Geological surveys at Mongolia’s Oyut Deposit uncovered 3,000-year-old nomadic burial mounds, revealing Bronze Age and medieval khirgisuur graves.
Geological exploration aimed at unlocking Mongolia’s mineral wealth has unexpectedly opened a new window onto the country’s ancient nomadic history. During large-scale surveys at the Oyut Deposit in central Mongolia, researchers identified a cluster of ancient burial sites that shed light on funerary traditions spanning more than a millennium. The discovery, reported by MONTSAME, highlights how industrial exploration can intersect with archaeological heritage when strict preservation laws are applied.
The findings emerged from mineral exploration conducted by the state-owned Erdenet Mining Corporation (EMC) under a government permit covering parts of Orkhon and Bulgan aimags, regions long known as cultural heartlands of ancient steppe civilizations. Exploration work at the Oyut Deposit began in 2023 and confirmed an estimated 357 million tonnes of ore containing more than 1.1 million tonnes of pure copper, marking the site as one of Mongolia’s most significant recent mineral discoveries.
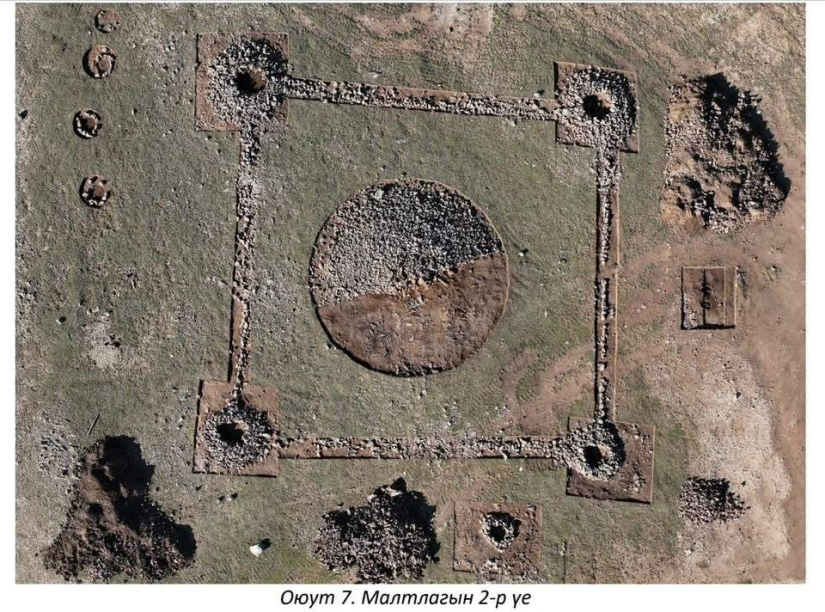
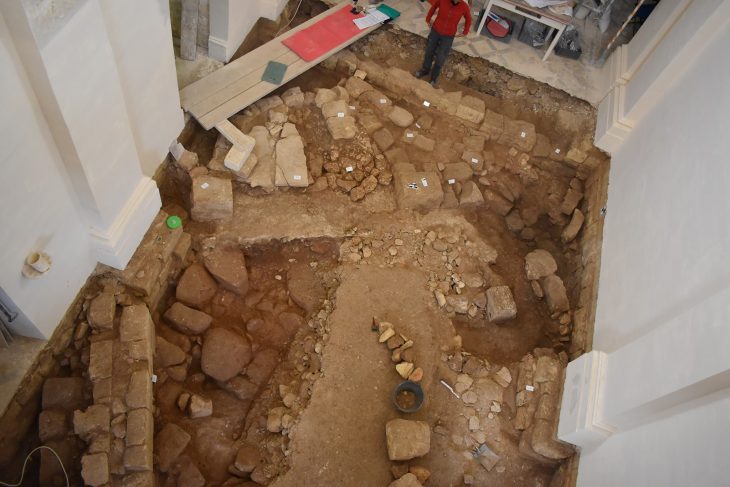
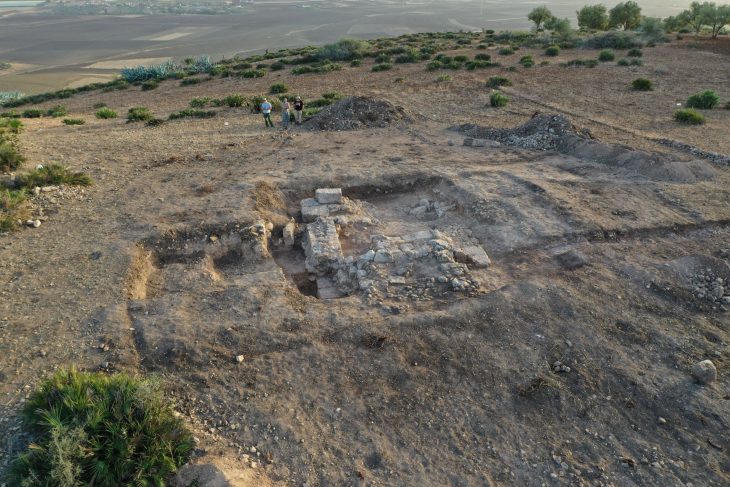
Yet alongside these economic results, geological teams encountered something far older. In 2024, surveys within the exploration field revealed 10 ancient burial mounds, locally known as khirgisuur. In line with Mongolia’s cultural heritage legislation, all industrial activity in the immediate area was halted, and archaeologists were brought in to document and study the sites.

