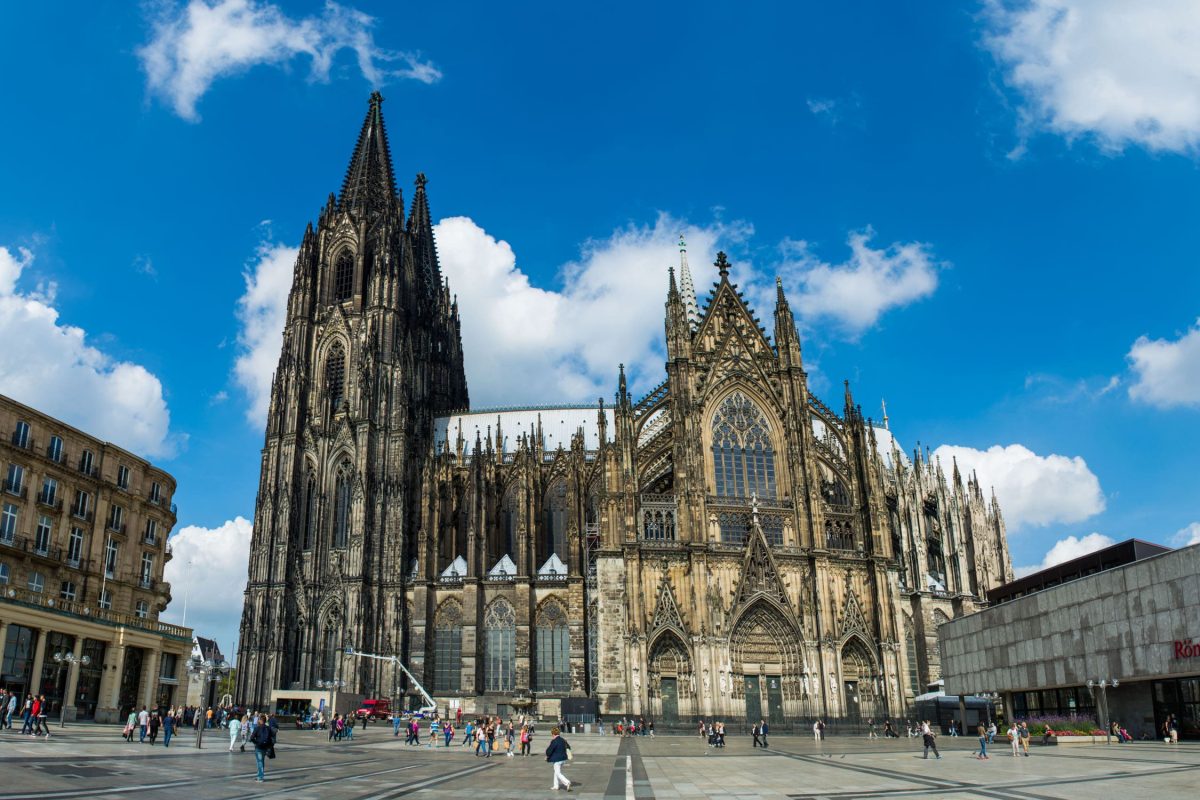
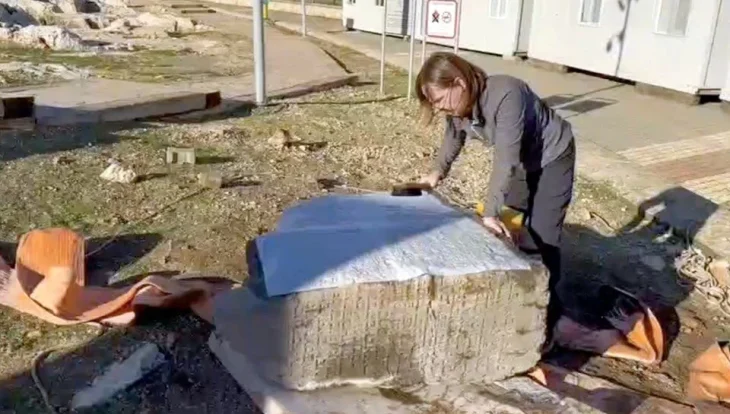
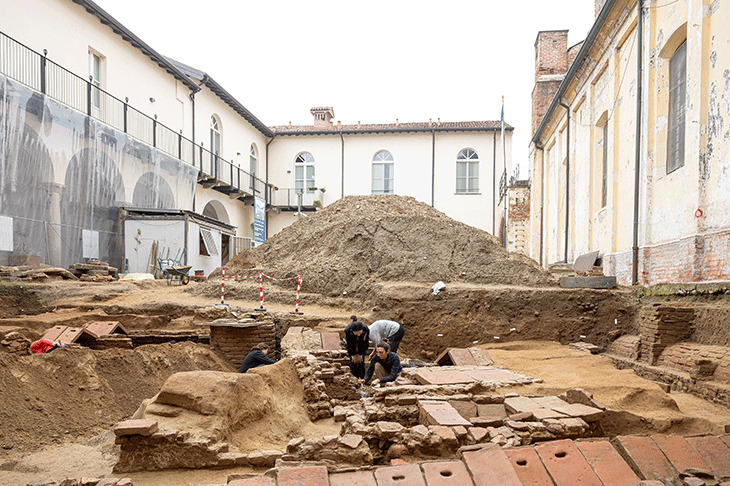
An area of around 4,000 square meters (43,055 square feet) is being discovered beneath the Cologne