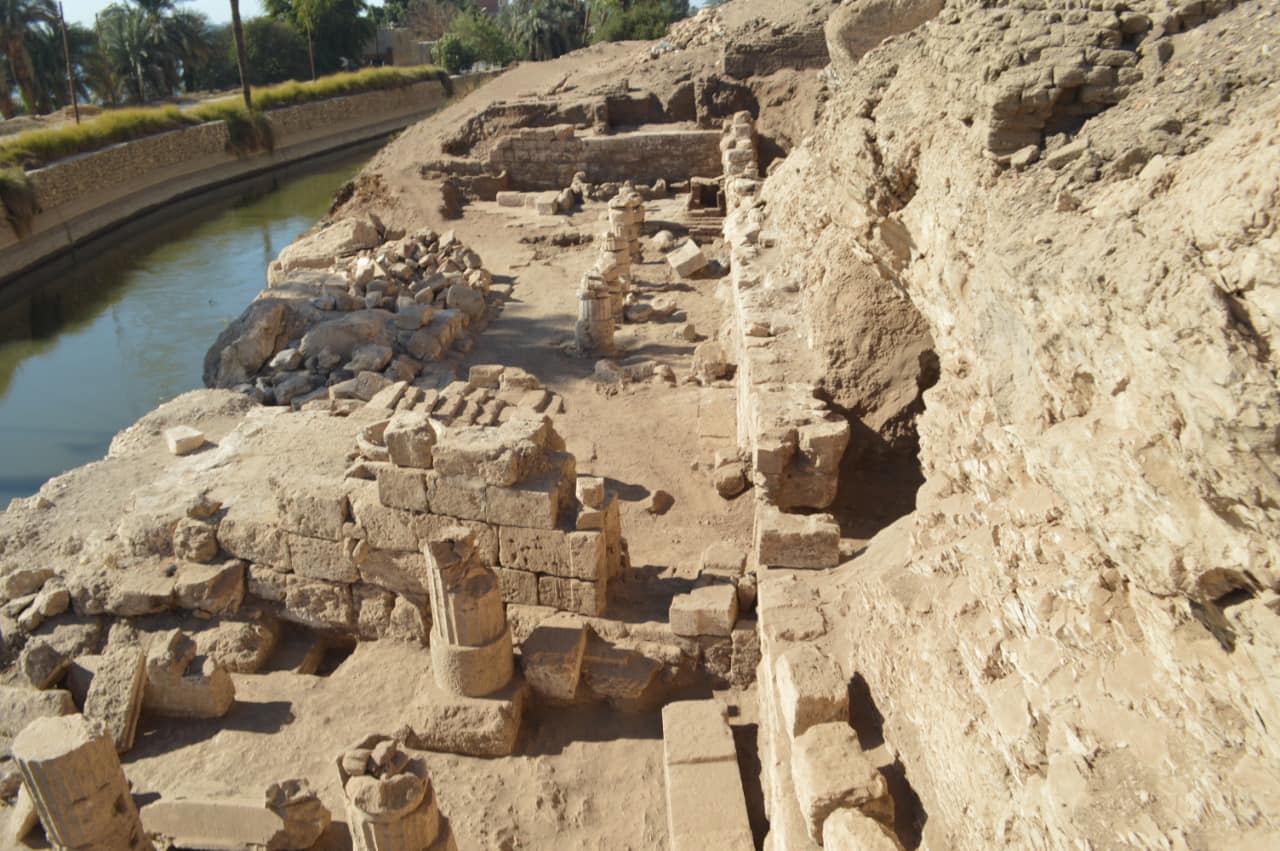
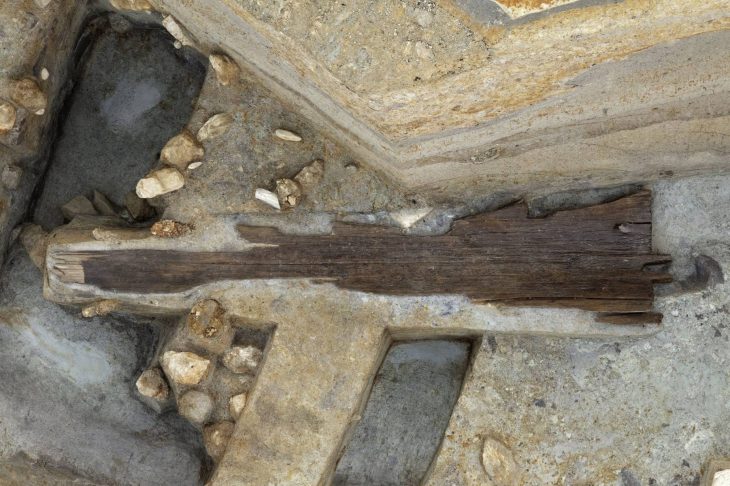
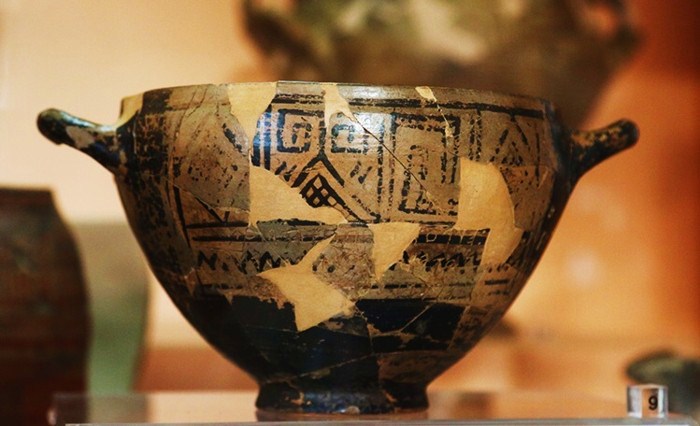
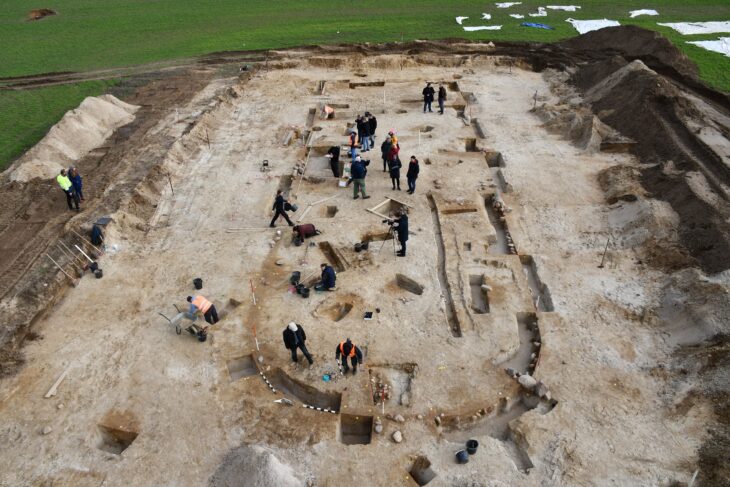
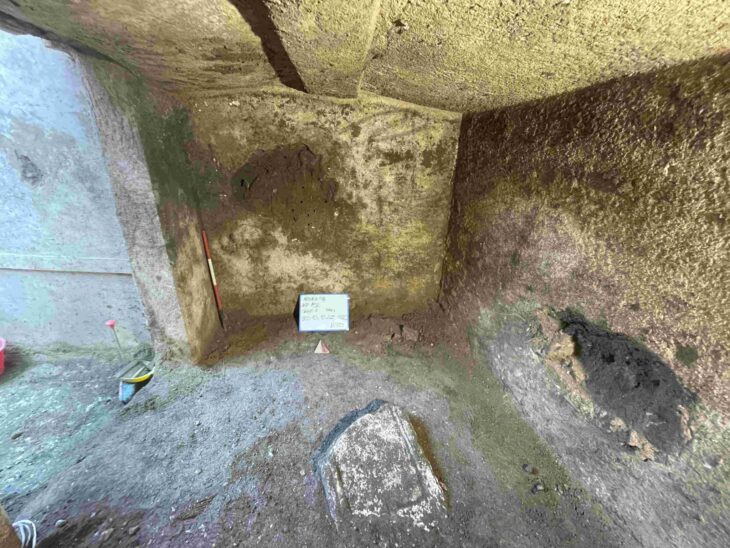
The Egyptian archaeological mission discovered 85 tombs, a watchtower, and a temple site in the Gabal al-Haridi area of Sohag, in southern Egypt.
During the most recent season of excavations, researchers discovered a mudbrick structure that was used to raise taxes and guard Nile River commerce.
Secretary-General of the Supreme Council of Antiquities Mustafa Waziri explained that the discovered checkpoint is a brick building similar to the so-called Tower House.
The team also discovered a Ptolemaic-era temple from roughly the same period that is dedicated to Isis, the Ancient Egyptian goddess first mentioned in the Old Kingdom (2700 BC to 2200 BC).