Collaboration Between Industry and Archaeology
EMC’s excavation team worked in cooperation with the Institute of Nomadic Archaeology at the National University of Mongolia (NUM). Fieldwork was carried out over several months and concluded in October, when researchers finalized a comprehensive archaeological report, according to MONTSAME.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
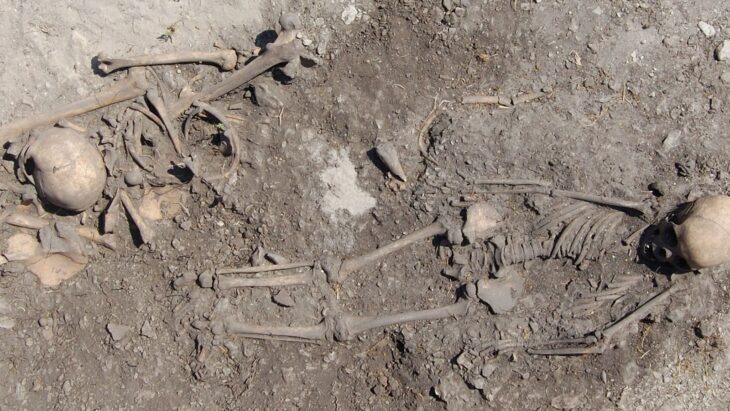
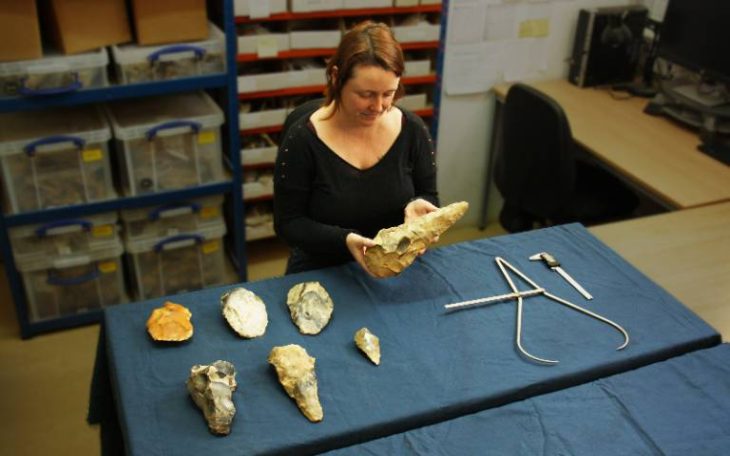
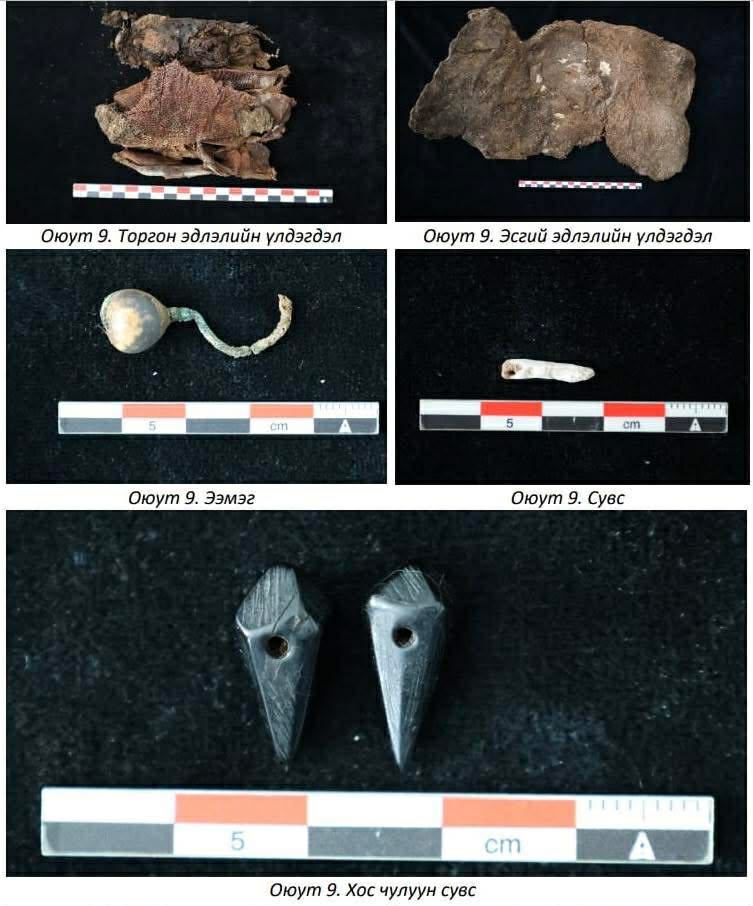
All ten graves were systematically excavated and recorded. Four were securely dated to the Bronze Age, four could not yet be assigned to a specific period, and two belonged to the Medieval era, roughly between the 8th and 13th centuries. The preservation level of the burials, particularly those from the Bronze Age, was described as notably high given the region’s harsh climatic conditions.