Cathedral, the largest Gothic church in northern Europe.
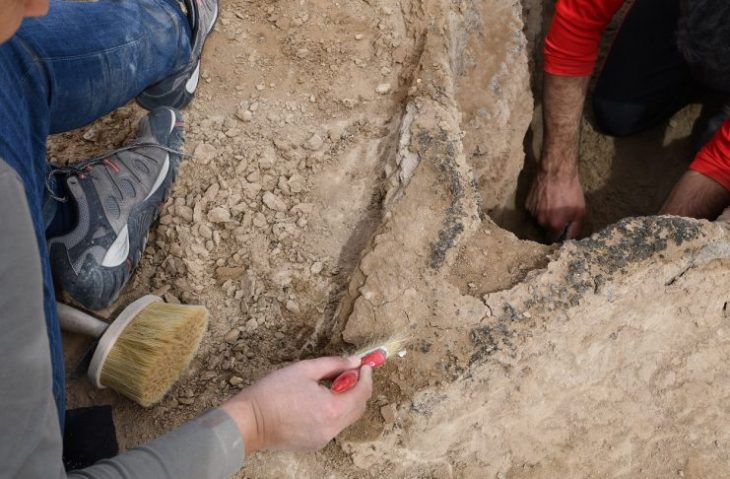
Excavations under the monumental building began in 1946. Since then, the abundance of finds has grown into a sea of contemporary evidence.
