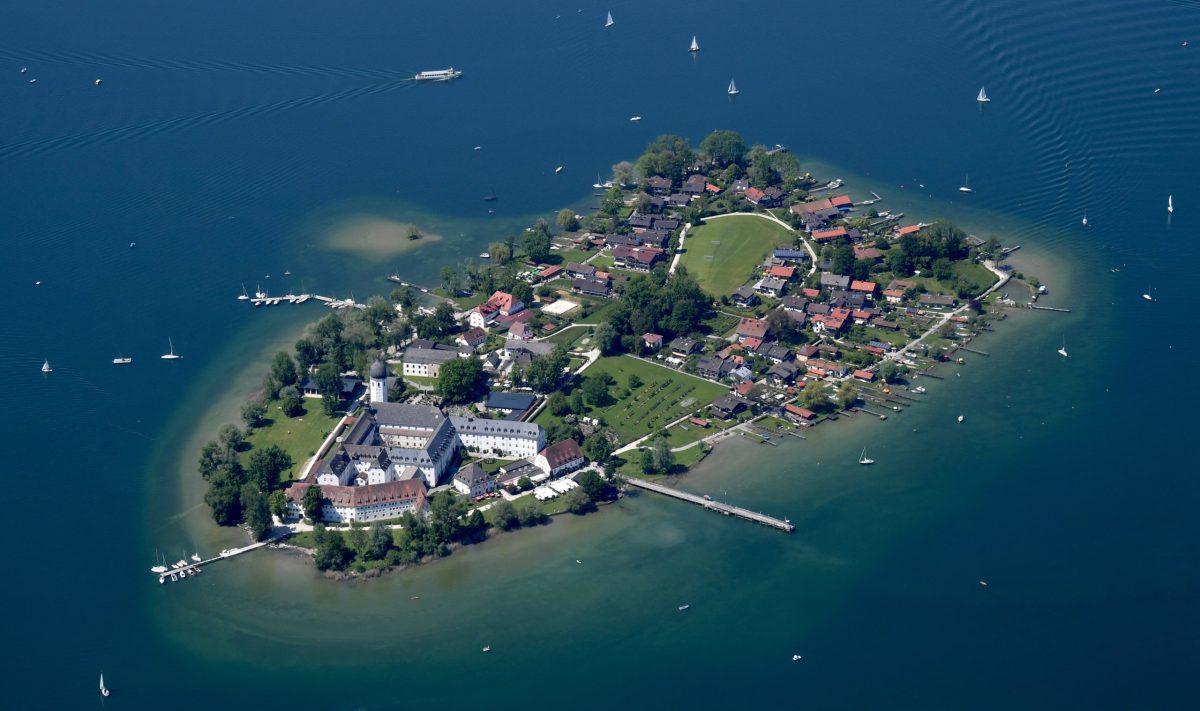
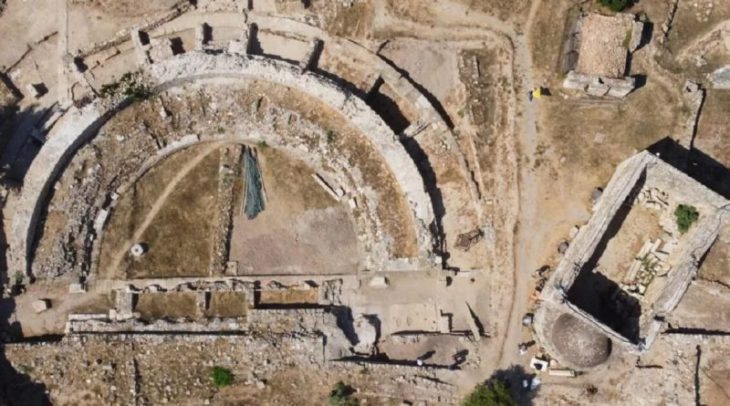
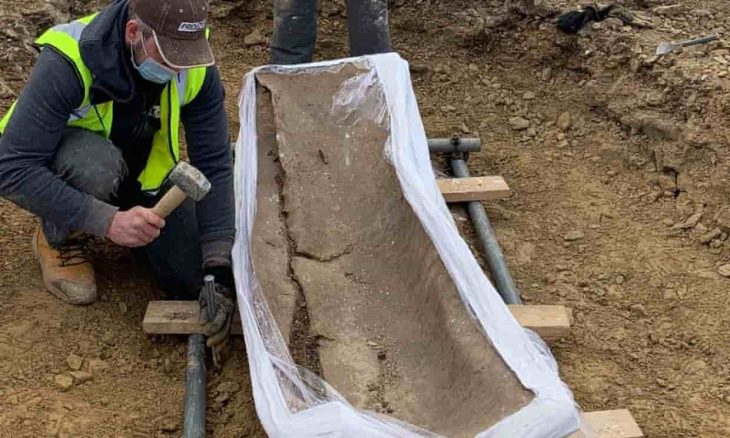
On Fraueninsel, an island in Germany’s Lake Chiemsee, archaeologists discovered a cult site that may have been slumbering underground for 1,000 years while searching for the remains of a 600-year-old church destroyed in the early 1800s.
