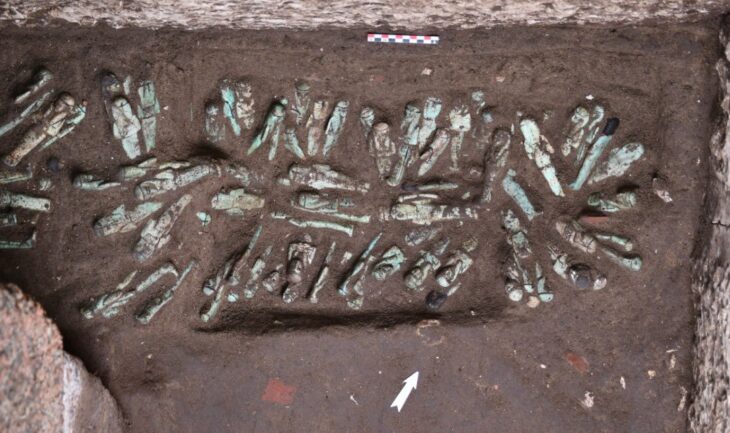
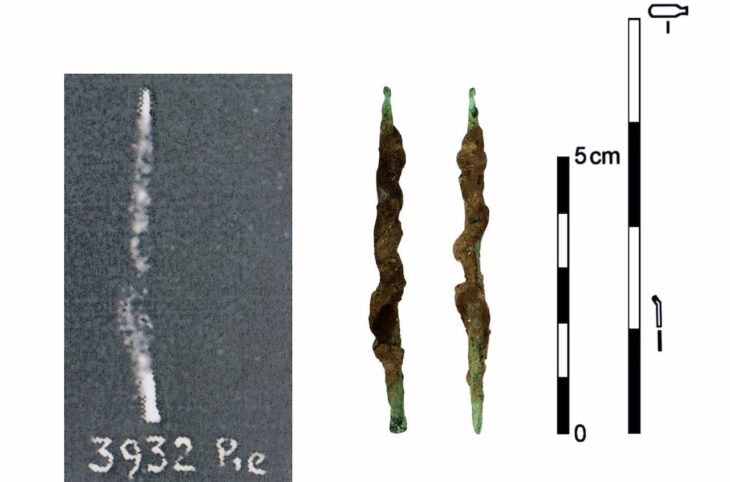
A 4,500-year-old structure containing a jar, many pots, and food fossils has been unearthed at the Yumuktepe Höyük (mound) in Turkey’s southern coastal city of Mersin.
Yumuktepe stands out as one of the oldest settlements in Anatolia with its history dating back to 7,000 B.C. It has hosted many civilizations to date which has given it the name “Cradle of Civilizations.”
The excavations in the Yumuktepe Höyük are being carried out under the presidency of Isabella Caneva, an archeology professor at Italy’s University of Lecce.
Isabella Caneva, an archeology professor at Italy’s University of Lecce and the head of the excavation team, told Anadolu Agency that important findings of changes in life, economy, and society in Yumuktepe are being obtained during excavations.

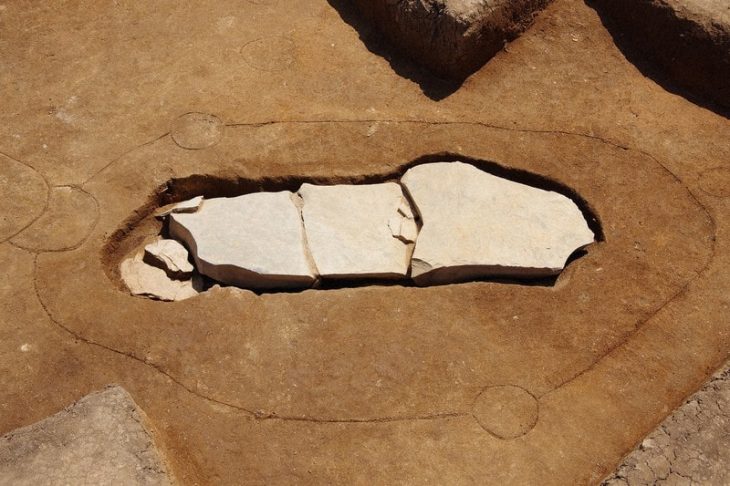
The tumulus, located four kilometers west of the city center, gave important clues about the lifestyles of civilizations, Caneva said, adding that they reached a large building made of adobe on the field.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
