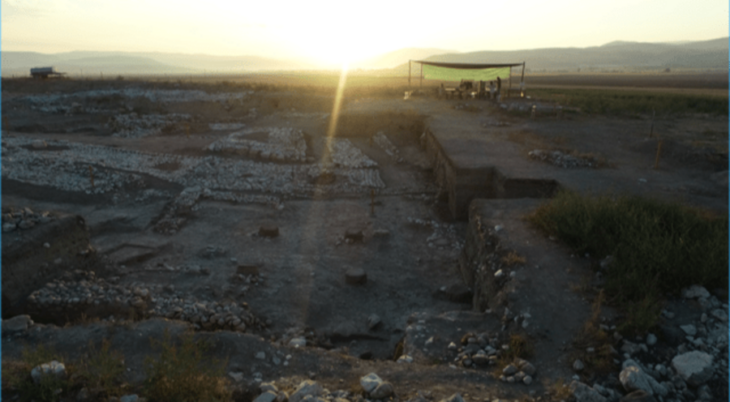
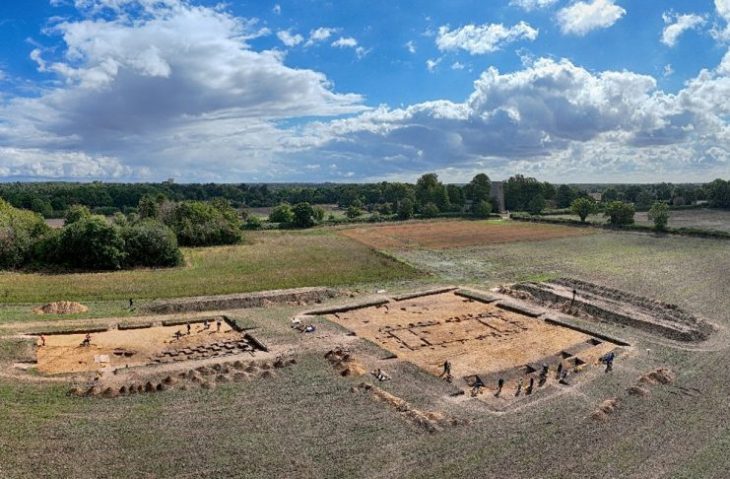
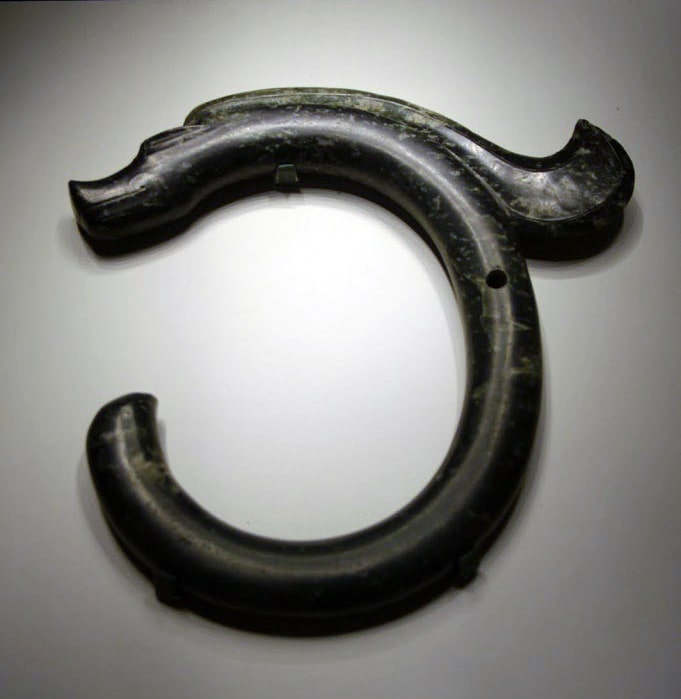
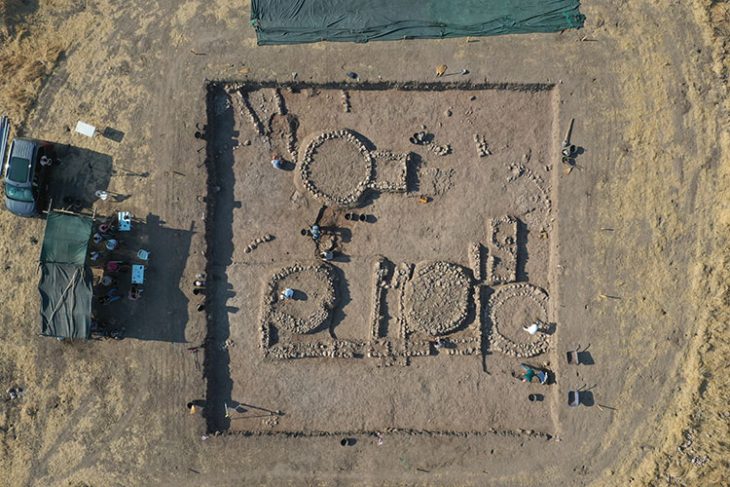Archaeologists discovered a dragon made of mussel shells earlier this week in Chifeng, North China’s Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, which dates back much further than the iconic C-shaped dragon made of jade, which is also from the Neolithic Hongshan Culture.
The city of Chifeng is located in the sprawling plains of North China’s Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Its historical significance has been enhanced this week by a monumental discovery that has the potential to rewrite aspects of ancient Chinese cultural narratives. Investigating this new discovery and its implications reveals a complex and captivating story of the ancient Hongshan Culture.
Historical records place the Hongshan Culture between 4700 to 2900 BC. Among its myriad contributions to ancient Chinese civilization, it is perhaps best known for its exquisite jade carvings.
