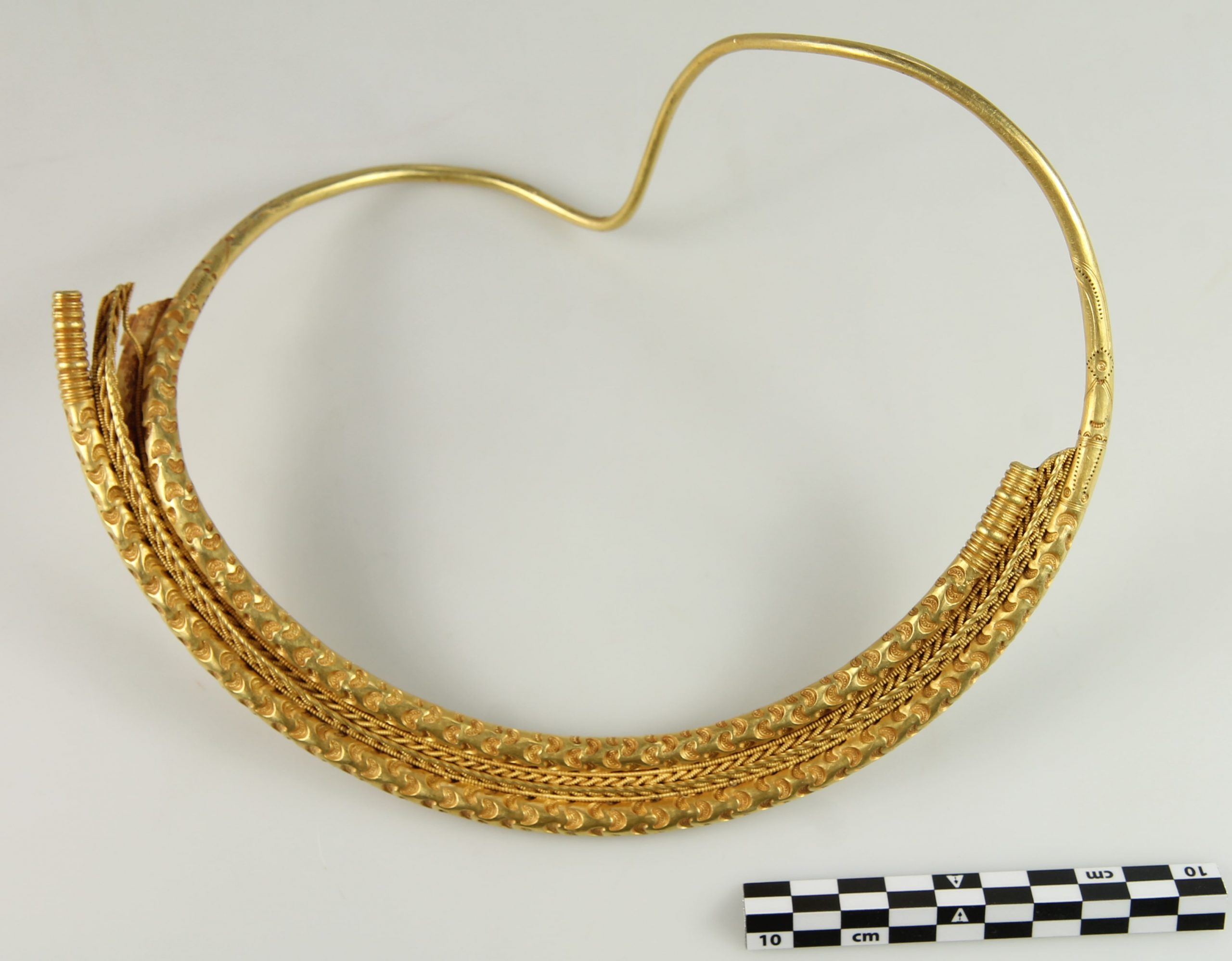
A one-of-a-kind golden neck ring from the Germanic Iron Age (400-550 A.D.) has been discovered in a field not far from Esbjerg on the Jutland Peninsula in mainland Denmark.