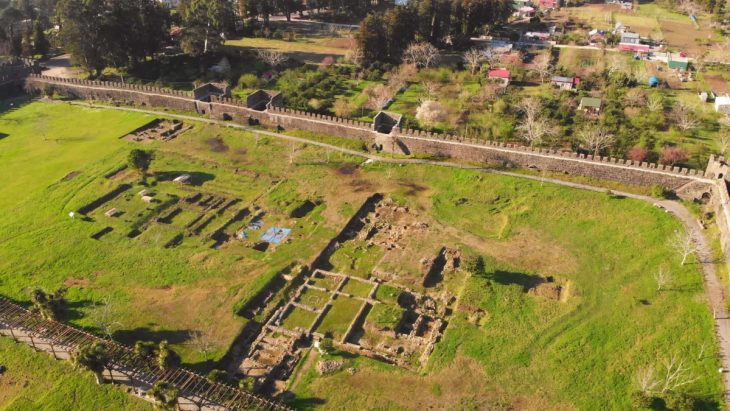
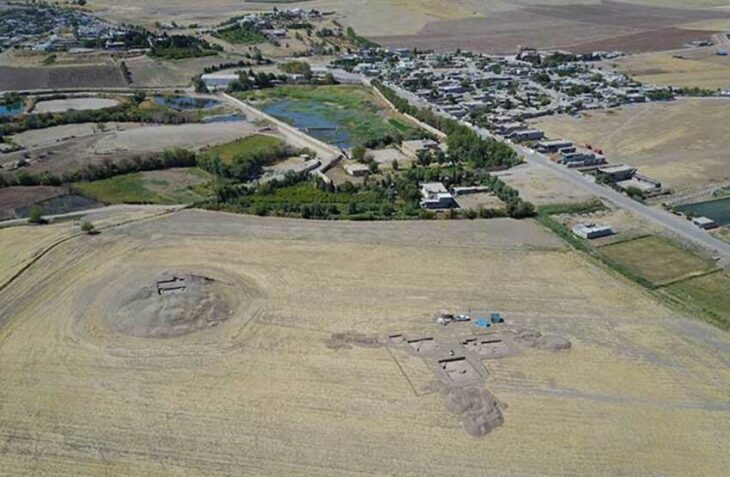
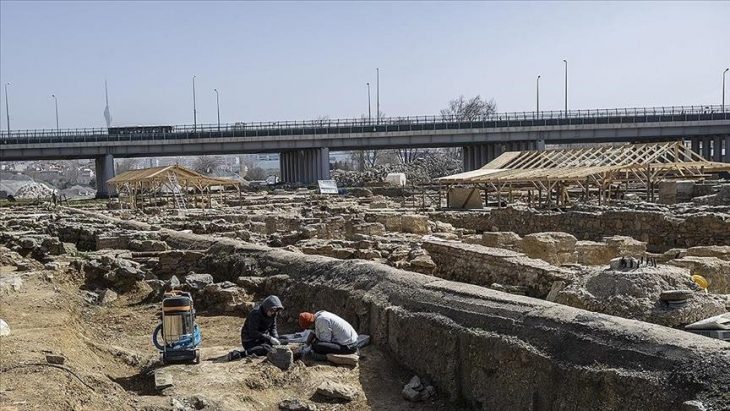
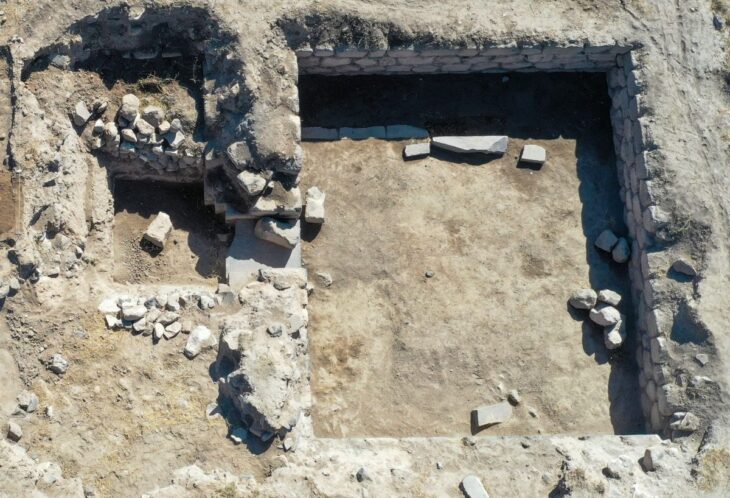
The first archaeological excavations inside the cathedral began under the direction of Otto Doppelfeld. They were continued over decades and continue in individual projects to this day. As a result of this work, rooms were created below the cathedral, which now extend under almost all areas of the current church floor and cover an area of around 4,000 square meters. This means that the Cologne Cathedral excavation is not only one of the most extensive church excavations in Germany, but it can also be visited on guided tours.
