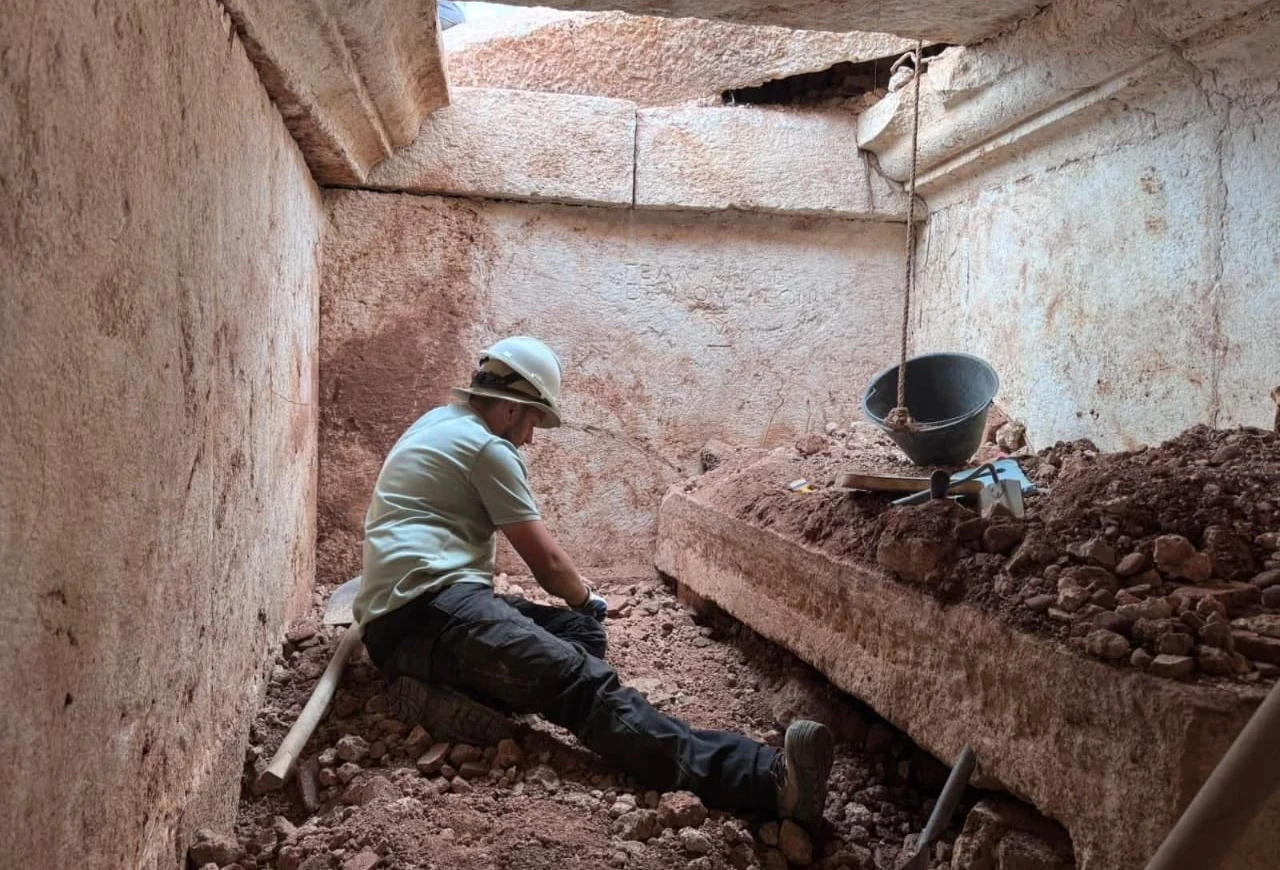
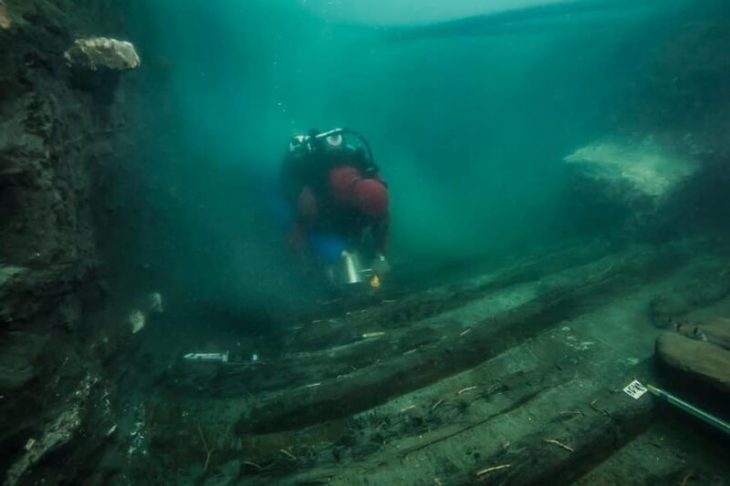
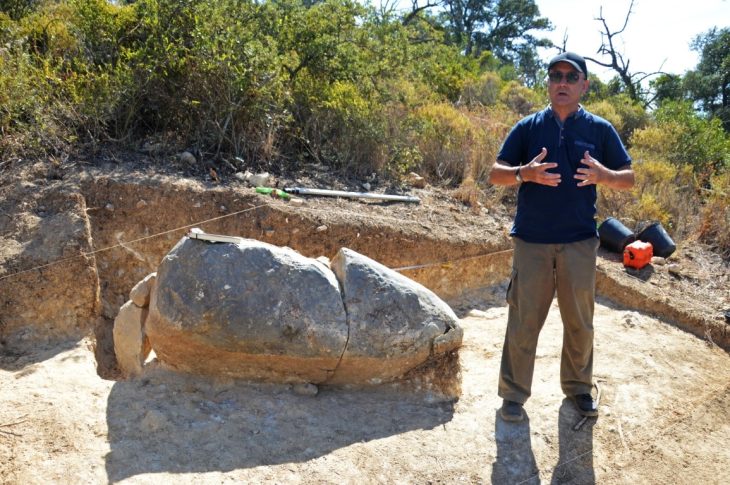
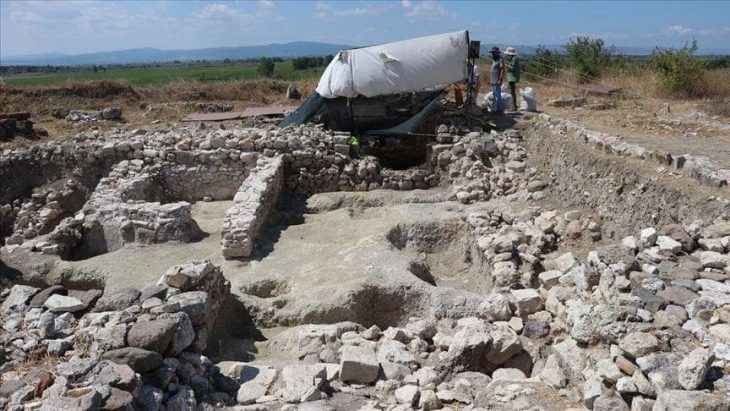
Archaeologists have uncovered a monumental Roman-era tomb in Strikçan, near Bulqiza, in northern Albania’s historic Dibra region, approximately 90 kilometers from Tirana. The tomb is remarkable for containing a rare bilingual Roman inscription dedicated both to the deceased, Gellianos, and the god Jupiter.
