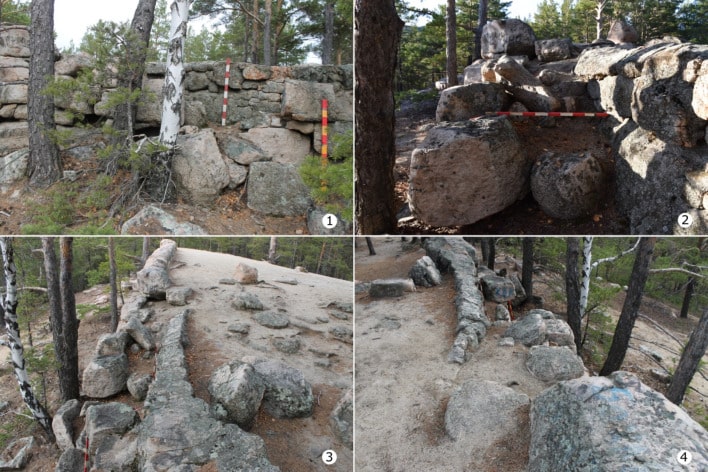
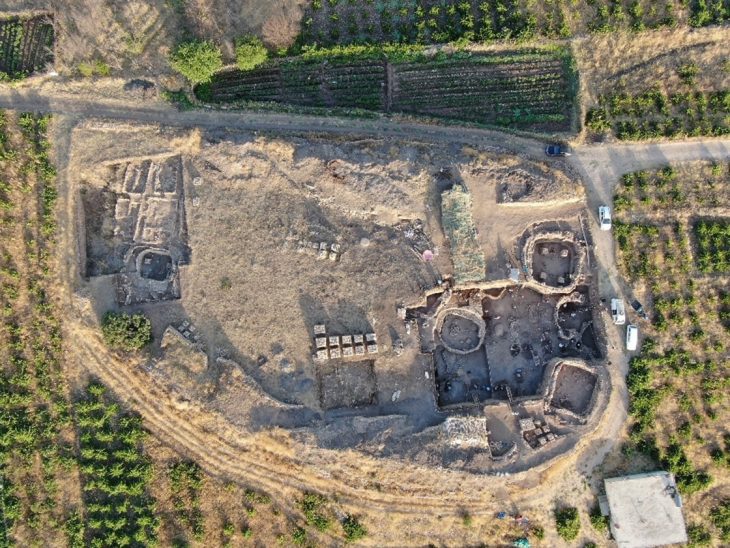
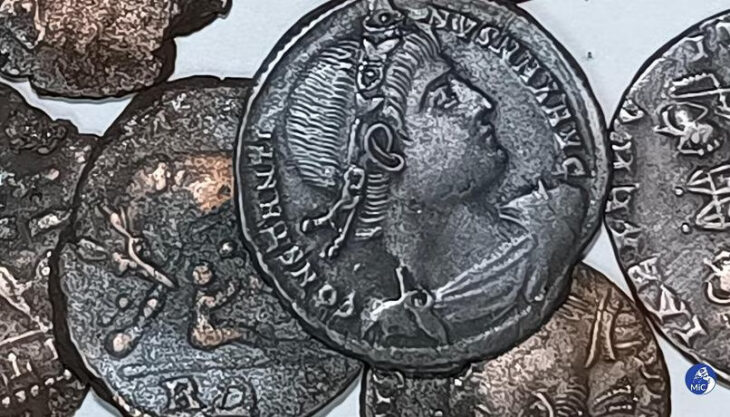
A team of researchers from the universities of Alicante (UA) and Zaragoza (Unizar) have discovered a Roman temple at Cova de les Dones, one of the largest rock art sites on the Iberian Peninsula. They also found fifteen Roman inscriptions and a coin from the reign of Emperor Claudius.
Researchers have discovered a remarkable Roman sanctuary in the Cova de les Dones, located in Millares, Valencia, Spain. This find, crucial for understanding the Roman presence in the Iberian Peninsula, is situated in a deep chamber of the cave, over 200 meters from the entrance.