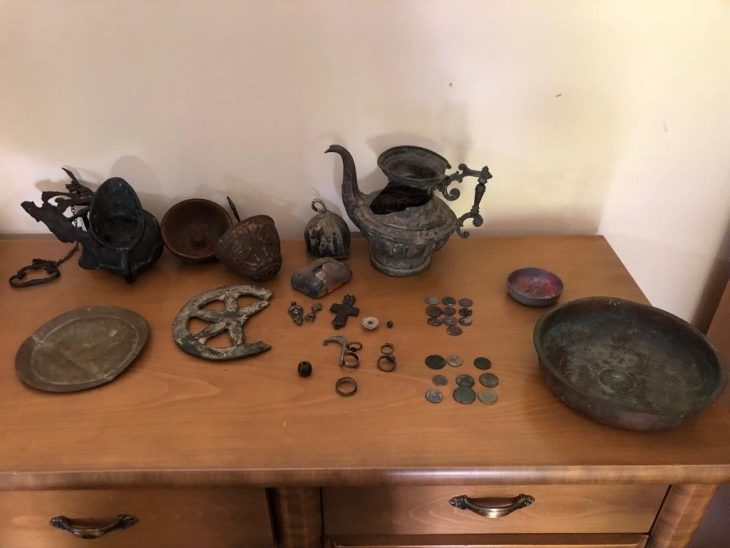
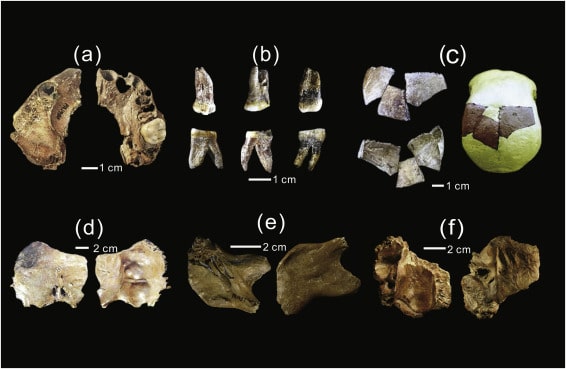
In the course of the archaeological investigations, floor plans and internal structures of various older buildings were uncovered, among which not only the Old Cathedral, which has also been handed down historically but also other previous buildings deserve special mention. Together with numerous architectural remains and an immense number of archaeological finds, around 260,000, they testify to the development from an upscale Roman city quarter to the Christian center of Cologne and, with a view of the huge foundations of the Gothic cathedral, also provide an impression of the effort and process of its creation.
“We’ve uncovered a huge area here and worked our way back to the ancient Roman period,” says archaeologist Ruth Stinnesbeck, with an area of around 4,000 square meters (43,055 square feet) under the famous church being explored.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

Originally, the current archaeology team wanted to learn more about an older cathedral building from the 8th and 9th centuries that no longer existed. Historical records told them it had once stood in that exact spot—and had an important significance. Charlemagne, the Frankish king who later became Holy Roman Emperor, appointed his close friend and advisor Hildebold as the first archbishop of Cologne around 795. To commemorate the appointment, he constructed a Romanesque-style cathedral on the site of a baptistery that had already existed for two centuries.
Although it was nowhere near the size of the Cologne Cathedral, which is one of the largest churches in the world, the former building was by no means small, confirms Stinnesbeck. “It was almost 100 meters (328 ft) long, which was very significant 1,200 years ago — that’s two-thirds the size of today’s cathedral,” she says.
