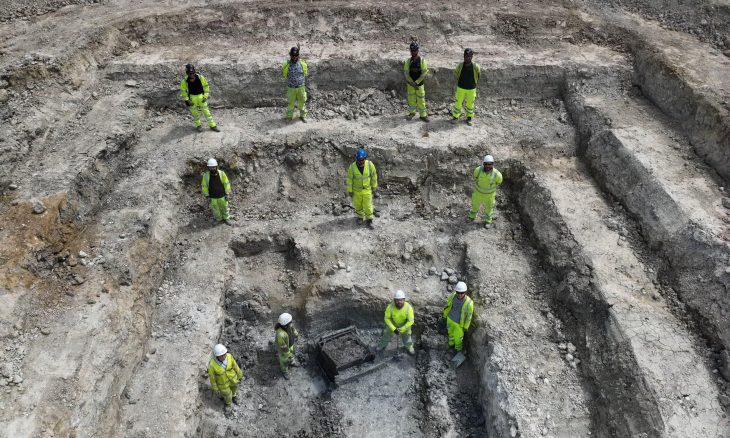
The site of a font of the medieval Ottonian dynasty, from the tenth century, has been discovered in the crypt of St Servatii’s Collegiate Church, Quedlinburg, in Germany. Archaeologists believe that it could be the oldest evidence of a four-passage font — with four arches — north of the Alps.
A baptismal font is an ecclesiastical architectural element that serves as a receptacle for baptismal water used during Christian initiation for both infant and adult baptisms.
According to the Saxony-Anhalt State Office for the Preservation of Monuments and Archaeology, it is conceivable that numerous prominent members of the Ottonian dynasty were baptized at this site.
These include Duke Henry I of Bavaria (around 922-955), Matilda (955-999), the daughter of Emperor Otto the Great and Empress Adelheid and the first abbess of Quedlinburg Abbey, and Adelheid I (977-1044), the daughter of the imperial couple Otto II and the Byzantine Theophanu.
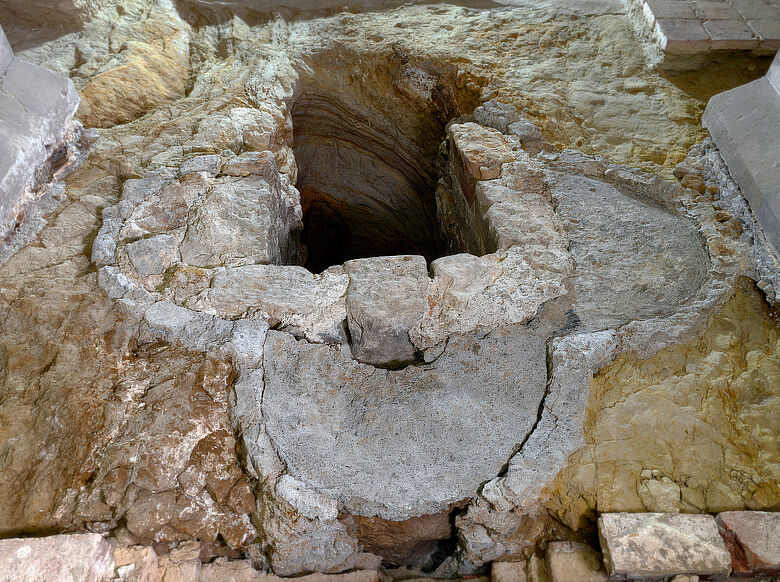
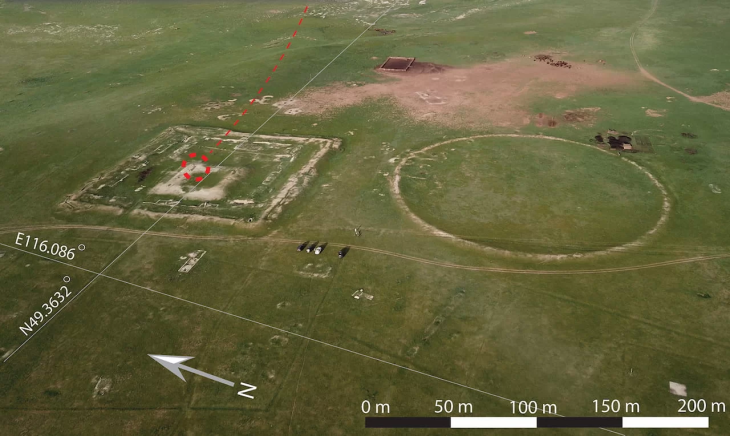
In the western area of the crypt of the Quedlinburg Collegiate Church, archaeological investigations uncovered a quatrefoil cut into the sandstone in the central axis of the room, about 0.5 meters deep and 2.0 meters wide. As a result of joint investigations by archaeology, building research, art history and restoration science using up-to-date documentation and analysis methods, the feature was identified as the location of a baptismal font.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
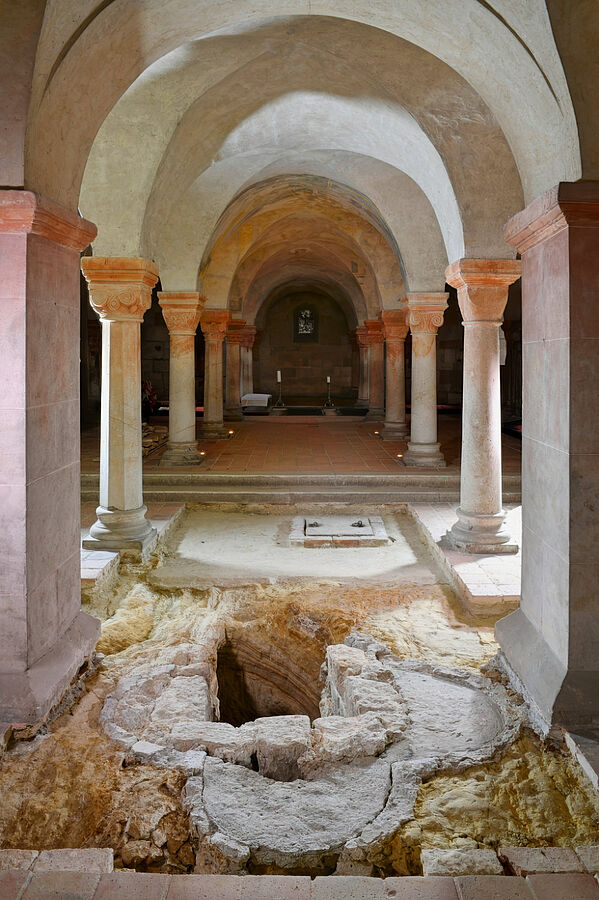

The walls of the depression, which was created in the 10th century before the crypt was built, were elaborately lined with pieces of plaster from a previous floor. This bedding held a baptismal font, which has not survived but was presumably made of high-quality material. Later, but also in the 10th century, the base was increased in height for reasons that are still unknown.