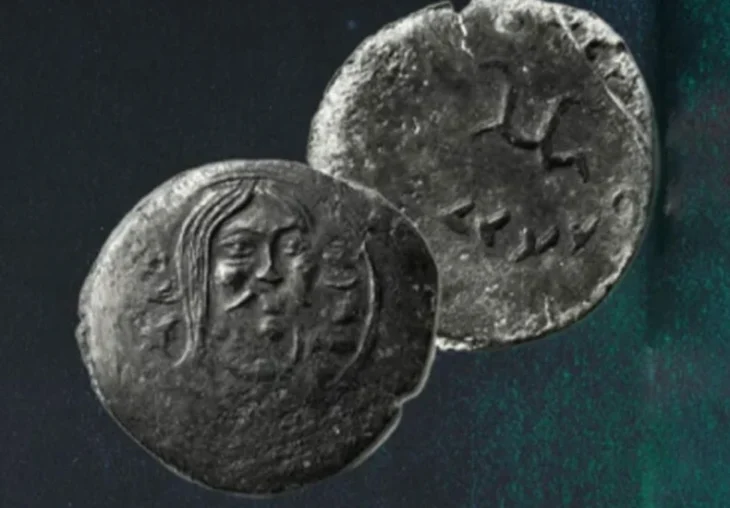
The team has documented around fifteen Roman inscriptions and a coin dating back to the reign of Emperor Claudius. This coin, discovered in a crack in the ceiling next to a stalactite, indicates that the site may have been used for ritual purposes during the 1st century AD.
This discovery builds on a previous finding in 2023 when a study published in Antiquity revealed more than a hundred rock art motifs within the cave. Experts assert that the variety of techniques and the number of representations make Cova de les Dones the most significant Paleolithic site along the eastern Mediterranean coast of the Iberian Peninsula.
The recent discoveries emphasize the exceptional nature of the site, revealing its archaeological significance through evidence of continuous use from prehistory to the Roman period. From its origins as a Paleolithic rock sanctuary to its reuse during Iberian times and its recent recognition in Roman culture, the cave has maintained its sacred character for millennia. The first documented explorations of the site date back to the 18th century.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
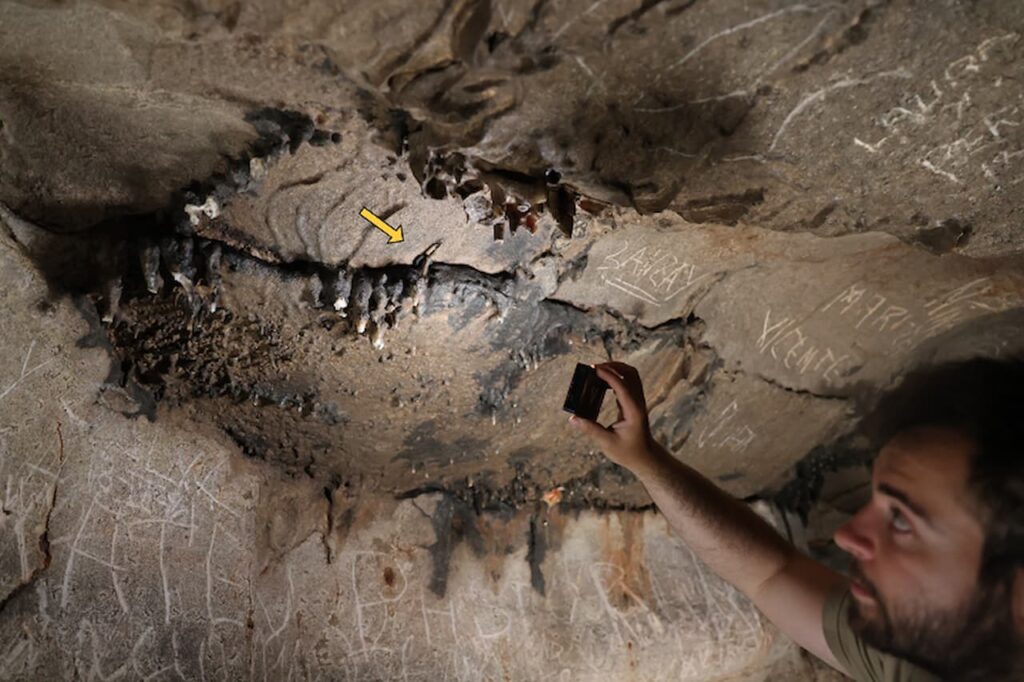

Previously classified as an Iberian sanctuary since the 1960s due to the presence of Iron Age ceramics, archaeological evidence confirming its Roman usage had been limited until now. The discovery of inscriptions in such a deep area of the cave provides compelling evidence that the sanctuary was either continuously used or repurposed by the Romans, enhancing our understanding of the persistence of cult practices in this sacred space.