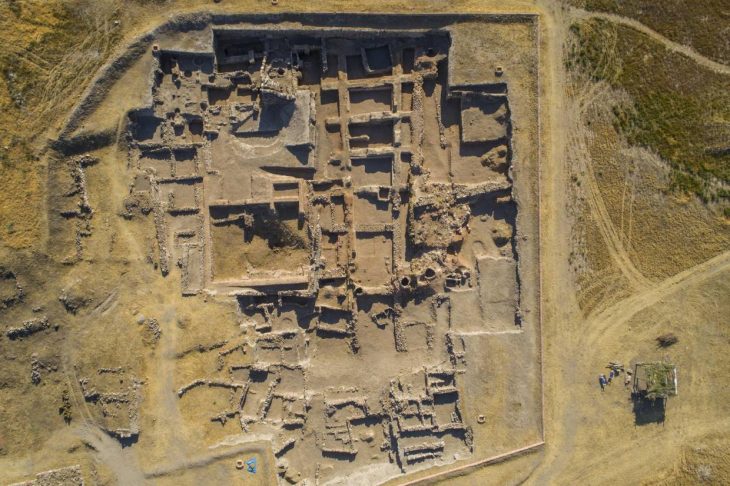
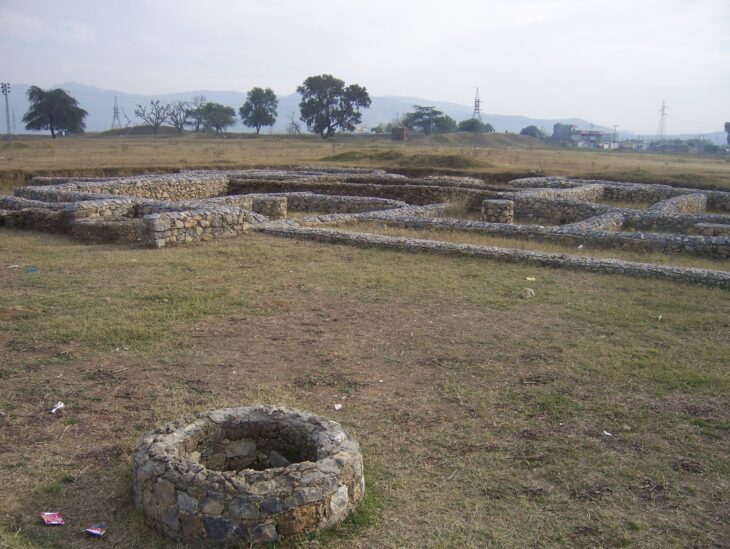
The tomb, dating back to the 3rd–4th centuries AD, is the first of its kind discovered in the area and measures approximately 9 by 6 meters. It features a 2.4-meter-high burial chamber and a monumental staircase adorned with geometric motifs, as well as evidence suggesting it may have functioned as a mausoleum.
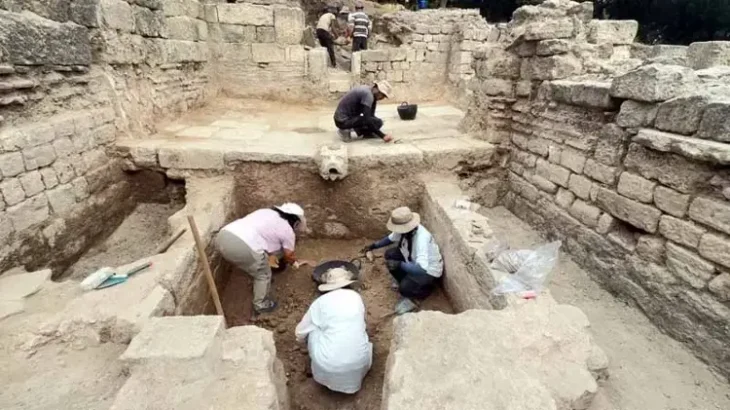
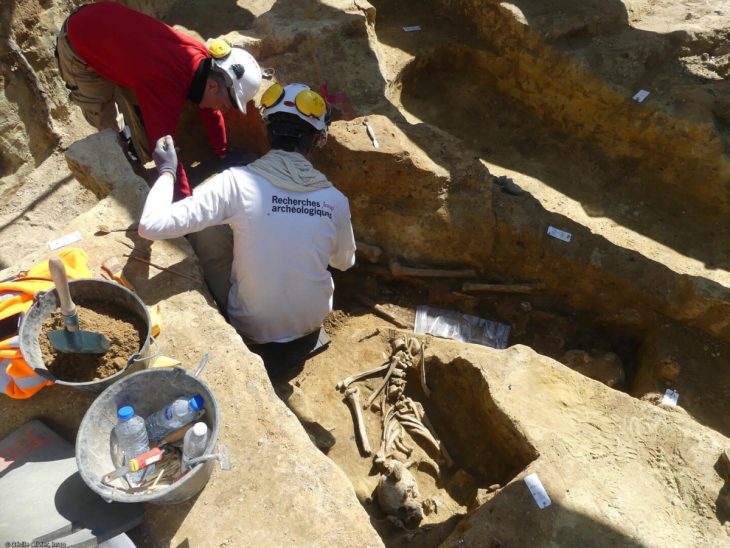
The discovery was officially announced by Albania’s Minister of Economy, Culture, and Innovation, Blendi Gonxhja, via his Facebook page, highlighting the significance of the find for both Albanian archaeology and cultural heritage. The tomb was uncovered during the scientific research project “Archaeological Research in the Bulqiza Valley,” led by the Institute of Archaeology alongside local experts, including Academician Adem Bonguri and MSc. Erikson Nikolli.
