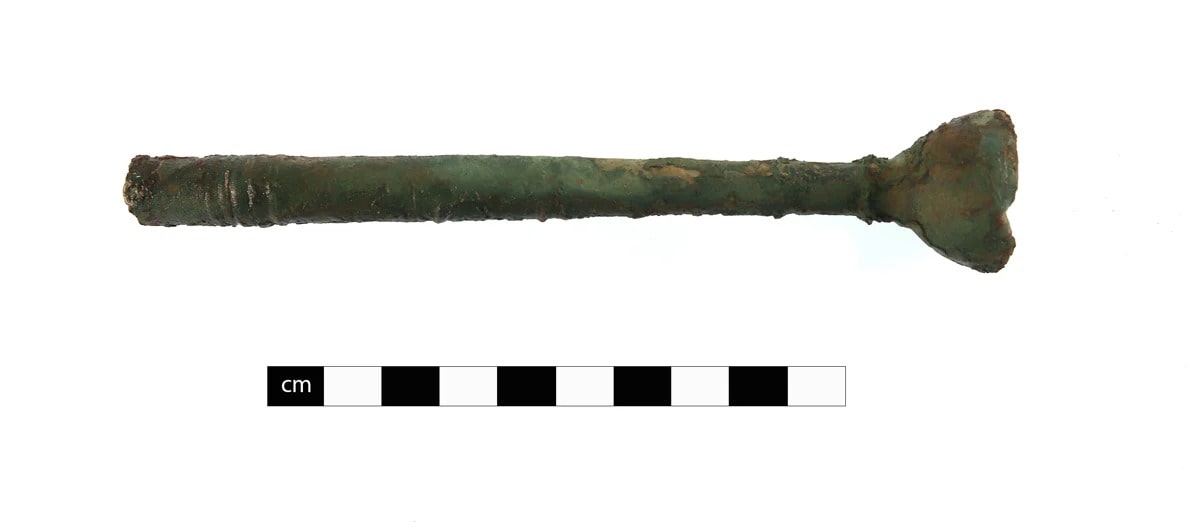
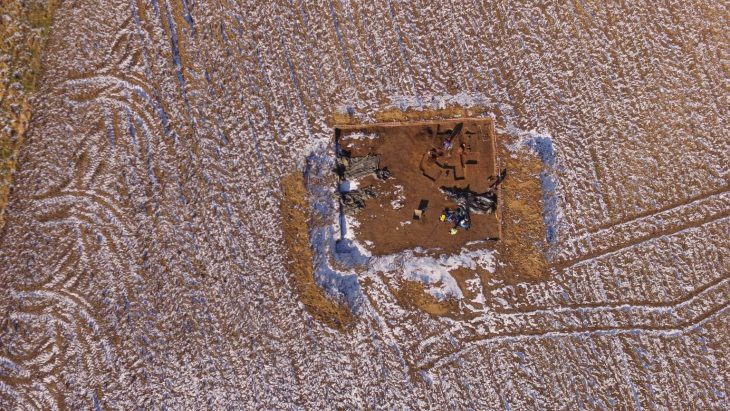
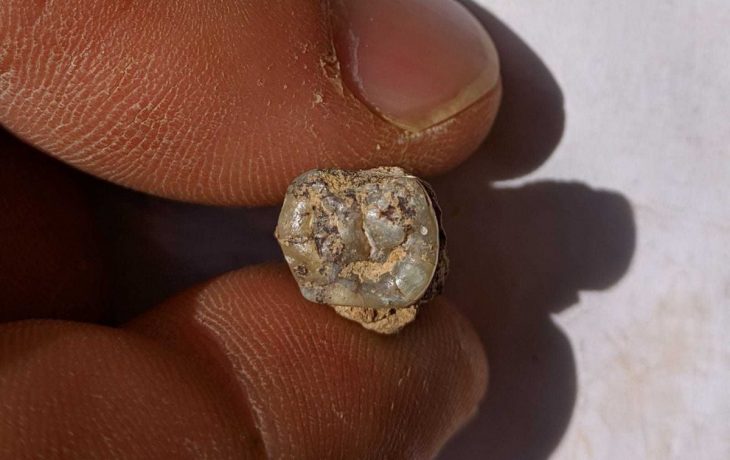
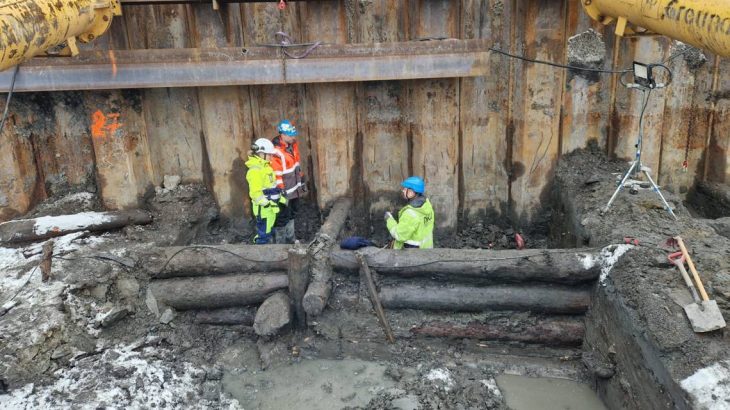
Just south of Hadrian’s Wall, archaeologists have discovered an extremely rare Roman cornu mouthpiece beneath the remains of the ancient officer’s club in the Vindolanda Roman fort.