The location of these inscriptions ranks Cova de les Dones among the deepest sites with Roman inscriptions documented in the Iberian Peninsula, surpassed only by Cueva del Puente in Junta de Villalba de Losa and possibly Cueva de Román de Clunia, both located in Burgos province.
Despite the progress made, research at Cova de les Dones is still in its early stages. Currently, only 20% of the area featuring Paleolithic decorations has been thoroughly analyzed, and the Roman inscriptions are still under investigation. Moreover, certain areas of the cave have yet to be explored, indicating that additional discoveries may be in store for archaeologists in the years to come.
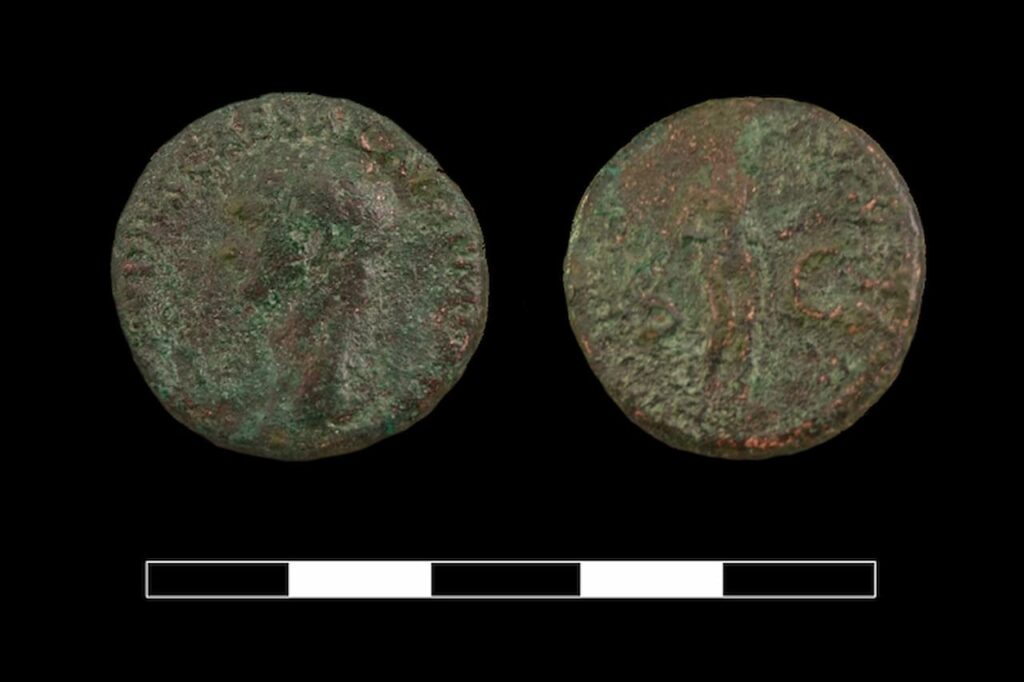

The discovery of the Roman sanctuary in Cova de les Dones marks a significant milestone in archaeological research within the Valencian Community. It not only confirms the continuity of the site’s ritual use across different historical periods but also opens new avenues for studying the interaction between Iberian and Roman cultures in the region. As research continues, further revelations are anticipated to deepen our understanding of the symbolic and religious significance of this underground sanctuary, solidifying Cova de les Dones as an invaluable archaeological site with a rich history yet to be fully uncovered.
The archaeological study at Cova de les Dones is part of the DONARQ project, which aims to analyze this rock sanctuary within its historical context. The research is led by Virginia Barciela González, a professor of Prehistory at the University of Alicante; Aitor Ruiz-Redondo, a professor of Prehistory at the University of Zaragoza; and Ximo Martorell Briz, an archaeologist from the Territorial Department of Culture of Valencia.
Epigraphic analysis is being conducted in collaboration with Víctor Sabaté Vidal, an epigraphy specialist at the University of Valencia, and Javier Velaza Frías, a professor of Latin Philology at the University of Barcelona and director of the LITTERA research team. The recovery and extraction of the Roman coin were carried out by Trinidad Pasíes Oviedo, head of the restoration department at the Museum of Prehistory of Valencia, and Carles Ferrer, curator of the same institution.
Cover Image Credit: A. Ruiz-Redondo, V. Barciela & X. Martorell