Fraueninsel Island in Lake Chiemsee is one of the smallest communities in Bavaria and the other two Chiemsee islands Krautinsel and Herrenchiemsee.
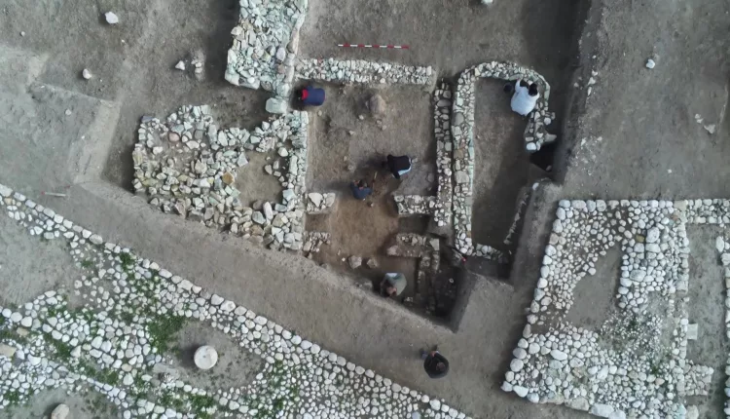
The discovery of the foundation of a 600-year-old church marked and was noteworthy in and of itself. However, when the radar technology descended 20 to 40 inches below this artifact from the Middle Ages, it revealed something even more remarkable. An older, eight-sided Romanesque building stood there, a rare example of Bavarian architecture and a sign of a hugely significant discovery.
Perhaps the history of Frauenwörth Abbey on Fraueninsel in Chiemsee now needs to be rewritten. The building development was probably carried out by Duke Tassilo III. The monastery, founded around 782, is considered well-researched, but relatively little is known about the rest of the island. Until now!
Now, during ground radar measurements, a team from the Bavarian State Office for Monument Preservation (BLfD) unexpectedly came across the foundations of a central building that had not previously been recorded, neither in writings nor on historical maps.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
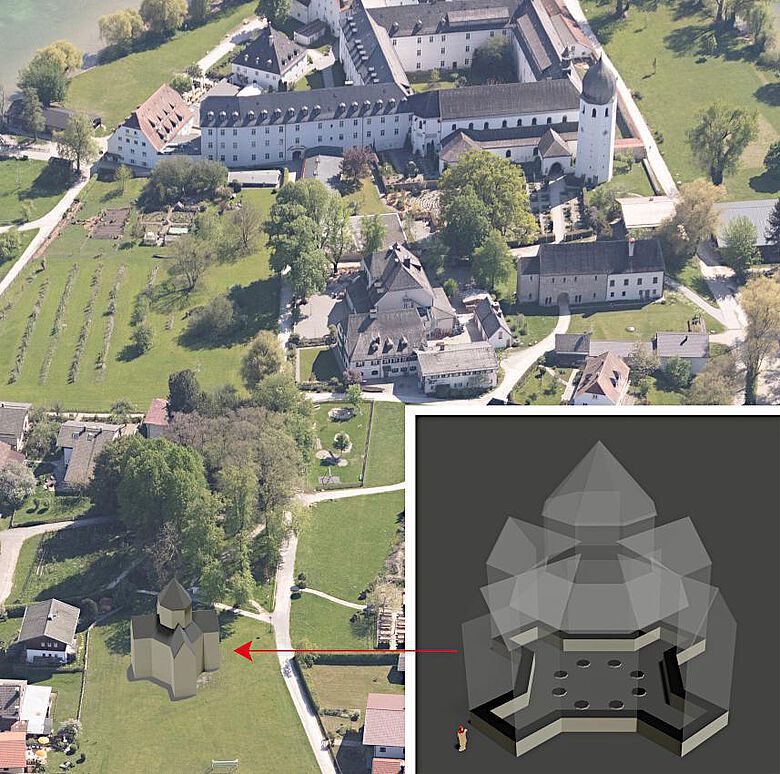
“In the area of the find was the church of St Martin, which belonged to the monastery and was first documented in 1393. It was located on the highest point of the island and was demolished in 1803 in the course of secularisation. But the fact that there was an older predecessor building is also a big surprise for us,” said Armin Krämmer, mayor of the municipality of Chiemsee.