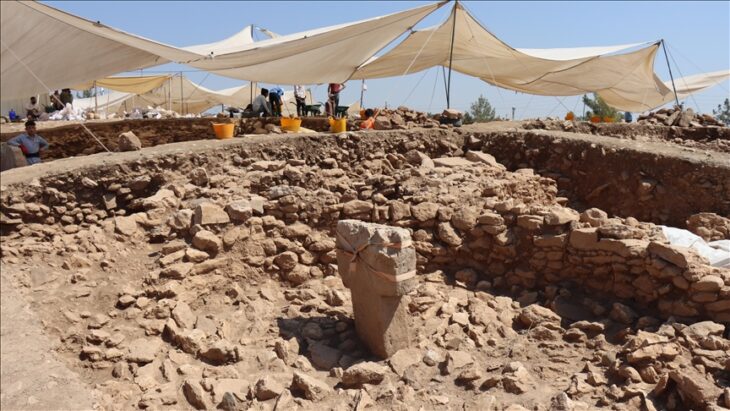
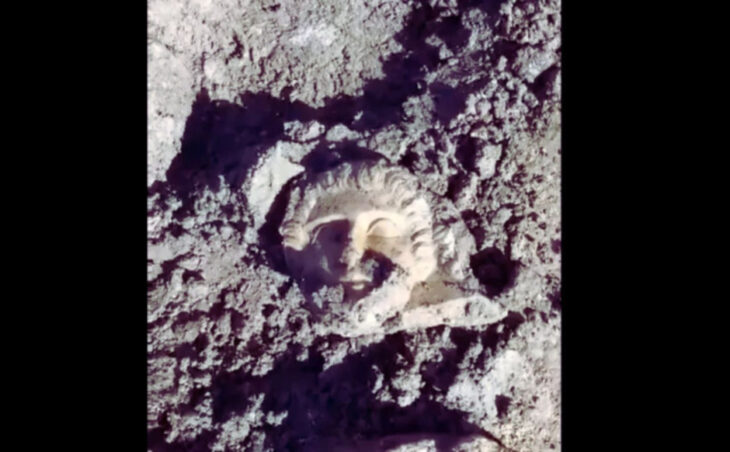
Archaeologists discovered not only Hildebold’s building, but also much older historical finds from Roman times. Cologne’s Roman period lasted from the first century BC to the mid-5th century AD, or approximately 500 years. Originally, present-day Cologne was just a Roman colony for wealthy families in the Rhineland called Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium. The remains of their luxurious villas, including murals and traces of an underfloor heating system, are currently being excavated beneath the cathedral.
The city was taken by the Ripuarian Franks in 462 AD, and the name Colonia Claudia Ara Agrippinensium was lost. Coarse stones from Roman times were used to support the foundations of the 9th-century Hildebold Cathedral.
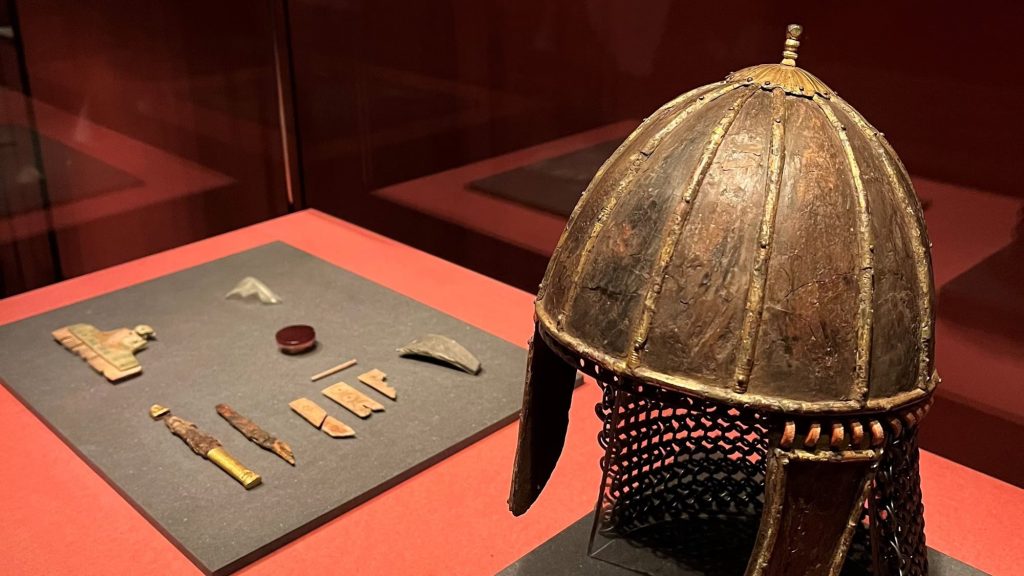

As a result, visitors can now climb the south tower of the cathedral and take a peek at the ongoing excavation. The exhibition in the Cologne Cathedral Treasury presents for the first time a selection of characteristic exhibits from the various eras of the cathedral’s history, right up to the early days of the Christian community and back to Roman times.