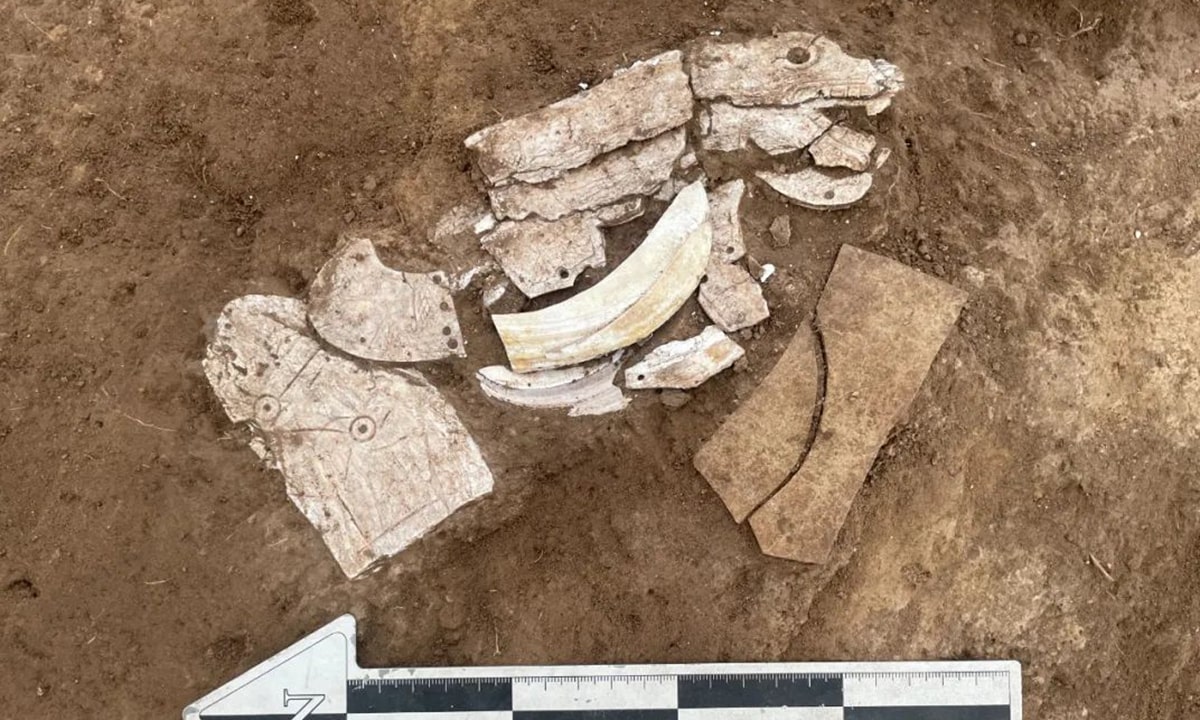
In a moment that can only be described as serendipitous, archaeologists stumbled upon a puzzling artifact: a dragon meticulously assembled from mussel shells.
The discovery is a significant find that fills a gap in archaeologists’ knowledge of the dragon symbol within the early Hongshan Culture, said Song Jinshan, president of Inner Mongolia Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
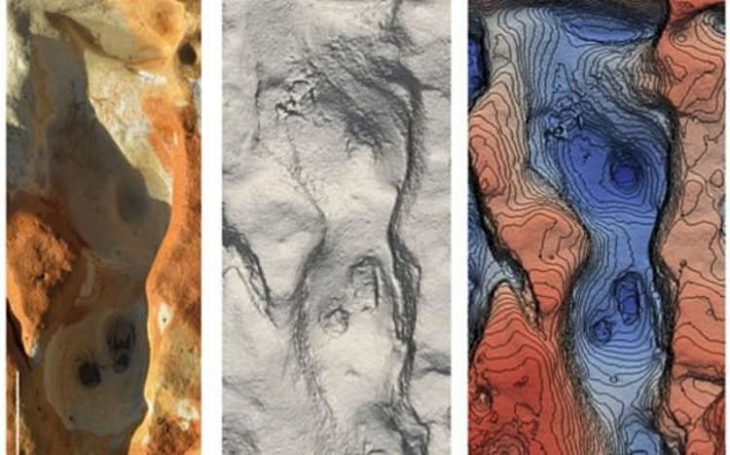
The puzzle-like dragon is pieced together from several mussel shells that form its head, body, and tail, according to Hu Chunbo, the head of the excavation project at the Caitaopo Site in the Songshan district in Chifeng.

This intriguing dragon, measuring about 20 centimeters long, is a mosaic of nature’s puzzles. The entire structure — from the head to the tail — reflects a keen understanding of anatomy and a commendable appreciation of art.
The unearthed items, which were found alongside the fragments of two pottery wares, are typical of the Hongshan Culture.
This mussel shell dragon differs greatly from the previously discovered C-shaped jade dragon of the Hongshan Culture in terms of carving techniques and styling. It is more delicate and realistic, and the teeth, tail and other parts of the carving are subtle.
Additionally, the shape is not a C-shaped dragon with a curled body, but a spread out image of a dragon.
Archaeologists believe that the previously discovered jade artifacts from the Hongshan Culture were placed at high-grade ritual buildings or ritual sites, while the dragon unearthed during the current excavation is a clue to the spiritual world of people living in low-grade settlements.
This distinction underscores the cultural diversity and societal stratifications of the Hongshan Culture, presenting a richer tapestry of their way of life, beliefs, and rituals.
Flourishing in the West Liao River Basin in Northeast China, the Hongshan Culture marked the Neolithic era with its distinct identity. Various archaeological sites linked to this culture stretch from the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region to Liaoning.
Cover Photo: Inner Mongolia Daily