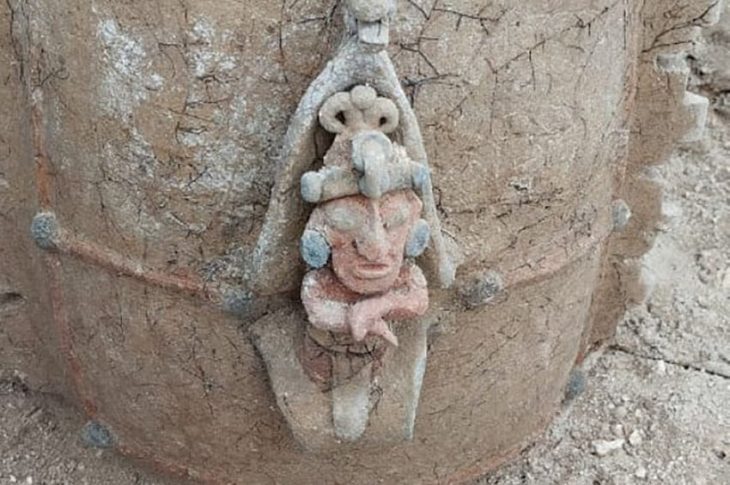
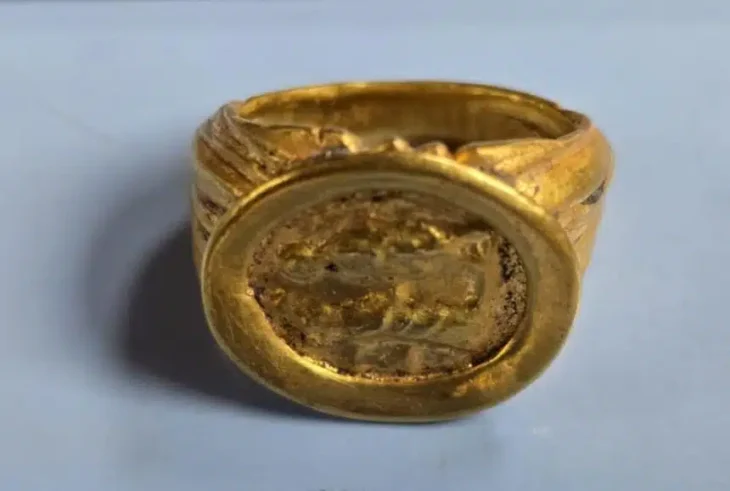
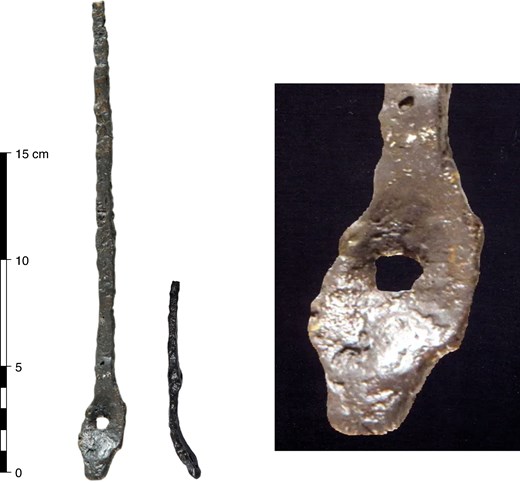
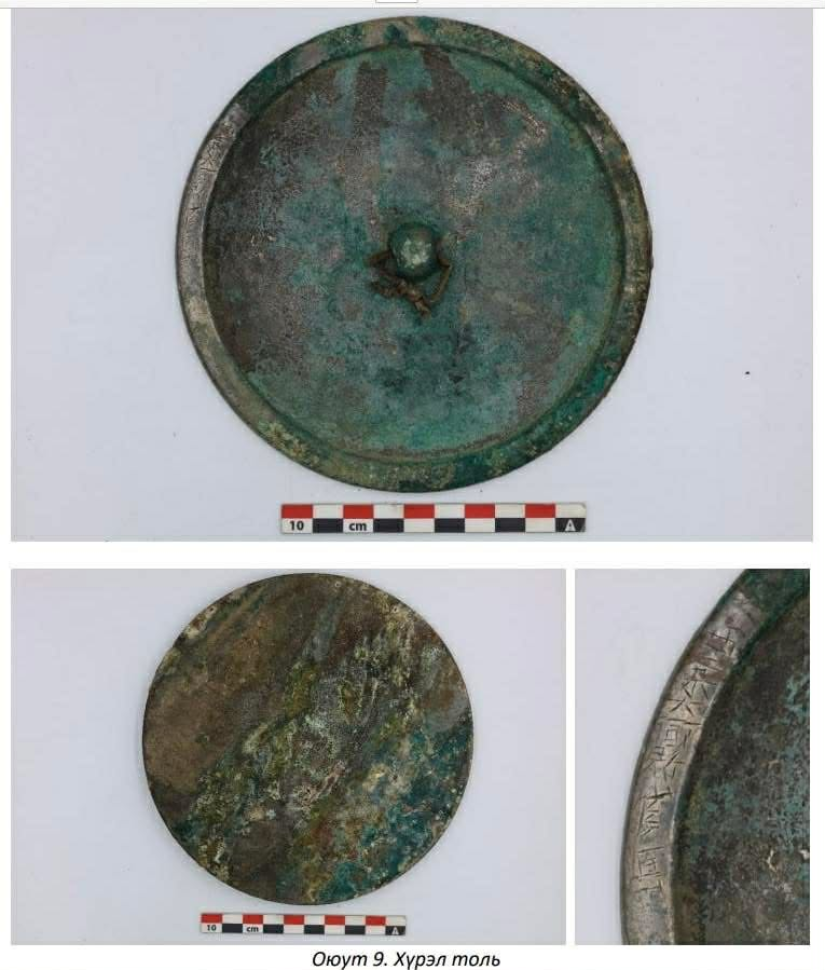
Artifacts recovered from the graves included bronze toli (mirrors), felt fragments, animal bones, and a range of funerary offerings. Such objects are typical of steppe nomadic burial customs, where personal belongings and symbolic items accompanied the deceased into the afterlife.
What Is a Khirgisuur?
The term khirgisuur refers to a distinctive type of burial mound found across Mongolia and parts of Inner Asia. Dating primarily to the Late Bronze Age, khirgisuur consist of stone-covered mounds often surrounded by satellite features such as standing stones or sacrificial animal remains. Scholars believe these monuments were not only graves but also ceremonial landmarks, reinforcing social memory and territorial identity among mobile pastoralist communities.
The presence of khirgisuur at the Oyut Deposit reinforces the idea that Orkhon and Bulgan aimags were central corridors of nomadic movement and ritual activity for thousands of years.