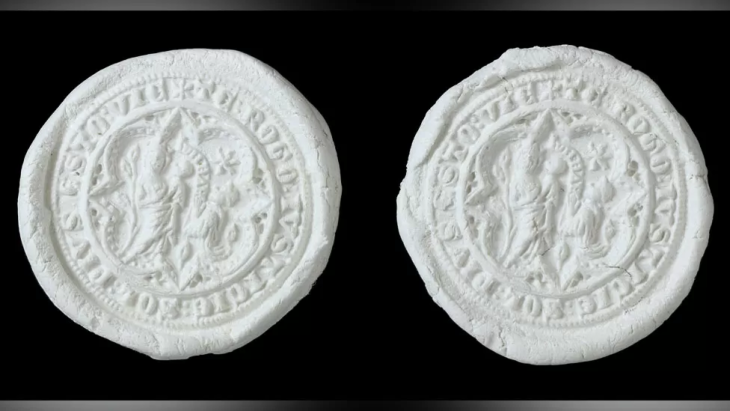
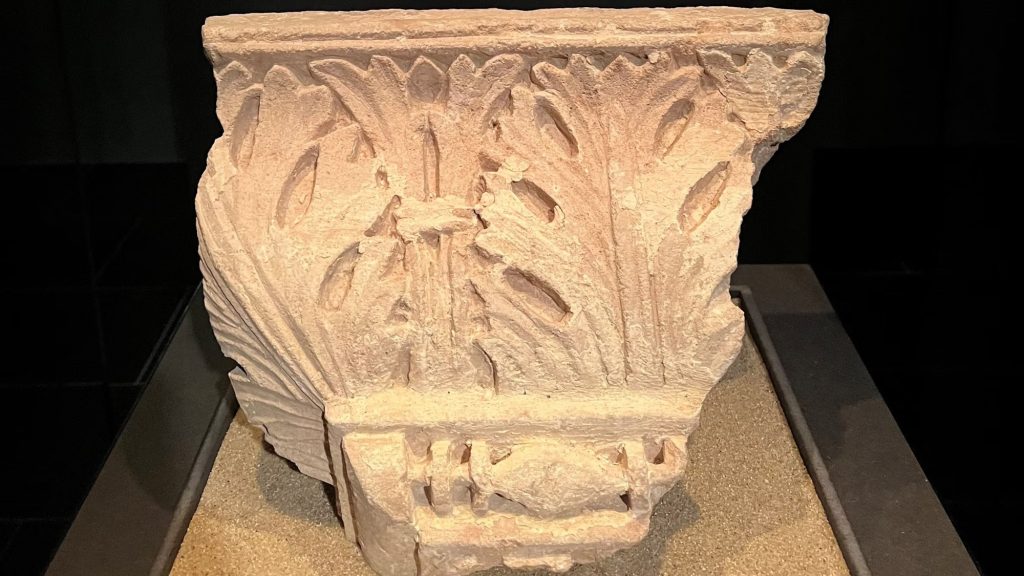
The fragments of a Roman matron’s stone are associated with various finds from the 4th to 6th centuries. Century, which refer to the noble Merovingian family, whose graves were discovered under the inner choir in 1959. Their important grave furnishings are part of the treasury’s permanent exhibition. From the well-documented Carolingian Old Cathedral, the predecessor of today’s Gothic cathedral, the exhibition shows valuable remains of the floor covering and wall painting fragments as well as a cornice stone with palmette decoration, which is one of the highest quality remains of architectural sculpture from this period.
The large Gothic construction site is documented by the workers’ everyday crockery, a gold finger ring and a gold coin, the location of which can be used to date the work on the south tower foundation. Textile finds from the graves of clergy illustrate burial rites of the 17th and 18th centuries. Finally, the secular finds from the 19th century provide an insight into the lives of the people around the cathedral until its completion in 1880.
Cover Photo: No Destinations