To pinpoint the exact location of the demolished hall church, measurements were taken on the village green north of the well-known Tassilo lime tree in the summer of 2023 as part of investigations for a municipal monument concept (KDK). At a depth of 50 to 70 centimeters, the monument conservators came across foundations whose ground plan corresponds to the view of the church on the engraving by Michael Wening published in 1701.
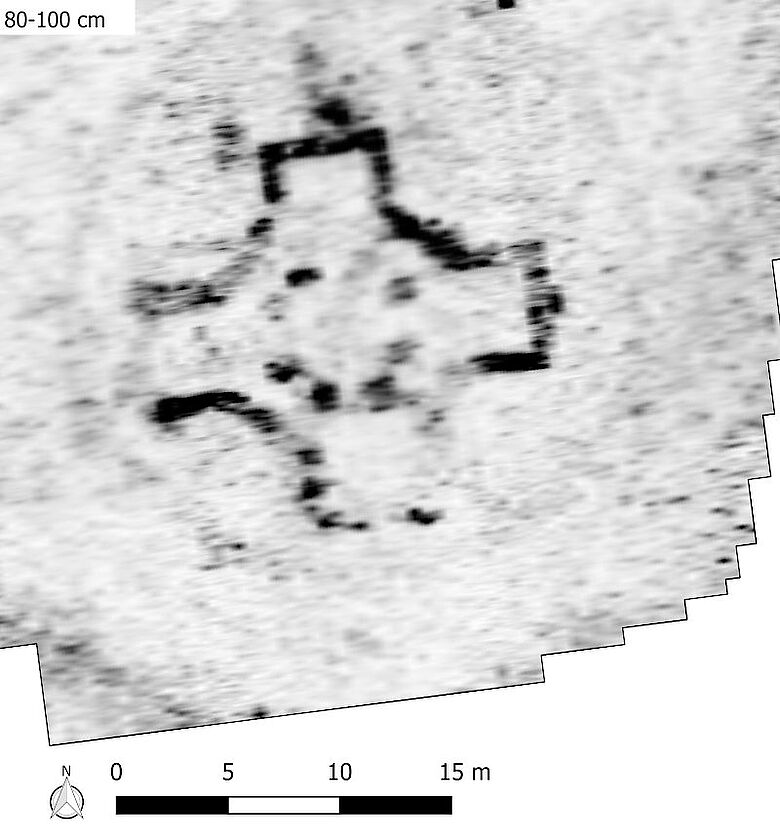
However, the radar data also showed that there had been an older building on this site: At a depth of 80 to 100 centimeters, further foundation walls emerged completely unexpectedly but very clearly, revealing an octagonal central building with a gallery formed by eight pillars and four annexes arranged in a cross shape. Overall, the building has an impressive diameter of 19 meters.
“Central buildings are rare in pre-Romanesque and Romanesque sacred architecture north of the Alps and are therefore a very individualized form of construction, which is often interpreted as a successor to the Palatine Chapel in Aachen or as an imitation of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem. In Bavaria, octagonal central buildings with an inner portico have so far only been archaeologically proven with St. Andreas in Bamberg, around 1050, and St. Gallus in Würzburg, around 1130. So we are talking about an absolute rarity here,” says Mathias Pfeil, General Conservator, Bavarian State Office for the Preservation of Monuments.
But how can this find be categorized historically? There may be a connection with the veneration of Blessed Irmengard, daughter of King Louis the German and great-granddaughter of Charlemagne. She was abbess of the Frauenwörth convent, which had risen to become an imperial monastery, and was buried in the abbey church in 866. Between 1001 and 1020, her tomb was opened for the removal of relics to promote her veneration. At the same time, a fundamentally new monastery building was erected, of which the gate hall, the early Romanesque abbey church and the bell tower are still preserved today.
The additional memorial building, which was intended to serve as a destination for pilgrims in the style of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre in Jerusalem, was perhaps built in this context. It is now up to scientists to evaluate and carefully analyze the latest data to provide answers to the many unanswered questions. The idea of visualizing the ground plan next summer in the form of a planting and thus making it possible to experience it is currently being considered.
“Bavaria’s rich cultural heritage is always good for a surprise – as the sensational discovery in Chiemgau proves once again! The foundation walls discovered during radar measurements on the Fraueninsel show that nothing really escapes the expert eyes of our monument conservators. Such a ground plan of a Romanesque central building is an absolute rarity north of the Alps. It therefore remains exciting to see how scientists will classify this find historically,” emphasizes Bavaria’s Art Minister Markus Blume (CSU).
