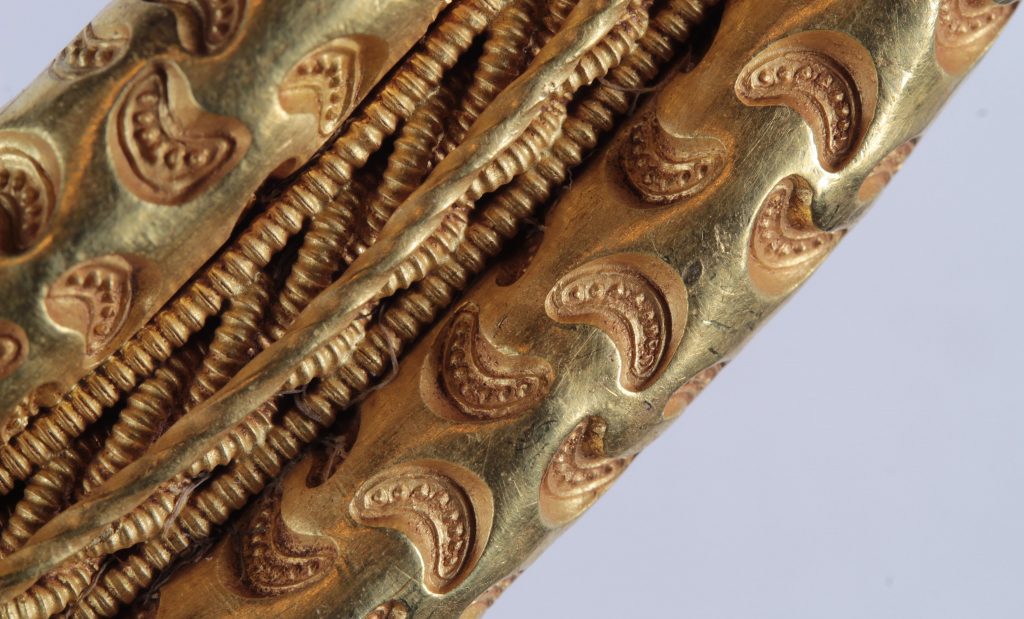
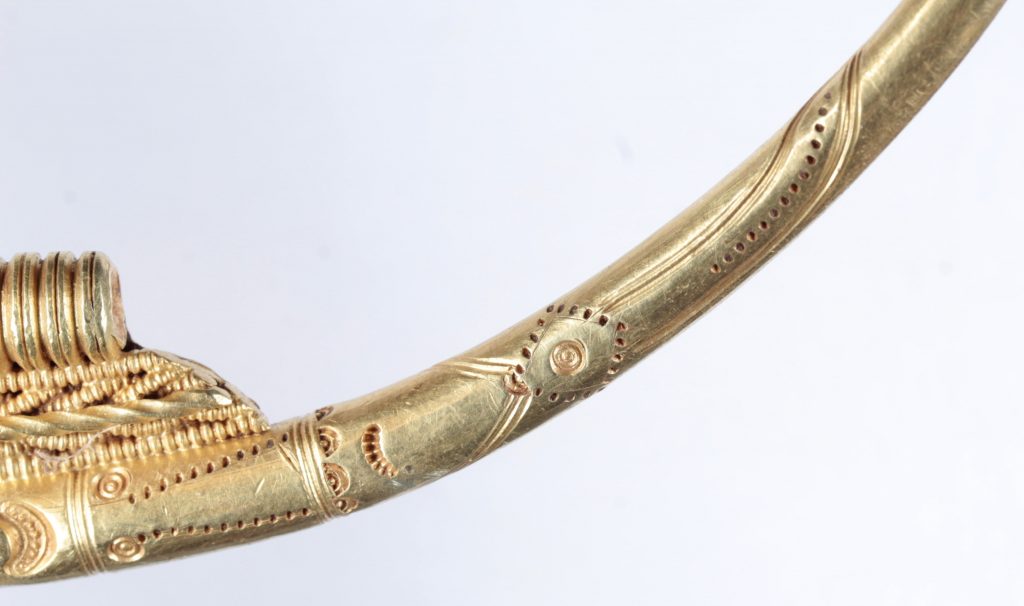
The ring weighs in at almost half a kilo (446 grams) and is designed with crescent-like depressions. The decoration is so meticulously detailed that the crescent shapes on the two rings are ever so slightly different: the crescents on the outer ring have eight decorative divots inside them, and the crescents on the inner ones have six. The broadest point of the ring measures 21 centimeters in diameter.
The embellishments on the ring are so rare, which makes it a “masterpiece of almost divine quality,” as termed by the South West Jutland Museum. That kind of decoration is only known from fewer than a dozen similar rings found in Denmark. And this is by far the most elaborate, most finely worked of them. It is the only one with a soldered plate with intricate gold thread decoration.
The experts noted that the ring was deliberately buried and hidden away and that the inhabitant to whom it belonged did not sacrifice the ring to the gods, which was common practice in that era.

“When sacrificing items at that time, it usually took place in wetlands and bogs and the like. We know a large wetland existed near the discovery site, so if it was sacrificed to the gods, it would have been located out there instead”, Claus Feveile, curator at the Ribe Viking Museum, said in a statement.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
The golden neck ring was discovered by metal detectorist Dan Christensen in October 2021. Christensen when he found the neck ring, immediately alerted museum staff. In the week following the discovery, the entire field was scanned with metal detectors in case the ring had been part of a larger grouping of precious objects scattered by agricultural activity. (Previous examples of neck rings from this period have been found in pairs.) Nothing turned up.

Subsequent full excavation of the find site revealed evidence of a settlement under a thin layer of plow soil, including roof-bearing post holes from multiple three-nave longhouses dating to between 300 and 600 A.D. The neck ring was found inside one of the longhouses. It was recovered from below the plow layer, so archaeologists believe it was buried where it was found.
Archaeologists don’t think it has been moved since, as the golden neck ring is in mint condition and has maintained its shape.
Initially, the neck ring will be exhibited at Museet Ribes Vikinger up until December 23.