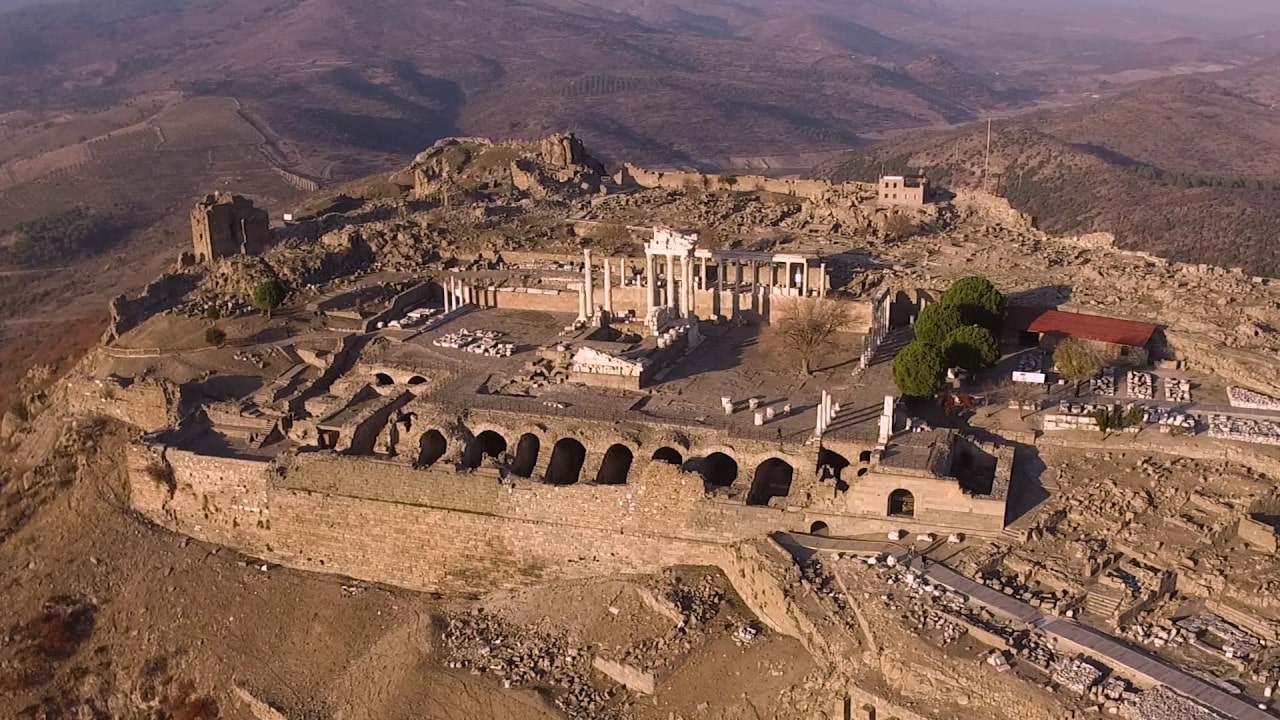
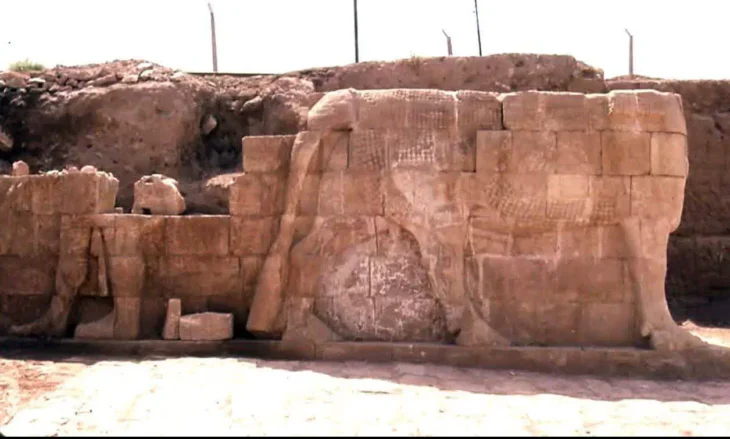
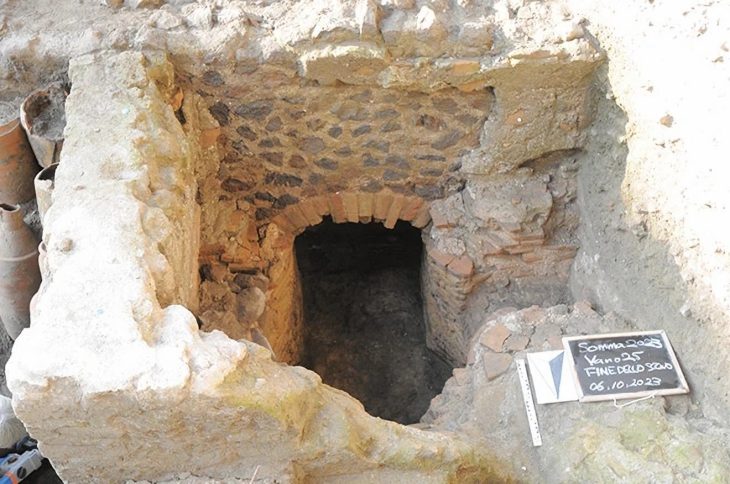
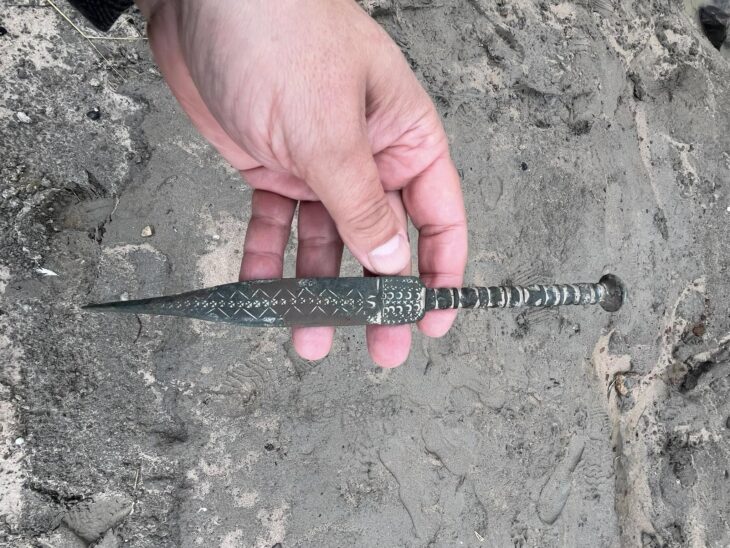
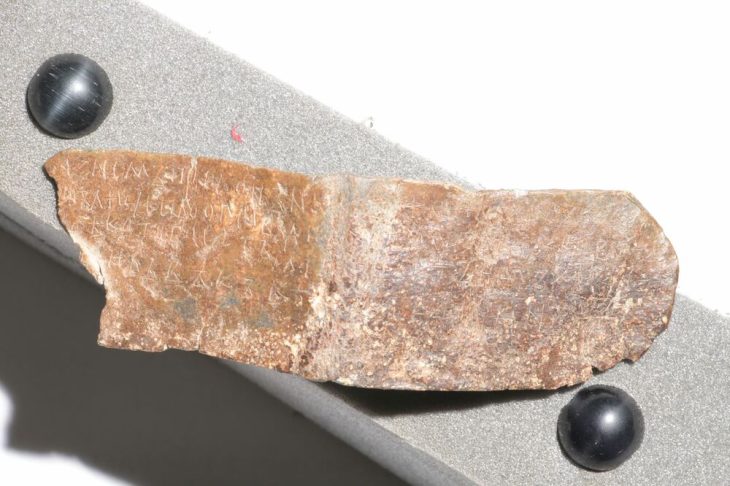
As a result of the studies carried out by the German Institute, Bergama Ancient City was It was transferred to the digital environment in the 3rd as it is century.
As it is known, the ancient city of Bergama was included in the UNESCO World Heritage list in 2014. The view of the Ancient City 2,300 years ago was moved to a digital platform and made available on the internet.
All the finds, tumuli and information about all archaeological structures in the region were transferred to an interactive environment.
The maps on the website of the German Institute were published in Turkish, English and German.
On the maps, there are many examples such as “Red Hall”, “Western Bath”, “Asklepion”, “Palace”, “Tower”, “Curiosity Stone”, “Bridge”, “Thermal Bath”, “12-Room Building”, “Musalla Cemetery” there are many details such as.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
Director of the German Archeology Institute Prof. Dr. Felix Pirson told the AA correspondent that the new studies serve as a geographic information system.

Pointing out that there are deficiencies in the data of the region from the 1970s, such as tumuli, Pirson noted that they felt the need to update maps describing the 3rd century BC.
Pointing out that they collaborated with Bergama Museum and Bergama Municipality within the scope of the research carried out with the permission of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism, Pirson said that architects, engineers, archaeologists and informatics experts collaborate on digital maps.

Prof. Dr. Felix Pirson said, “It is possible to see many ancient fields on the map. New information can also be integrated.We have added the work of the last 30 years. Archaeologists and tourists only look at the Acropolis. However, Bergama does not only consist of the Acropolis, it is a city. In the Hellenistic period, the city was built on a hill, but in Roman times it reached much wider borders. There was no research on this subject because these sections were not exactly shown on the old map. The new map has also been surprising to me. It contained a lot of information and links. It giving us much more accurate information. We preferred the open data system in the digital map. We shared the antique characteristics of Bergama with the whole world. We want this information to reach a large number of people, ”he said.
Prof. Dr. Pirson stated that they continue to work to add new data to the maps.
Stating that they have deepened their research around the tumulus and the Asclepion and examined the entire Bakırçay Valley, Pirson said, “We want to explain the city and its connections better. Where did the stones and metal they used come from? What sources were used? We conduct research on economy and ecology. Digital maps are of great importance to show the results of these studies. ” he spoke.
Interactive digital maps, are accessible on the website of the German Archaeological Institute.