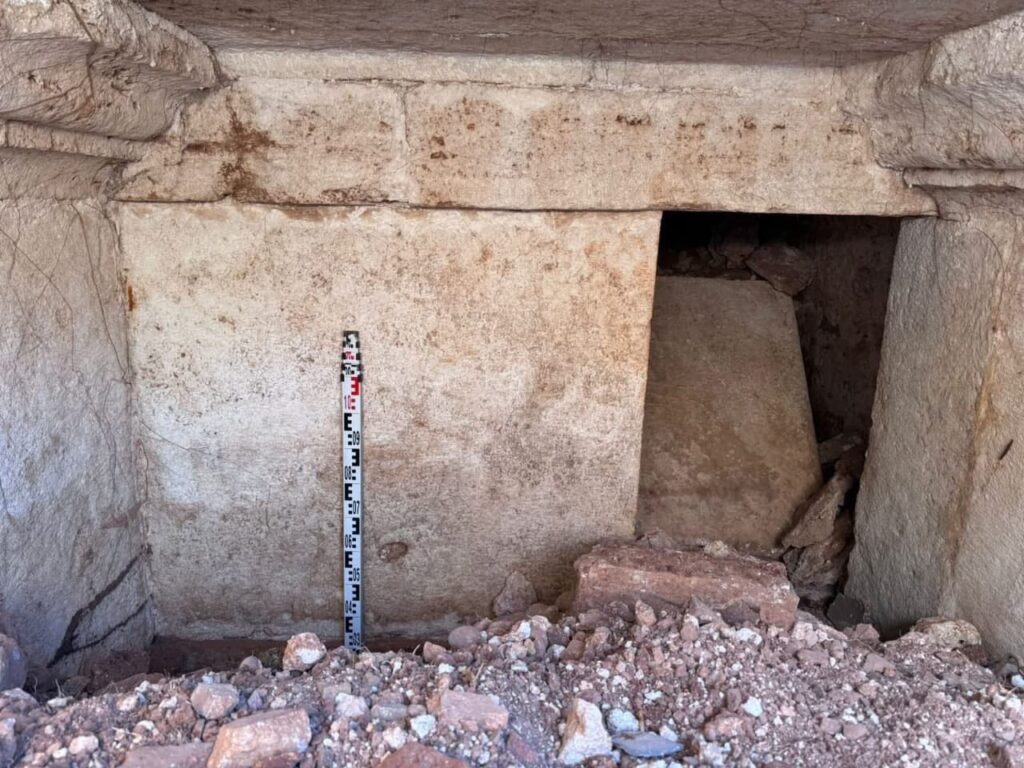

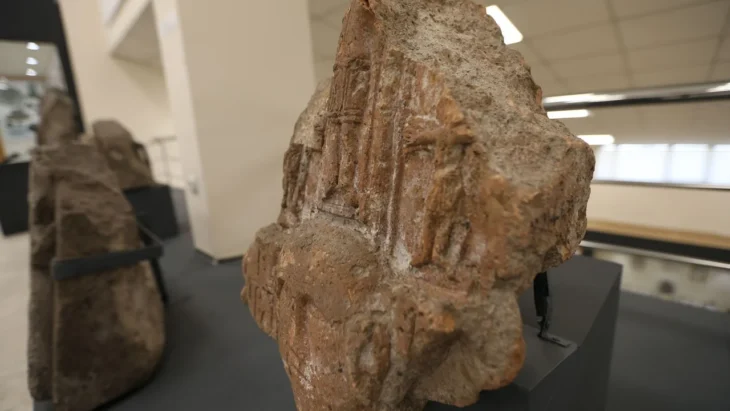
The tomb contains a rare bilingual Roman inscription dedicated to the deceased, Gellianos, and the Roman god Jupiter. According to Minister Gonxhja, this is the first bilingual Roman inscription ever found in the Dibra region, offering invaluable insight into the ancient cultural and religious practices of the area.