A Region Rich in Steppe History
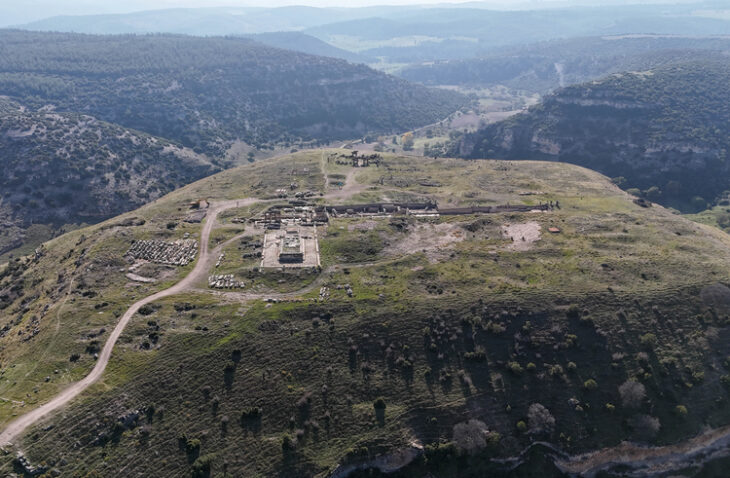
The broader Orkhon Valley is already recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site for its role in the rise of steppe empires, including the Turkic Khaganates and later the Mongol Empire. The newly documented burial mounds add further depth to this landscape, demonstrating continuity in ritual practices from the Bronze Age through the medieval period.
Archaeological research at the Oyut Deposit covered a total area of 1,032 hectares, making it one of the more extensive heritage assessments linked to mining exploration in recent years.
As Mongolia continues to balance economic development with cultural preservation, discoveries like these underscore the importance of cooperation between industry, government authorities, and academic institutions. What began as a search for copper has instead revealed enduring traces of the people who once shaped the Eurasian steppe—long before modern borders or mines existed.
Cover Image Credit: Montsame