The fact that this finding is the oldest evidence of a quatrefoil-shaped baptismal font north of the Alps is of great importance in terms of art and architectural history. In addition, its location is also crucial for the reconstruction of the architectural history of the buildings on the Stiftsberg. The room in which the baptismal font originally stood must have been the laity room of a sacred building. There is no evidence that a palatium (prestigious residential building) existed at the site in this period. The baptismal font belonged to a church and also dates from the oldest decades of the Stiftsberg’s medieval history in the Ottonian period, about which little is known so far.
Places and dates of death of members of the ruling families are mentioned frequently in contemporary written sources but information on baptism has not survived. This means that the present archaeological find is extremely rare material evidence of the Christian sacrament of baptism. According to the Roman-Germanic pontifical in the 10th century, unlike today, baptism took place once a year, on Holy Saturday, as a collective baptism of infants or small children by immersion.

The candidates for baptism were immersed in the water in the shape of a cross, in the present case in the direction of the quatrefoils, with their heads facing first to the east, then to the north, and finally to the south. The baptismal formula “I baptize you in the name of God the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit” was spoken. The ceremony was carried out in candlelight accompanied by incense as well as liturgical songs and litanies. A few days later, on the Saturday before White Sunday (the Second Sunday of Easter), the baptismal garment was finally removed and the water was drained from the font.
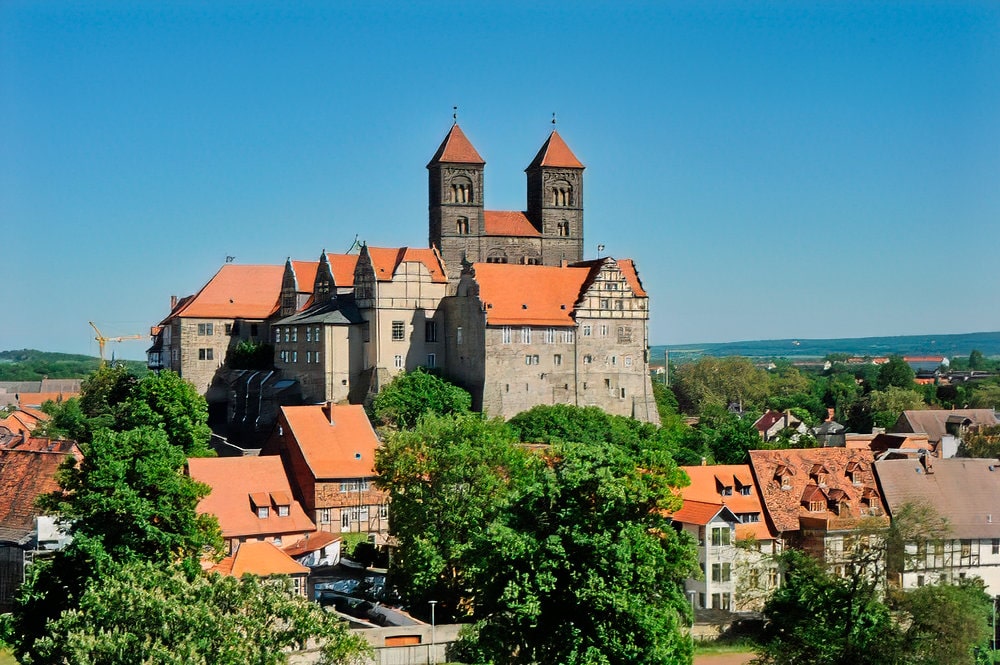
The collegiate church of St Servatii was built on Quedlinburg’s Stiftsberg in the 11th and 12th centuries. Together with the neighboring castle and the old town, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1994.
Saxony-Anhalt State Office for the Preservation of Monuments and Archaeology
Cover Photo: Andrea Hörentrup- Saxony-Anhalt State Office for the Preservation of Monuments and Archaeology