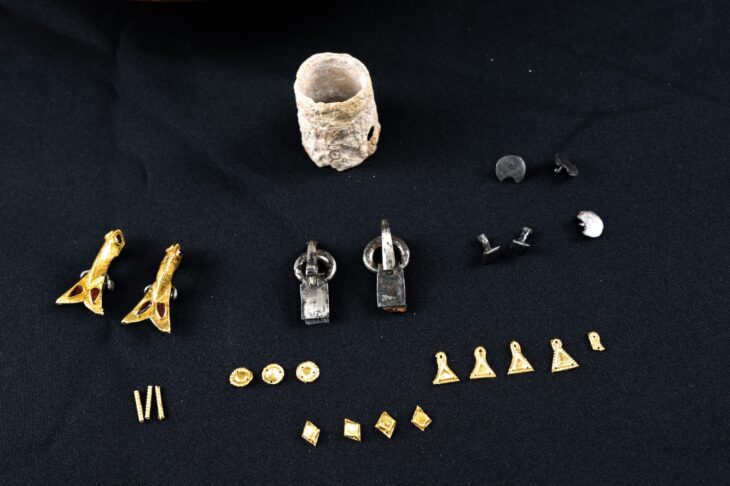
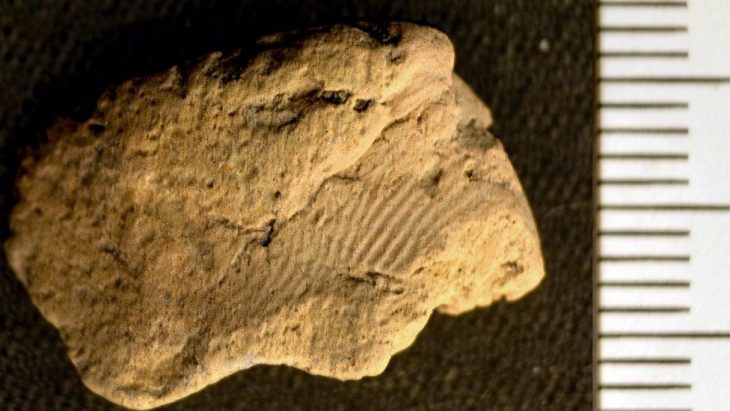
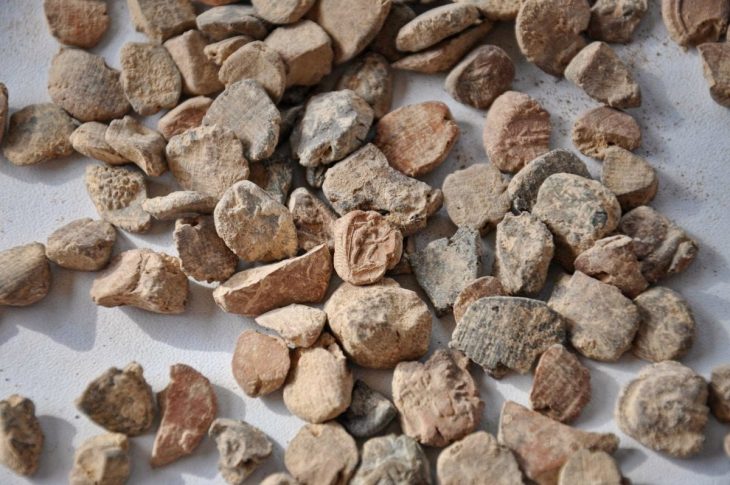
Although the tomb had been looted in antiquity, archaeologists were able to recover part of its original inventory, including glass vessels of various types, bone combs, knives, and a large section of textile woven with gold threads that had been used to wrap the deceased. The tomb is structured into three main areas: the burial chamber, an antechamber, and the monumental staircase. Additional wall structures above the tomb suggest it may have served as a small mausoleum rather than a simple grave.