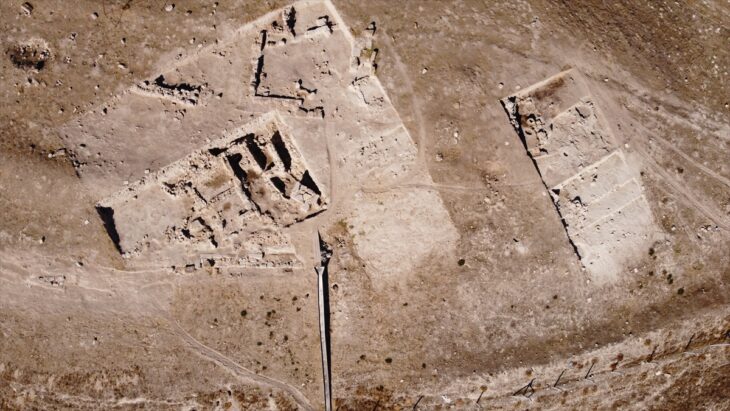
The temple site measures 33 meters long by 14 meters in width it consists of an open, rectangular hall, in the middle of which is a row of four columns, followed by a transverse hall with two columns in the middle, leading to the Holy of Holies, and in the middle of the temple is a staircase. The floor of the temple was formed from stone slabs of local limestone.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
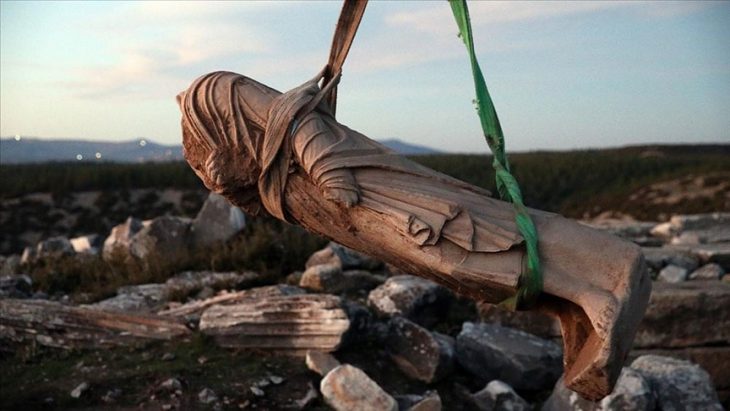
Excavations have also revealed 85 tombs carved into a mountainside. Tombs dating from the end of the Old Kingdom to the end of the Ptolemaic period, their layout varied, including tombs dug at several levels in the mountain, tombs with a well or several burial wells, and other tombs with a ramp ending in a burial chamber.

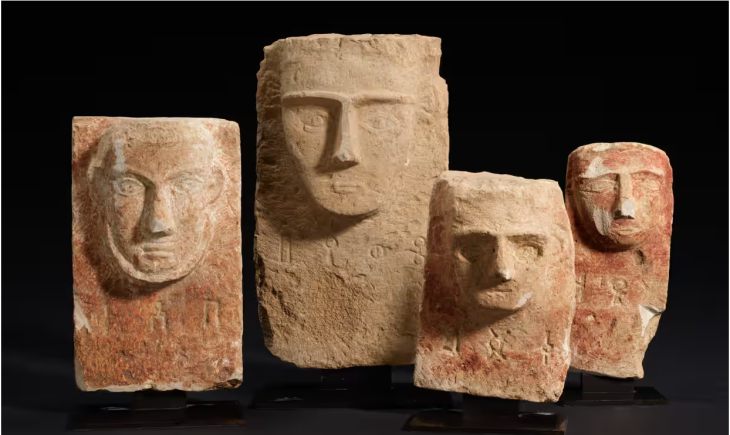
In the tombs dating back to the Ptolemaic era, besides the mummies, archaeologists found 30 death certificates inscribed with old Greek letters and ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs, showing the deceased’s name, occupation, age, and parent’s names.
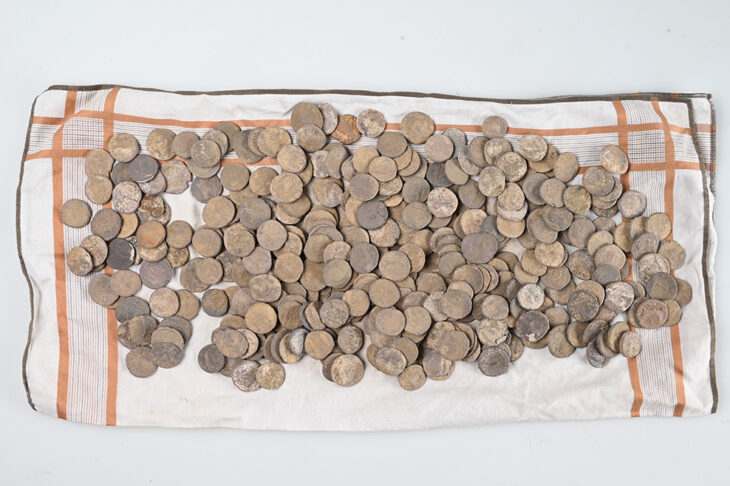
During the excavations, the mission found a limestone purification basin on the northern side of the temple and a votive plaque for the temple. On the northern side, the mission also found five ostraca with Demotic inscriptions, 38 coins dating back to the Roman era, and a small part of a limestone pillar, in addition to unearthing some animal bones, which through their study showed that they represented the food of the temple priests.