Anthropologists believe that for millennia, individuals have used personal decorations to communicate about themselves without the hassle of dialogue.
They had interpreted beads and other personal ornaments made from seashells as the most common and earliest material manifestations of symbolic behavior.
According to anthropologists, humans have been doing this for millennia, finding methods to communicate about themselves without the hassle of talking.
Shell beads discovered in a cave in western Morocco and dated between 142,000 and 150,000 years old show that this behavior may date back far more than previously believed. The discovery, which was published in the journal Science Advances on Wednesday, was found by a team of archaeologists led by Steven L. Kuhn, an anthropology professor at the University of Arizona College of Social and Behavioral Sciences.
The beads, Kuhn and his colleagues say, are the earliest known evidence of a widespread form of nonverbal human communication, and they shed new light on how humans’ cognitive abilities and social interactions evolved.
“They were probably part of the way people expressed their identity with their clothing,” Kuhn said. “They’re the tip of the iceberg for that kind of human trait. They show that it was present even hundreds of thousands of years ago, and that humans were interested in communicating to bigger groups of people than their immediate friends and family.”
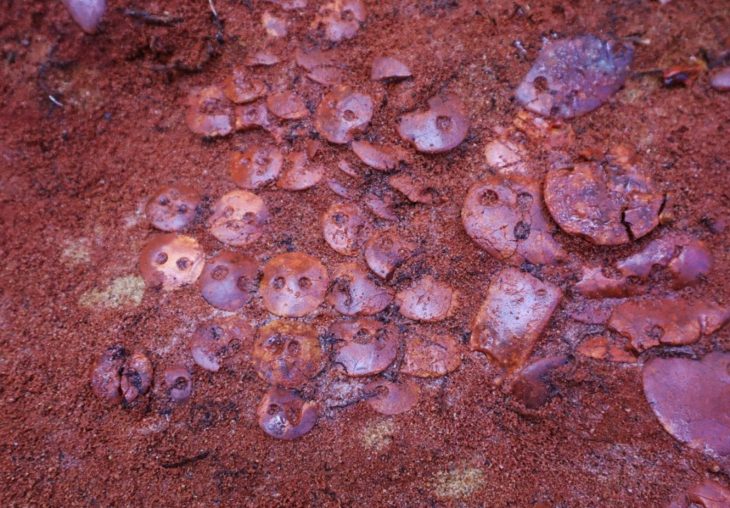
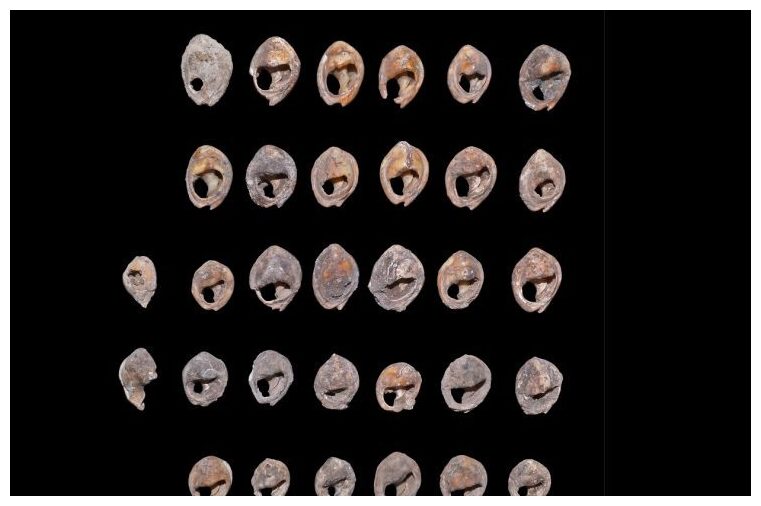
Kuhn and an international team of archaeologists recovered the 33 beads between 2014 and 2018 near the mouth of Bizmoune Cave, about 10 miles inland from Essaouira, a city on Morocco’s Atlantic coast.
Kuhn co-directs archaeological research at Bizmoune Cave with Abdeljalil Bouzouggar, a professor at the National Institute of Archaeological Sciences and Heritage in Rabat, Morocco, and Phillipe Fernandez, from the University Aix-Marseille in France, who are also authors on the study. El Mehdi Sehasseh, a graduate student at the National Institute of Archaeological Sciences and Heritage, who did the detailed study of the beads, is the study’s lead author.
The beads uncovered by Kuhn and his collaborators were made from sea snail shells, and each measure roughly half an inch long. Holes in the center of the beads, as well as other markings from wear and tear, indicating that they were hung on strings or from clothing, Kuhn said.
The beads are like many others found at sites throughout northern and southern Africa, but previous examples date back to no older than 130,000 years. Ancient beads from North Africa are associated with the Aterian, a Middle Stone Age culture known for its distinctive stemmed spear points, whose people hunted gazelles, wildebeest, warthogs, and rhinoceros, among other animals.
The beads serve as potential clues for anthropologists studying the evolution of human cognition and communication. Researchers have long been interested in when language appeared. But there was no material record of language until just a few thousand years ago when humans began writing things down.
The beads, Kuhn said, are essentially a fossilized form of basic communication.
“We don’t know what they meant, but they’re clearly symbolic objects that were deployed in a way that other people could see them,” he said.
The beads are also notable for their lasting form. Rather than painting their bodies or faces with ochre or charcoal, as many people did, the beads’ makers made something more permanent, Kuhn said, suggesting the message they intended to convey was a lasting and important one.
In many ways, the beads raise more questions than they answer. Kuhn said he and his colleagues are now interested in learning why the Aterian people felt the need to make the beads when they did. They’re exploring several possible explanations. One, Kuhn said, involves a growing population; as more people began occupying North Africa, they may have needed ways to identify themselves.
It is also possible that people in North Africa started using the method of communication at a time when the climate was cold and dry. They may have developed clans or other allegiances to protect limited resources, then perhaps used the beads to express their ethnicity or other identities to show they belonged in a certain area, Kuhn said.
