The mouthpiece, which is made of copper alloy, was uncovered on a workshop floor during the Hadrianic era (117–138 A.D.). It dates to 120–128 A.D. based on stratigraphy.
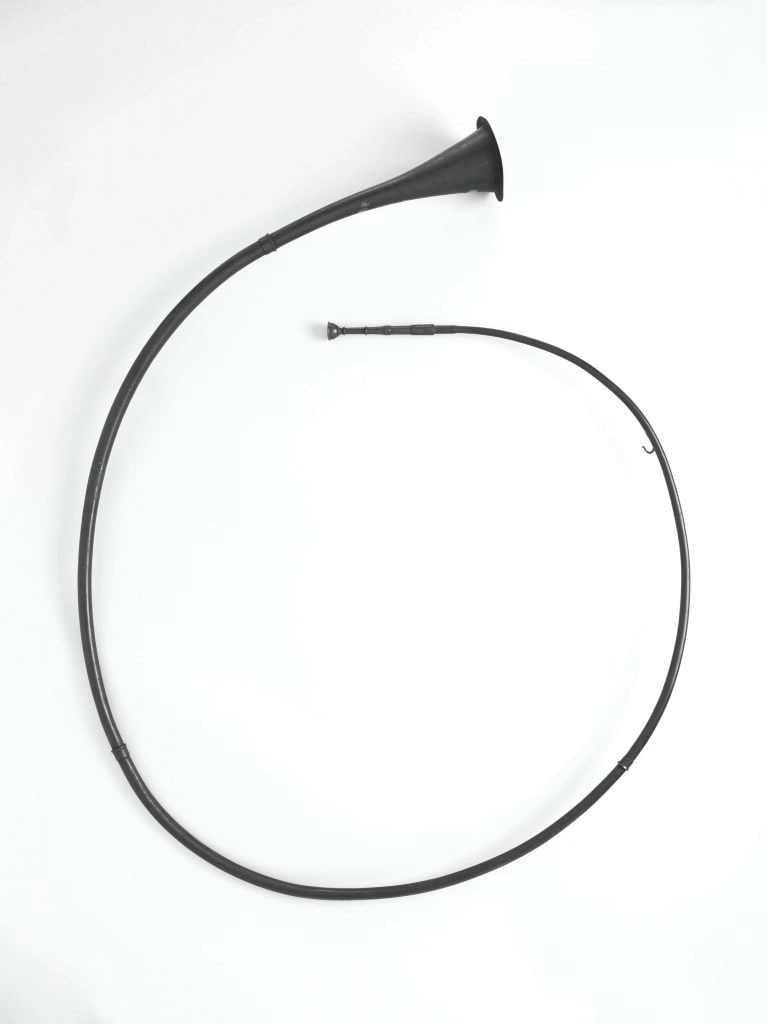
The cornu (Latin “horn”, both musical and animal) was an instrument around 3m long, curled into a letter ‘G’ shape, and was commonly supported by a wooden pole, allowing for some of the weight to be held on the shoulder. Cornua are depicted in many Roman settings on imagery with military, ceremonial, and entertainment use.
Roman military art, such as the Trajan’s Column in Rome, depicts the cornu as accompanying the movement of the standards. The Roman army used the cornu to transmit orders to the troops in battle.

During battles, the cornu was carried by the cornicen (horn-blower), who coded the general’s orders into signals and broadcasted them over the field.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
A cornu was a brass instrument in the shape of a G with no holes or valves. It was played by controlling the air flow, much like a French horn. Its design was Etruscan in origin, but the Romans adapted it for use as a military signaling device. Cornicenes used loud notes to communicate orders to the army on the march and during battle. Several large examples have been discovered in Pompeii, and exact replicas have been used to recreate the sound of Roman armies at war.
“This is a really exciting find here at Vindolanda”, stated the Trust’s Curator Barbara Birley. “We know that instruments like the cornu existed in the ancient world but when you find part of a musical instrument it helps us to build a better picture of not just what the army looked like but also how they sounded. This discovery along with exceptional artifacts like the Vindolanda writing tablets, thin handwritten wooden letters, add so much more to our historical understanding of this remarkable Roman fort”.

Dr. Andrew Birley, Director of Excavations at the Trust commented “Finds like this bring another dimension to our appreciation of life and the ruins left behind, a soundscape to go with the smellscape of the Hadrianic forts and remains and it is apt that we made this discovery in the year that we celebrate 1900 years since the building of Hadrian’s Wall commenced”.
Analysis of excavated cornua as well as other instruments has allowed reproductions to be made so that we can hear how they may have sounded. On September 25, 2022, a live performance at Vindolanda will take place, with musician Letty Scott performing on a replica cornu.
The newly discovered mouthpiece will be displayed alongside other exciting artifacts from the 2022 excavations in the Vindolanda Museum beginning Easter next year.