During a routine grave dig in Türkiye’s Diyarbakır province, archaeologists uncovered a remarkable 1,500-year-old mosaic featuring the Star of David and a cryptic six-line inscription in ancient Greek.
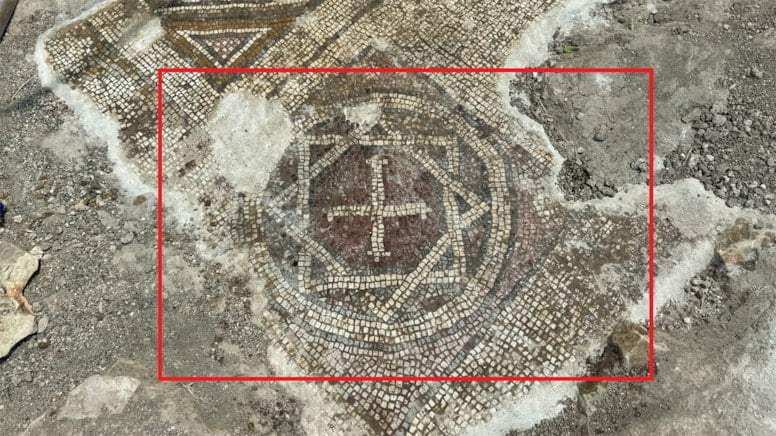
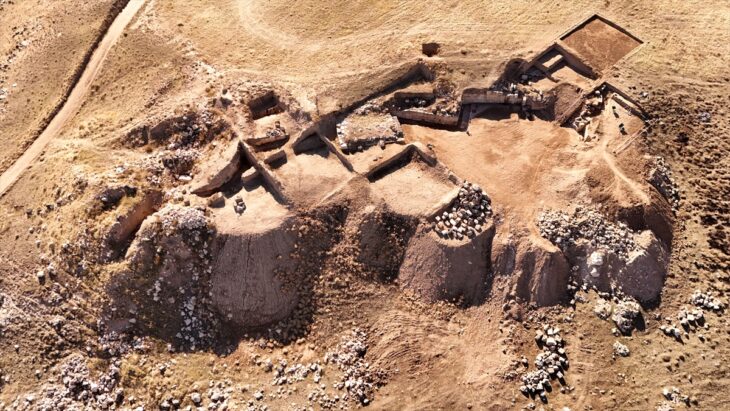
A routine burial in southeastern Türkiye has led to an extraordinary archaeological discovery. While digging a grave in the rural Özbilek neighborhood of Ergani district, local residents uncovered a stunning 35-square-meter mosaic floor believed to date back to the late Roman or early Byzantine period.
What makes the find even more fascinating is the presence of a six-line inscription in ancient Greek, resembling a formal petition or plea, along with a unique Star of David containing a Christian cross motif — a symbol rarely seen in combination. The mosaic was unearthed on March 8 during preparations for a burial, but the find has only recently been detailed by local museum authorities.
A Burial That Changed Everything
The mosaic came to light when villagers began preparing a grave for a deceased resident. As soon as the decorated floor emerged, the community halted the burial, opting to move the ceremony elsewhere and notify local authorities.
Responding swiftly, the Ergani District Gendarmerie secured the area and informed the Diyarbakır Museum Directorate, whose experts arrived the same day. After preliminary evaluations, the area was classified as a historically significant site, prompting the initiation of an emergency archaeological excavation.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!

