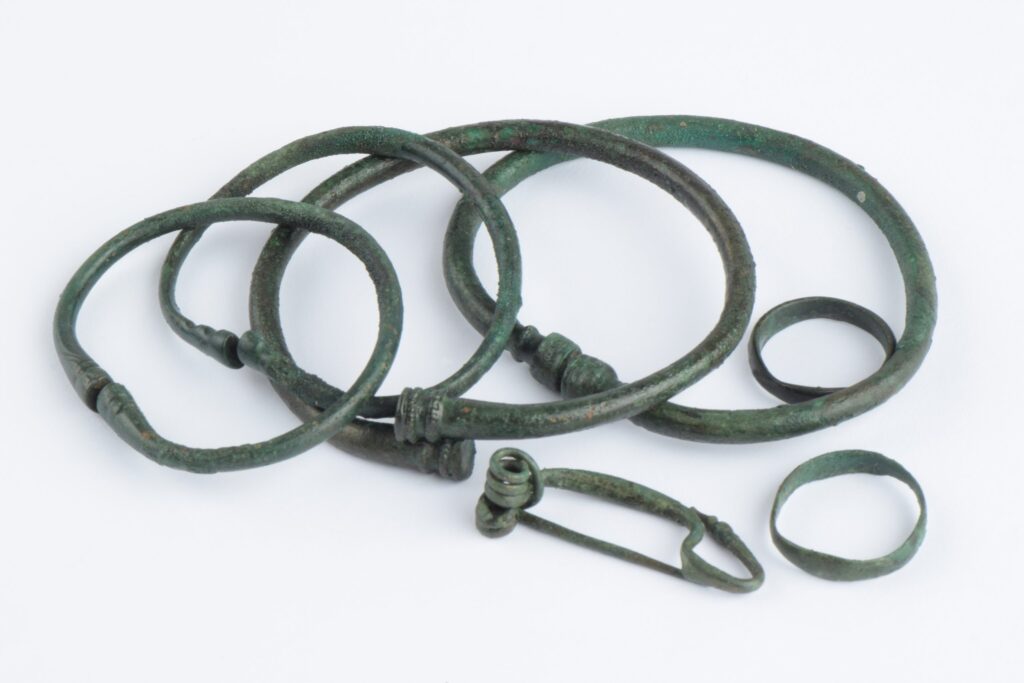
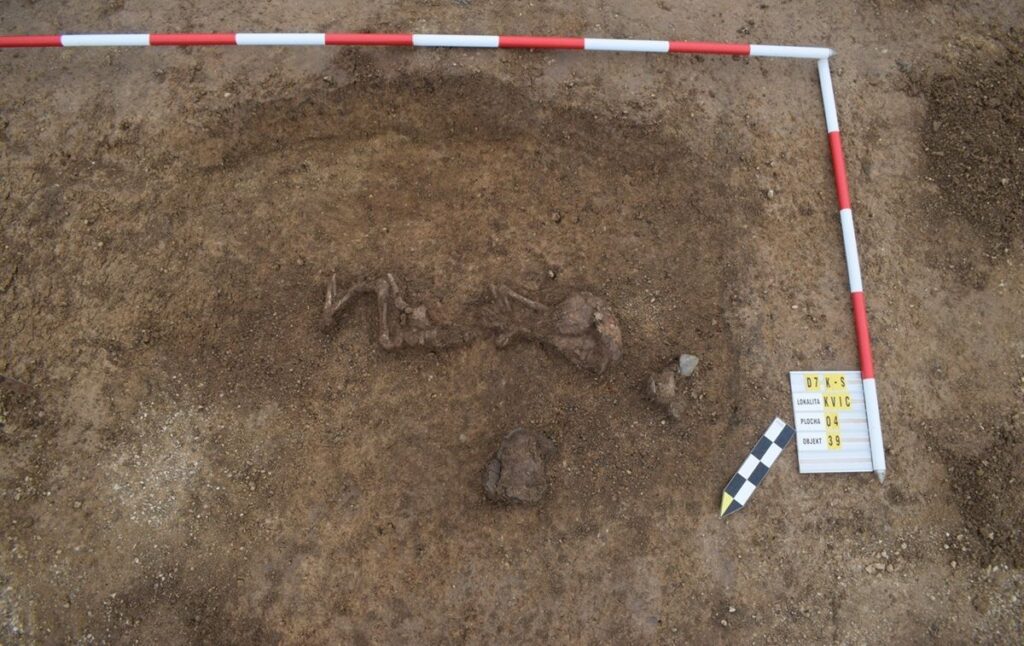
In the vicinity of Slaný, archaeologists uncovered the grave of a woman estimated to be between 20 and 30 years old. She was buried with an impressive collection of bronze jewelry, including a pair of arm and ankle bracelets with seal-like ends, two bronze rings, and a Duchcov-type brooch with a free foot. Each item exhibits unique decorative features, suggesting a highly individualized burial. Based on these artifacts, the grave is preliminarily dated to the mid-4th century BCE, during the La Tène period, a time associated with early Celtic culture in Central Europe.
Specialized analyses are currently underway to shed more light on the life of this woman. Markéta Zahnašová, the archaeologist responsible for the finds, explains, “Using stable strontium isotope analysis, we hope to determine whether she was born locally in the Slaný region or came from elsewhere. Comparing her DNA with other contemporary remains in the area may also reveal familial links and social connections.”

