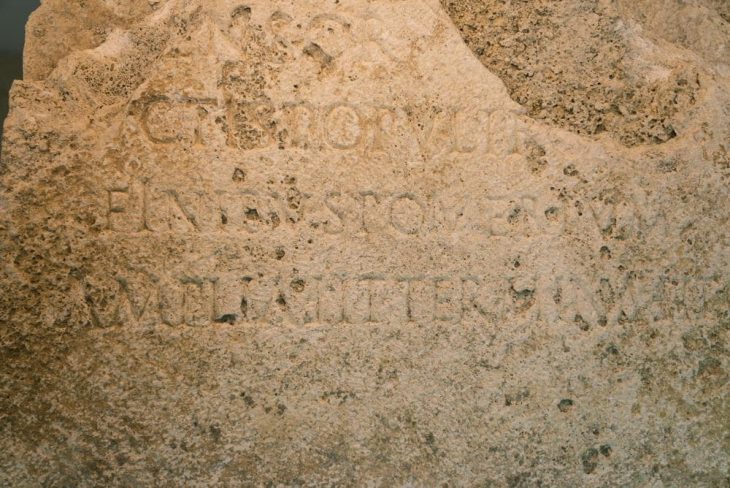An inscription in both runic and Latin script on a church wall in Denmark turned out to be legally valid proof of debt dating back 800 years.
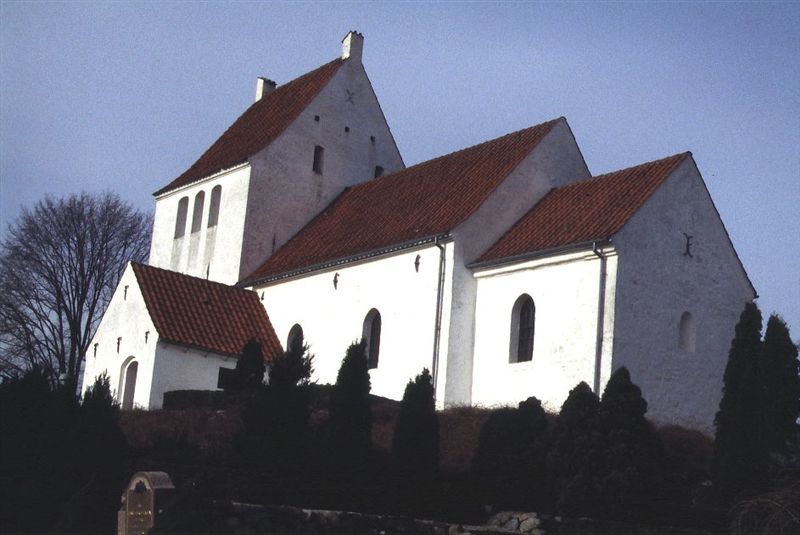
According to Via Ritzau, the inscription in Runic and Latin script on the wall of the Sender Asmindrup church was discovered more than a century ago. It is located near the town of Holbaek, on the eastern Danish island of Zealand.
The inscription has two lines of text. The top line is written in Old Danish runes and was deciphered in 1909. It says, “Toke took silver on loan from Ragnhild.” Scholars were unable to decipher the bottom line because it was written in both runes and Latin letters in an idiosyncratic manner.
Only now the experts were able to read the second line of the text, which allowed them to identify this inscription as a legally valid receipt of the existence of debt 800 years ago.
