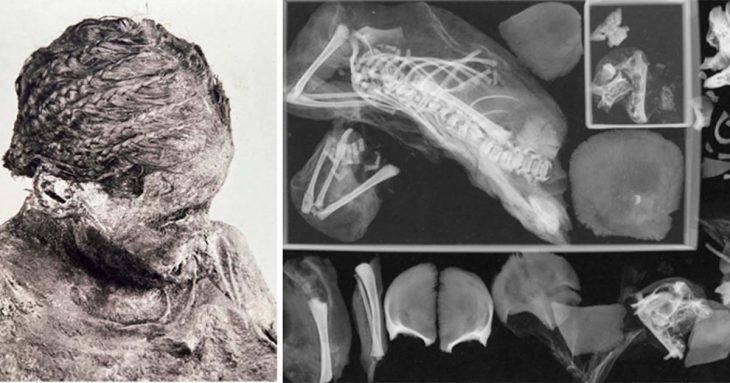
Researchers have discovered a rare instance of delicate cranial surgery, possibly the earliest of its kind in the Middle East, in a Late Bronze Age grave at the Megiddo archaeological site in Israel.
For thousands of years, people have practiced cranial trephination, a medical procedure that involves cutting a hole in the skull, according to archaeologists. They’ve turned up evidence that ancient civilizations across the globe, from South America to Africa and beyond, performed the surgery.
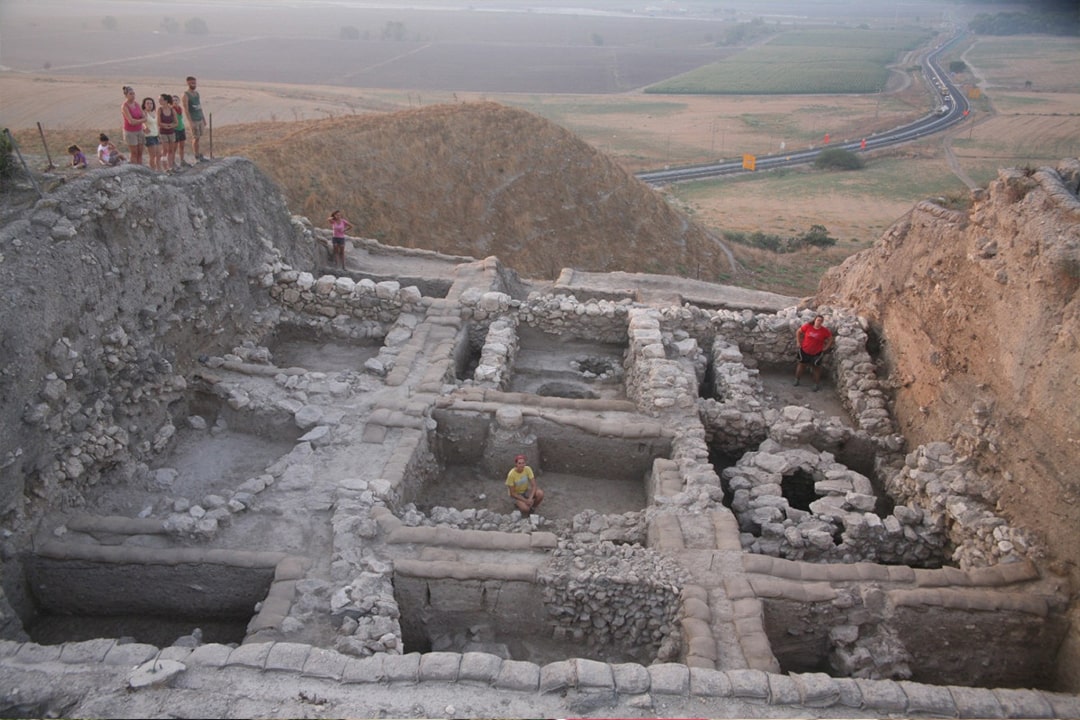
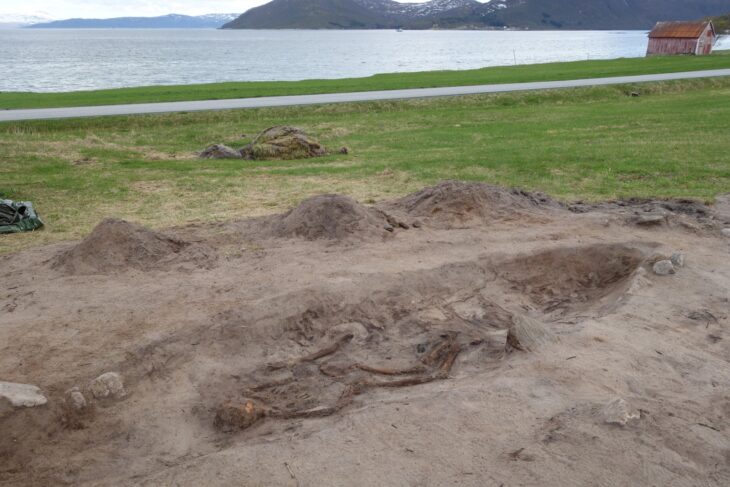
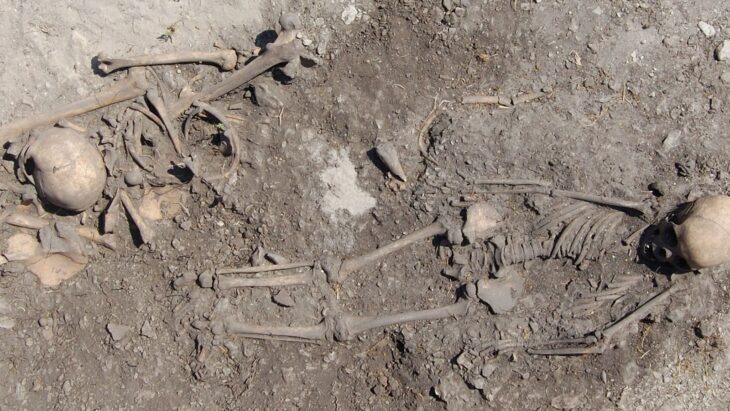
In 2016, archaeologists excavated a pair of tombs in the domestic section of a palace in the famous Biblical city Megiddo, uncovering the remains of two brothers, individuals buried together nearly 3,500 years ago.
Now, researchers from the United States and Israel have published the findings of an analysis of their skeletons, revealing a tragic story of two brothers whose wealth was insufficient to save them from an early death.
The findings mark the earliest example of trephination, a surgical procedure of creating a hole in the skull without affecting underlying tissue, the outlet further said. The brothers lived between 1550 BC and 1450 BC.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