Evidence of Health Challenges
Skeletal analysis indicates that the woman may have suffered from metabolic disorders, with signs of physiological stress and iron deficiency. These findings provide a poignant glimpse into the health conditions faced by Iron Age populations, offering researchers a rare opportunity to study ancient disease patterns and their social implications.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Complementary Discoveries
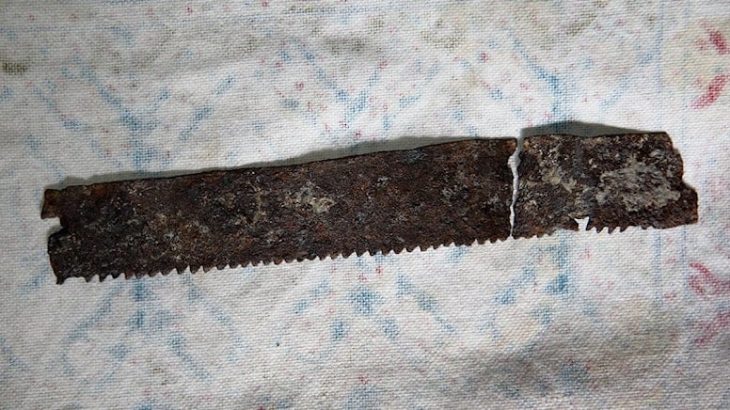
Alongside the woman’s grave, archaeologists also uncovered several other intriguing burials. Five graves were attributed to the Corded Ware culture, including two children’s graves containing objects such as a perforated deer tooth amulet and miniature axes, suggesting ritualistic or symbolic burial practices. In one child’s grave, aged three to four years, experts found a tiny axe crafted from a broken larger tool, highlighting the importance of miniature objects in ceremonial contexts.
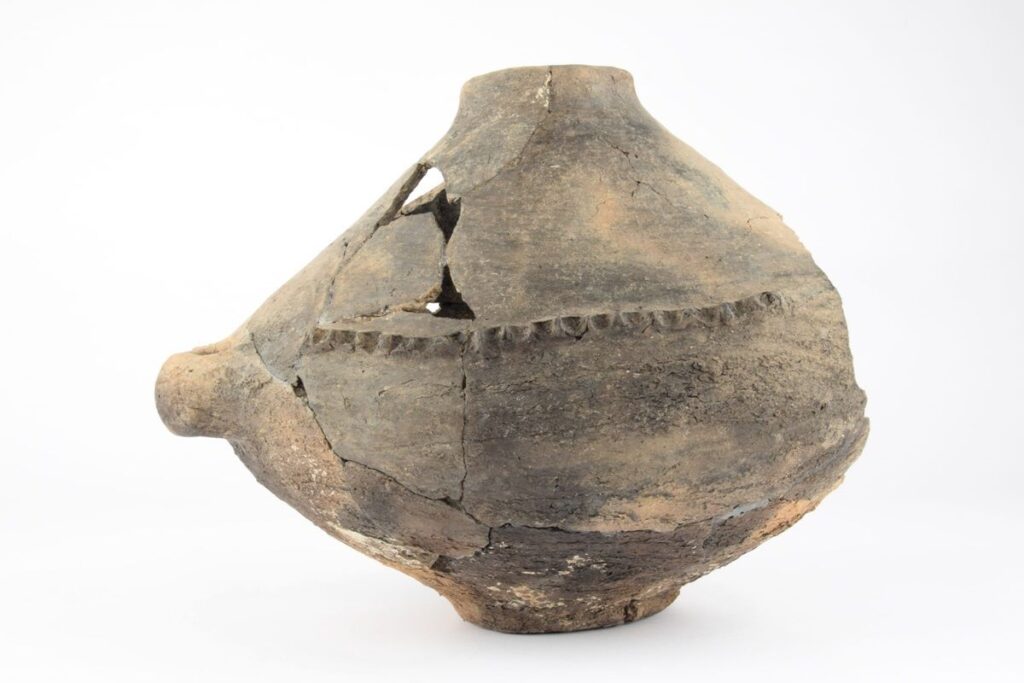
A notable artifact from the nearby village of Kvíc was a thorn-studded ceramic vessel from the Late Bronze Age. Chemical analysis revealed traces of fat and wax, prompting hypotheses that it may have been used for fermenting food or performing other specialized functions.

Broader Context of the Excavation
The excavation also produced early La Tène artifacts, including a bronze belt buckle featuring a snake motif, as well as decorated ceramics from pit-houses. Early medieval settlement and burial activities were also documented, such as ceramic vessels with wave patterns and poorly preserved graves lined with stones.
The ongoing documentation, conservation, and laboratory analyses aim to determine the age, function, and cultural significance of all recovered objects. This meticulous work, involving anthropological, traceological, and phosphatic studies, promises to deepen our understanding of the region’s complex historical tapestry.

Conclusion
The discovery of the young woman’s grave offers a remarkable window into the life and death of individuals in early Iron Age Central Europe. Her richly adorned burial underscores both personal identity and cultural practices of the La Tène period, while ongoing scientific investigations may reveal her origins, health, and familial connections. As archaeologists continue their work along the future D7 route, each artifact, from miniature axes to thorned vessels, contributes to a broader narrative of human activity in the Czech lands spanning thousands of years.
Cover Image Credit: Grave of a woman with bronze jewelry from the La Tène period. Archaeological Centre Olomouc