A Team of Experts Moves In
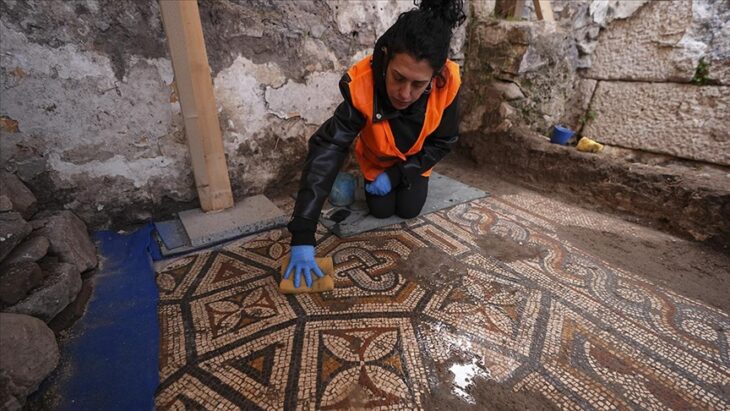
According to Mehmet Çelebi, Deputy Director of Diyarbakır Museum, a multidisciplinary team of archaeologists, art historians, restorers, and anthropologists was quickly assembled. On March 11, the team began a three-week rescue excavation, ultimately uncovering an intricately decorated mosaic spanning 35 square meters.
“Based on the style and motifs, we concluded that the mosaic likely dates to the late Roman or early Byzantine period,” said Çelebi. “It appears to have been the floor of a substantial structure — possibly a villa or religious building — and features rich geometric patterns.”
Star of David with a Cross and a Greek Petition
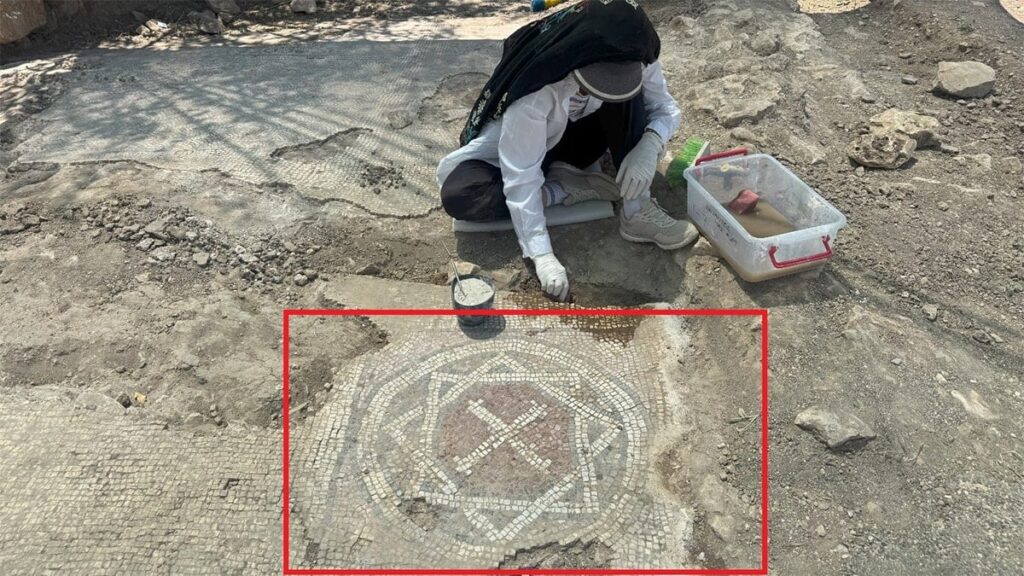
One of the most captivating aspects of the mosaic is the Star of David enclosing a cross, a striking fusion of Jewish and Christian iconography. This unique symbol has sparked widespread interest among historians and religious scholars.
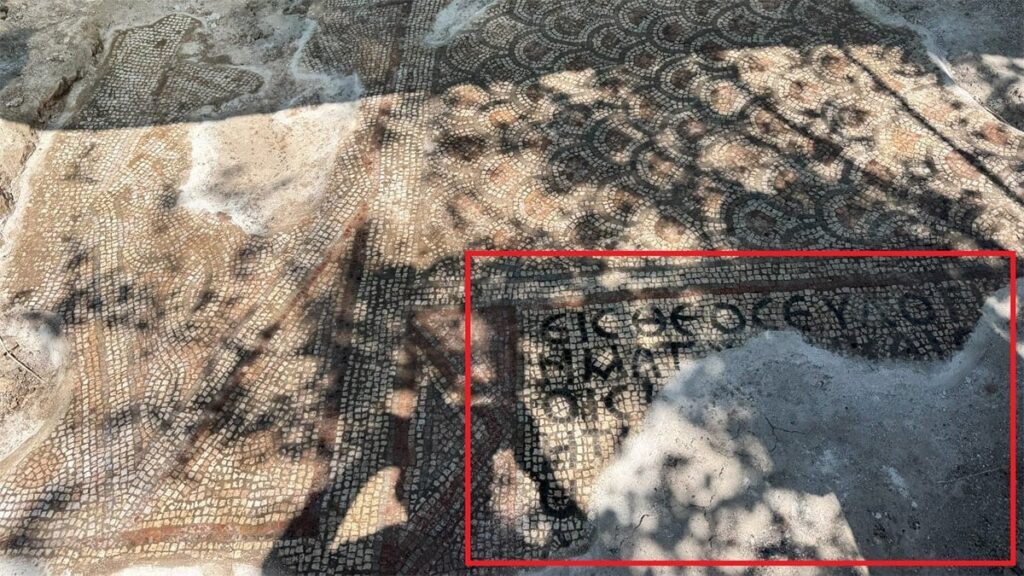
Adding to the mystery is a six-line inscription written in ancient Greek, believed to be a petition or formal plea. While translations are still underway, early interpretations suggest it could relate to a spiritual request or legal declaration, possibly made by the structure’s owner or builder.
“This type of inscription, especially combined with such symbolic imagery, is rare and raises many questions about the religious and cultural interactions in the region during that period,” noted Çelebi.

Preserving a Hidden Piece of History
Following the excavation, the entire site was covered with protective materials, including geotextiles, and cordoned off to prevent damage. The area falls within what is believed to be the ancient city of Memalan, which further supports the historical significance of the discovery.
Due to its location within the modern cemetery, concerns arose among local villagers and the neighborhood muhtar (village chief) about future burial activities. However, the Cultural Heritage Preservation Board ruled that all future burials must be carried out in a separate area away from the mosaic site.
“A new burial zone will be designated to protect the mosaic,” said Çelebi. “Until then, no grave will be dug near the discovered site. The current mosaic area is now officially under protection.”

A Portal into the Past
Archaeologists believe that the site may be part of a larger, undiscovered settlement. Given the presence of such a high-quality mosaic and complex symbolic elements, future excavations in the Memalan region may yield further insights into the religious and social life of southeastern Anatolia during antiquity.
The discovery offers a rare glimpse into the cultural syncretism of the region, where different religious traditions and artistic expressions coexisted and intertwined.
As translation efforts on the Greek inscription continue, and scholars analyze the symbolism of the Star of David and cross motif, this seemingly routine burial has opened the door to one of the most intriguing archaeological finds in recent Diyarbakır history.