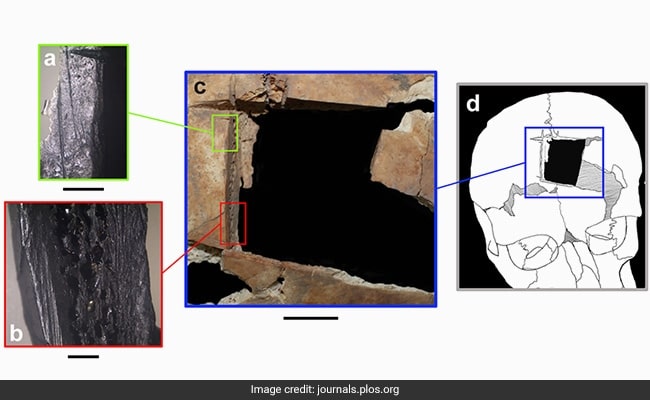
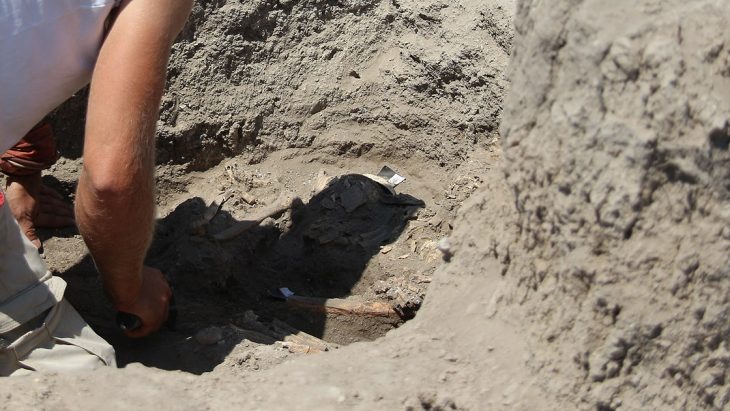
The older brother, who is thought to be between the ages of 20 and 40, had signs of surgery on his skull. The archaeologists said that after cutting off his scalp, a square piece of his skull was removed from his frontal bone using a sharp instrument.
Study lead author Rachel Kalisher is quoted by CNN as saying in a statement, “We have evidence that trephination has been this universal, widespread type of surgery for thousands of years.”
Ms Kalisher said she initially thought the skull fragment had been taken as a DNA sample by colleagues.
“Usually when you study human remains, you’re studying the accumulated change that they experienced throughout their lives, but this was one moment captured,” she added.
The study detailing the discovery has been published in the journal PLOS ONE.
Megiddo, 130 kilometers (80 miles) north of Jerusalem, was a thriving urban center with numerous palaces, fortifications, and temples. Many will recognize it by its Greek name, Armageddon, which is prophesied to be the site of the final battle before the end times.
Cover Photo: Ancient city of Tel Megiddo