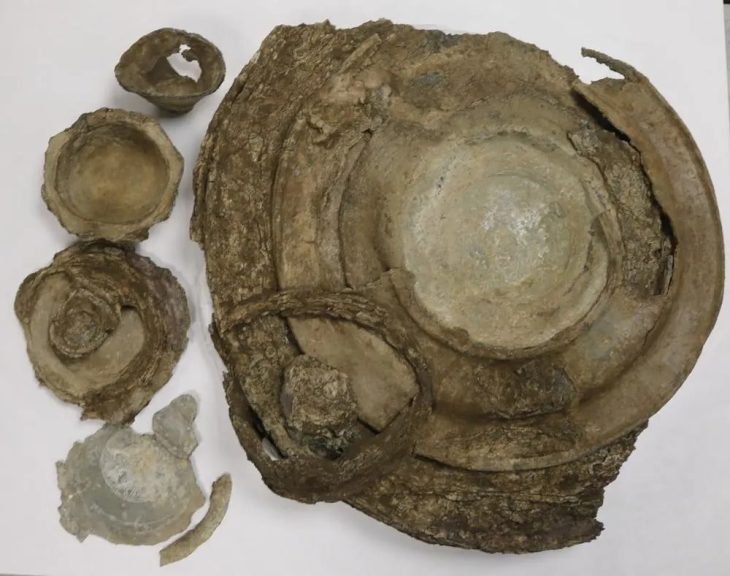
“There were many potteries inside the building. These pieces belonged to one type of product. These bowls are all the same, mass-produced. There were around 700 bowls in this building. This is a big place for a standard family or restaurant. We think that this is a place where public or ceremonial meals are held or food is distributed to the public,” she said.
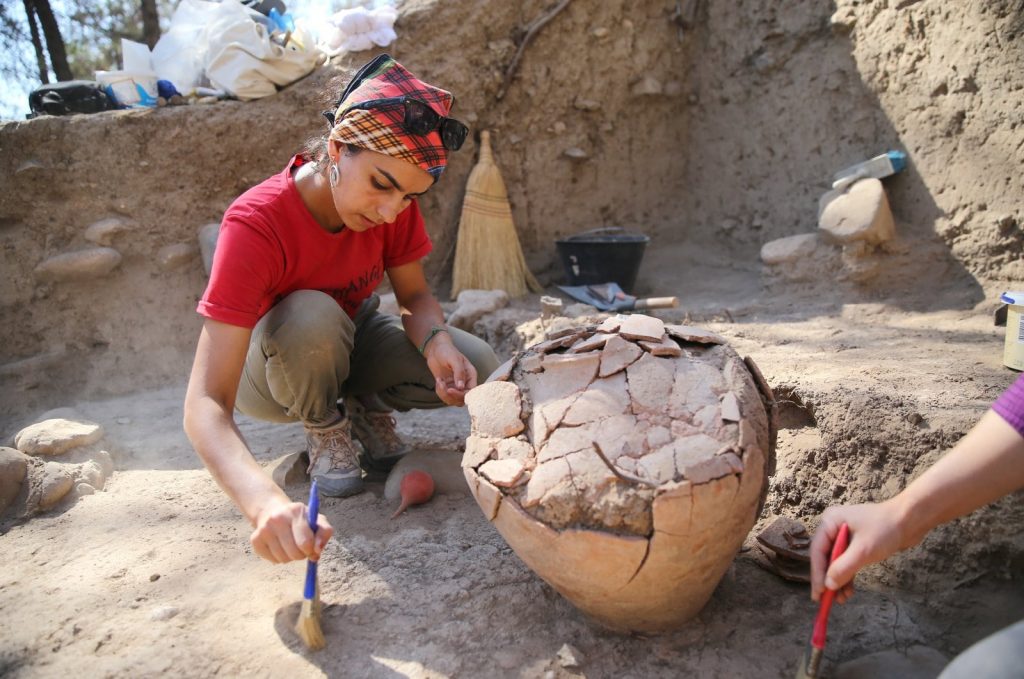

The team of 25 also found a 4,500-year-old jar belonging to the Middle Bronze Age, Caneva added.
Noting that the soil of the jar, which features decorative symbols on it, and olive-grain fossils found near this cup will be examined later, Caneva added: “We will investigate what exactly this building was used for in the past. With the answers that we will find, we can learn how life, economy, and society have changed in every period in the Yumuktepe from the 7,000 B.C. to the present day.”
The Yumuktepe Höyük has been home to many civilizations where skulls from the Hittite period and seals from the Neolithic period were previously found.