The National Museum’s scribe researcher and runologist Lisbeth Imer has succeeded in decoding the text in collaboration with Anders Leegaard Knudsen, who is a senior editor at Diplomatarium Danicum – Denmark’s Kingdom Letters, which publishes documents from the Middle Ages.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
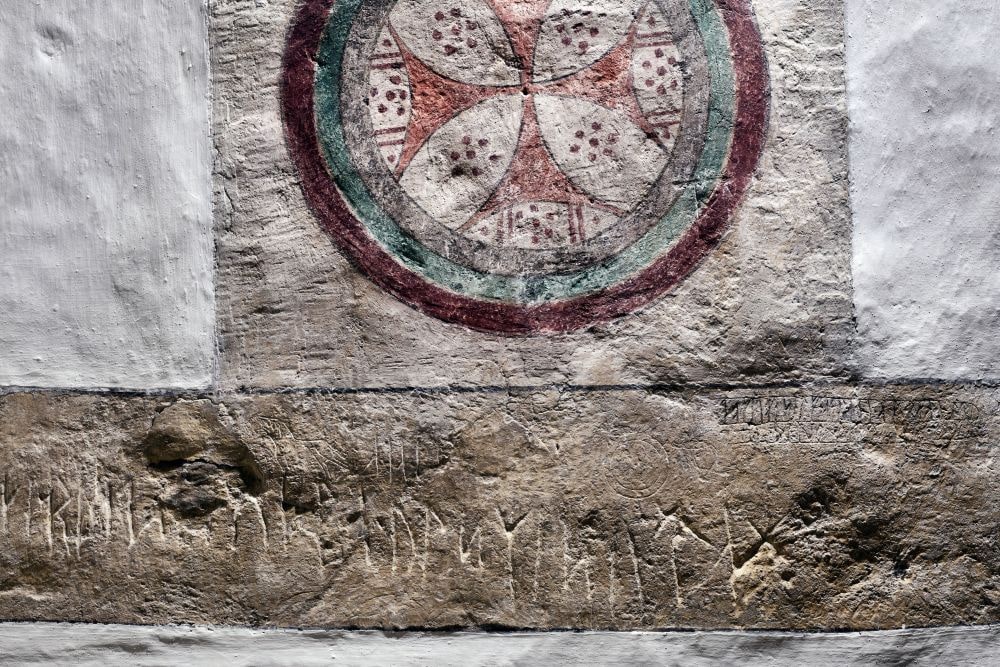

The translation of the second line reads: “2. May in the year of salvation 1210.” According to Lisbeth Ymer, this means that the date Tocke borrowed from Ragnhild was clearly documented. And this already makes the registration a document that still has legal force.
“It is unique in the Danish context and rare internationally,” says Lisbeth Imer.
There are only three similar examples: a road use contract on a parish church on Gotland, Sweden, a land sale on a wall in St. Sophia Cathedral in Kyiv, Ukraine, and a debt case judgment in the church of Saint Panteleimon in Galich, Russia.
Corresponding legal documents are typically only preserved on parchment and from the very highest social strata – often only because they are found preserved in a younger copy. The new discovery shows that there was a widespread writing culture in the Middle Ages.
“Until now, we have had almost no knowledge of how agreements were made, or to what extent writing was used. Our knowledge of it has, so to speak, been in the dark, and there have been only a few and scattered testimonies about the use of writing. The inscription in Sønder Asmindrup shows that written agreements were made among what we must believe were ordinary farmers at an early stage in the Middle Ages – we simply did not know that before,” says Lisbeth Imer.

It’s also a unique testament to how commoners in a rural parish crafted legal contracts comparable to the kind of work done by professional scribes for the elites.
At court, people usually wrote in Latin and with letters, while church inscriptions are mainly written in the mother tongue and with runes. And where the king’s documents almost all have to do with the state’s interests, the inscription in Sønder Asmindrup deals with ordinary farmers out in the countryside.
“Precisely that makes it so interesting, because it shows that writing was probably more used and widespread than we have otherwise thought. The promissory note is a serious use of writing, it wasn’t just a name scrawled on the wall for fun. It shows that a fairly advanced use of writing also took place out in the countryside, and it is not something we have seen such good examples of before,” says Lisbeth Imer.
Inscriptions on church walls are not unusual in themselves. In about 50 churches in the Old Danish area (incl. Scania) there are about 200 individual inscriptions that have been scratched into the lime plaster on the wall.
Presumably, there have been similar proofs of debt on several Danish church walls, but when they were plastered over in connection with the Reformation, many of the inscriptions have been lost – or are still hidden under the plaster.