📣 Our WhatsApp channel is now LIVE! Stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates, just click here to follow us on WhatsApp and never miss a thing!!
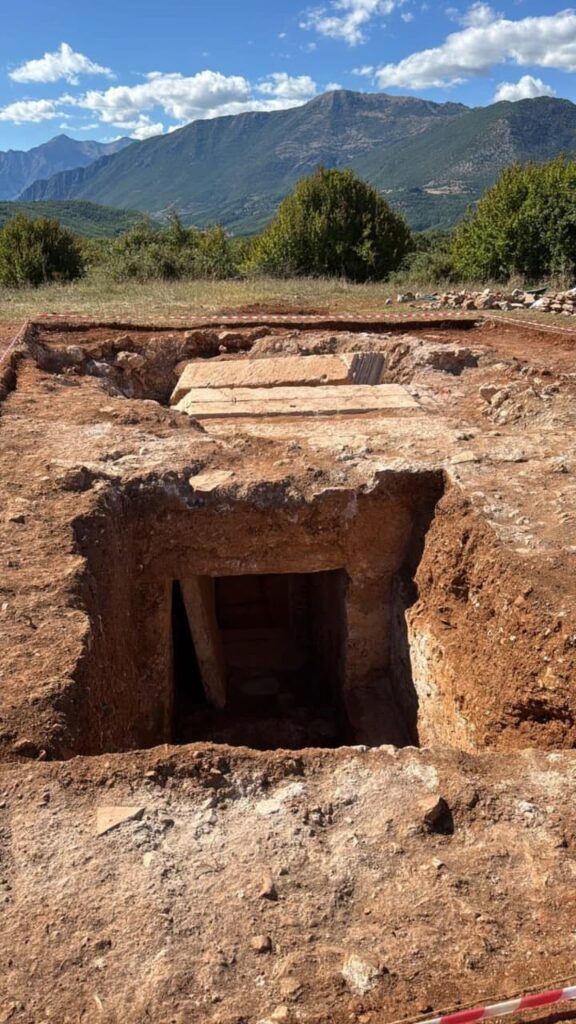

The construction of the tomb highlights remarkable architectural and engineering skills for the period. Large stones were quarried from distant sites and precisely shaped to form the tomb’s structural framework. The combination of carefully carved stones, monumental staircases, and decorative stucco suggests a high level of craftsmanship and indicates the social status of the individual buried there. A nearby damaged funerary inscription is currently under study, which may offer further insights into local funerary customs and the social structure of Roman-era Dibra.
Historically, Dibra was part of the Roman province of Moesia, serving as a crossroads for trade, military, and cultural exchange. Discoveries like this monumental tomb give archaeologists a rare glimpse into the funerary practices, religious beliefs, and architectural sophistication of northern Albania during Roman times. They also enhance the cultural heritage map of Albania and demonstrate the region’s historical significance in the Balkans.

The announcement by Minister Gonxhja has drawn national attention to the site, emphasizing both its historical value and potential for tourism. As excavations continue, researchers hope to uncover additional tombs, inscriptions, and artifacts that will shed light on the lives, beliefs, and artistry of ancient communities in Dibra.
With its combination of historical, architectural, and cultural value, the monumental tomb in Strikçan stands as a testament to Albania’s rich Roman heritage and the enduring influence of ancient civilization in the Balkans.
Cover Image Credit: Albania’s Minister of Economy, Culture, and Innovation, Blendi Gonxhja,